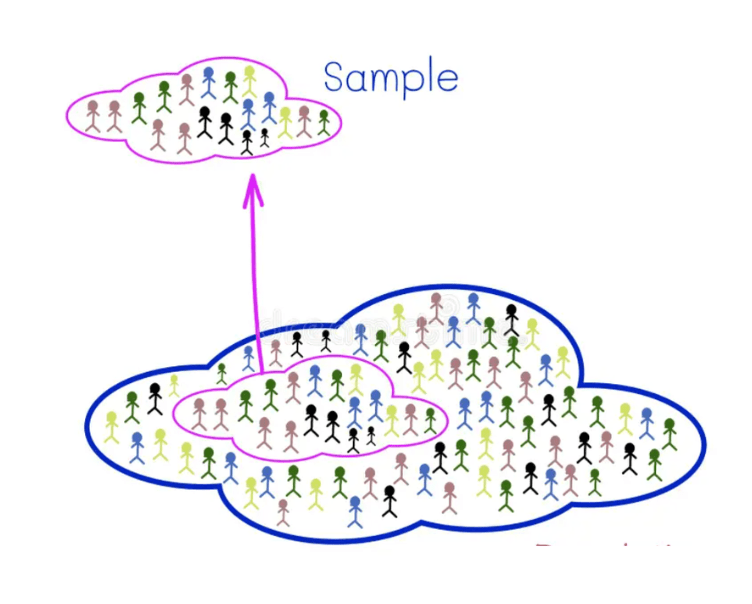
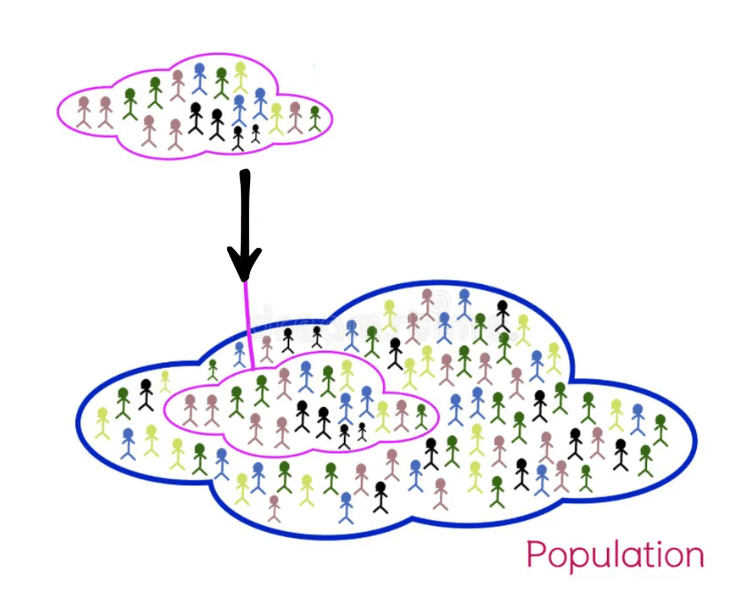
This type of group is a smaller, manageable subset of an entire group used to make inferences about the whole.
What is a sample?
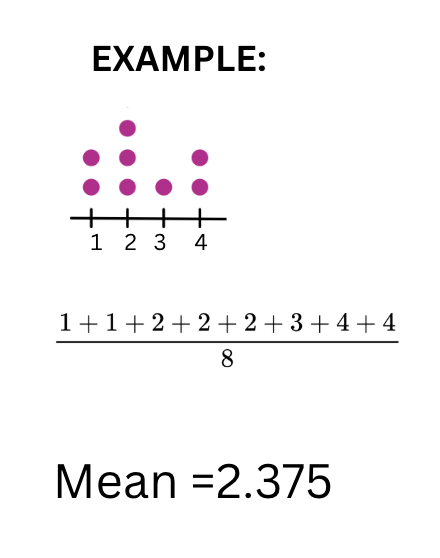
You find this value by adding all the numbers in a data set together and dividing by how many numbers there are.
What is the Mean?
This measure describes how spread out the values in a data set are from the mean.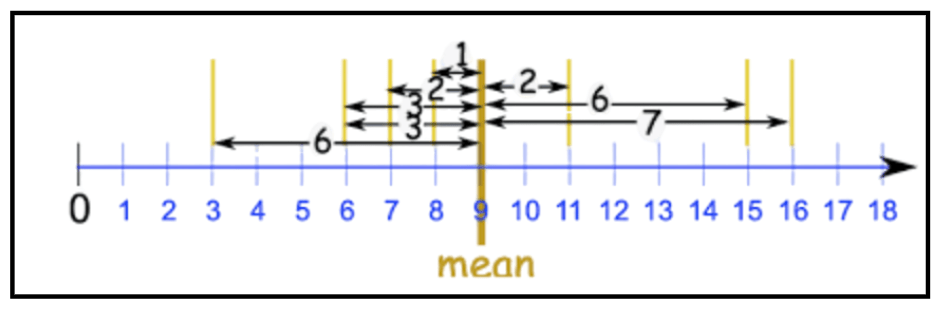
What is the Mean Absolute Deviation?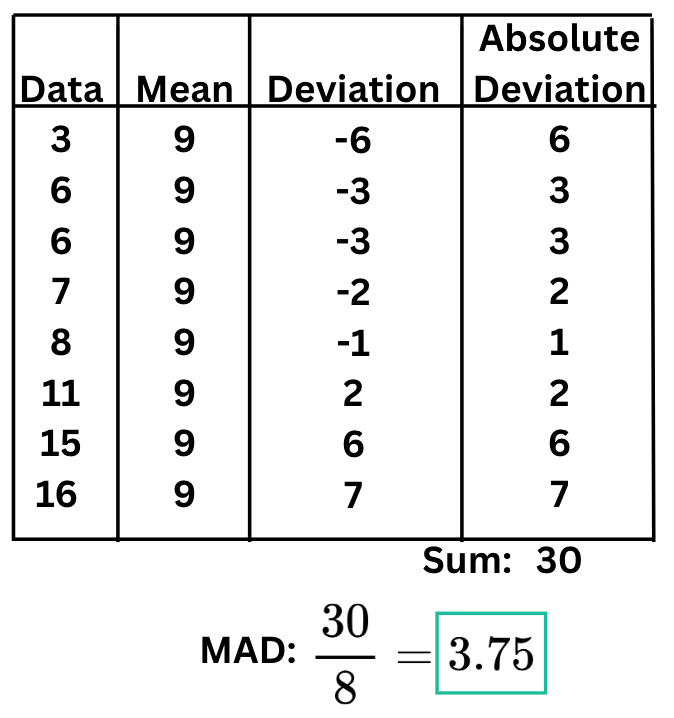
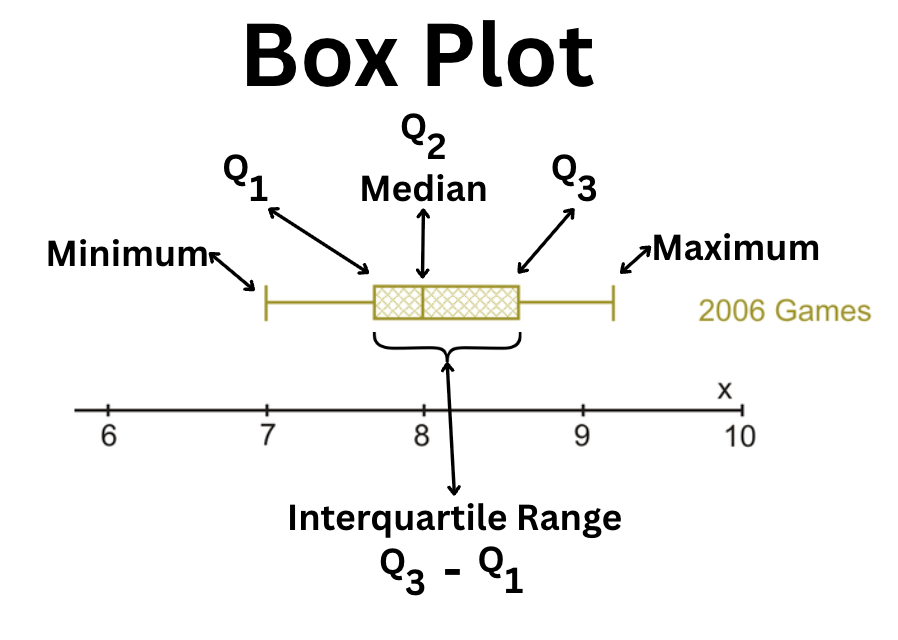
This type of graph includes "whiskers" to show the distribution of data across four quartiles.
What is a Box Plot?
This is the process of using an experiment or a model to mimic a real-world situation when the real thing is too difficult to perform.
What is a simulation?
This is the entire group of people or objects that a researcher wants to gather information about.
What is a population?
This is the middle number in a data set when the numbers are listed in order from least to greatest.
What is the Median? 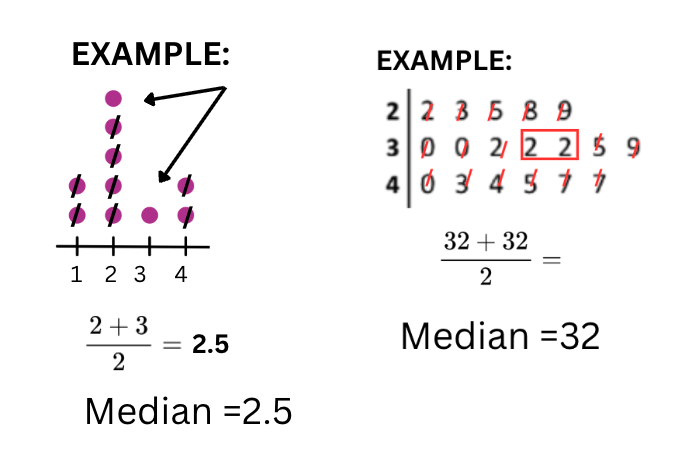
This is the first step in calculating the MAD, which involves finding a measure of central tendency.
What is calculating the Mean?
This display shares a central "trunk" and allows you to compare two sets of data using their single digits.
What is a Back-To-Back Stem Plot?
This is the specific part of a simulation where you actually record the results of your trials.
What is data collection?
This occurs when certain individuals are more likely to be selected for a survey than others, leading to results that don't represent the whole group.
What is under representation bias?
This is the most frequently occurring value in a data set.
What is the Mode?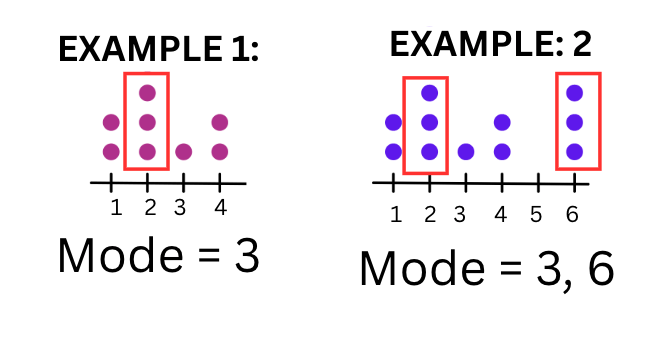
If a data set has a very small MAD, it means the distribution or spread of the data is this.
What is close together or clustered?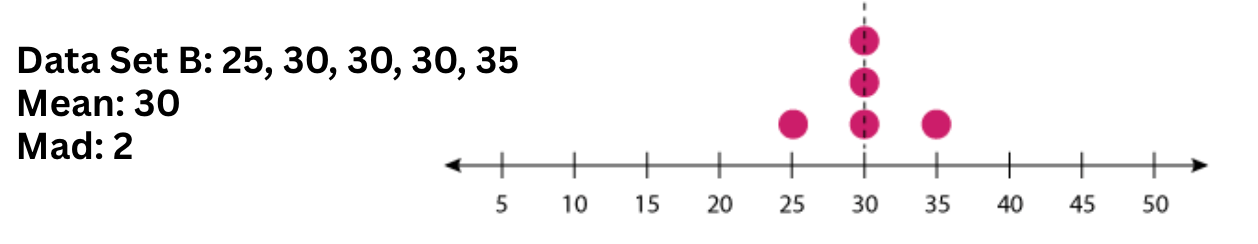
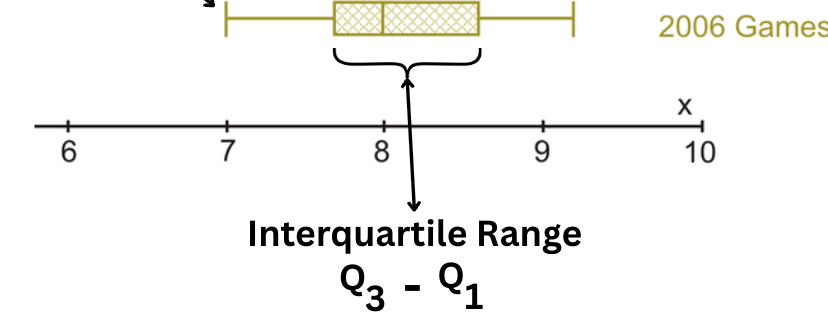
This is the visual representation of the distance between the first quartile (Q1) and the third quartile (Q3) in a box plot.
What is the Interquartile Range?
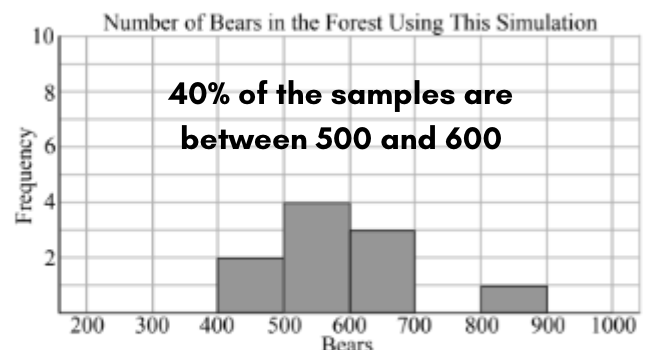
After gathering data from 100 simulation trials, you calculate this to find out how often a specific event occurred out of the total.
What is percent or the frequency?
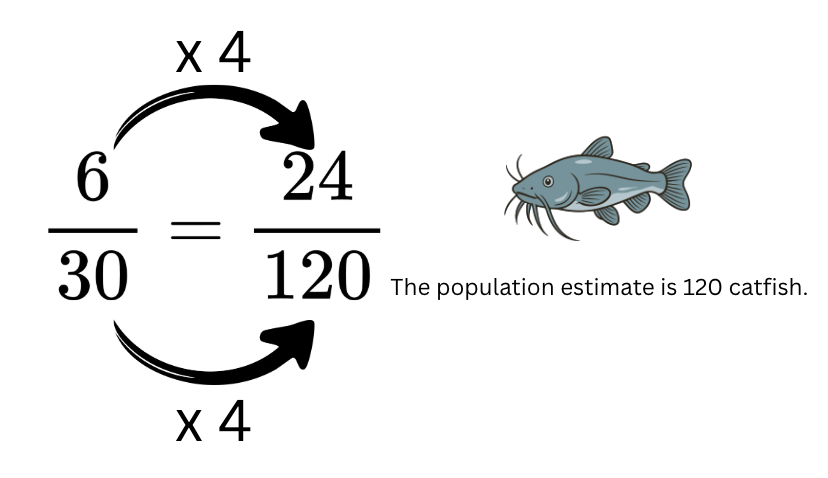
This specific method of data collection involves tagging a small group of animals, letting them go, and then catching a new group later to estimate the total population size.
What is Capture, Mark, Release, Recapture or CMRR?
This is one of the three measures of central tendency and is the best one to use if there are outliers in a data set.
What is the Median?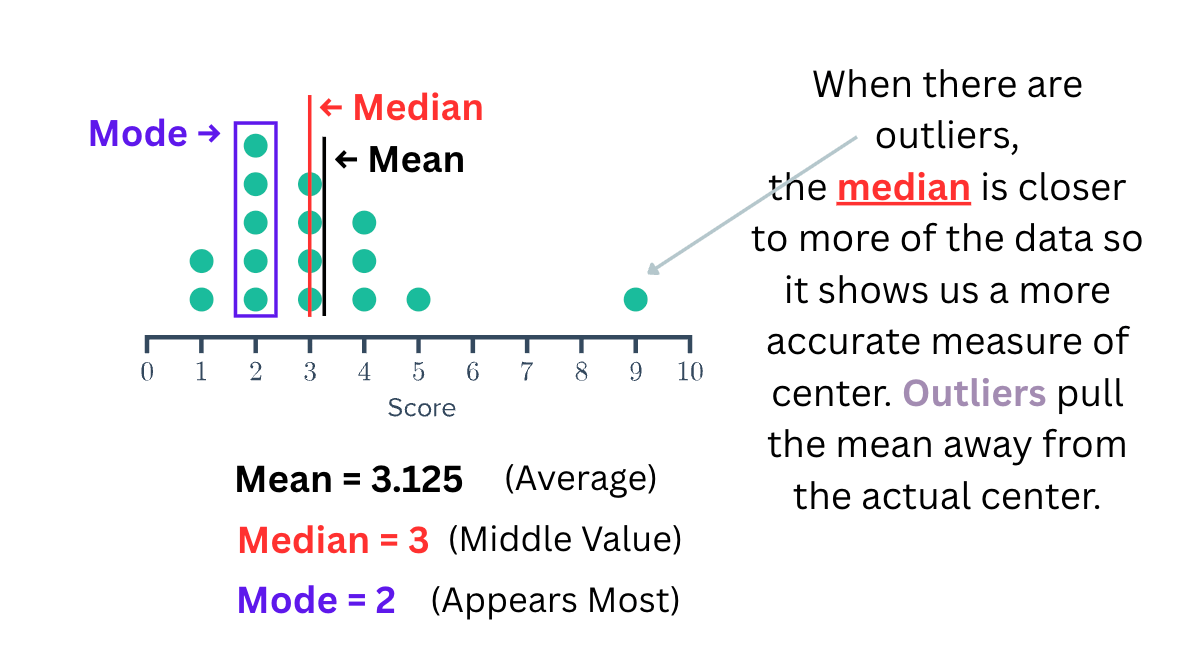
This is the mathematical term for the distance a single data point is from the mean (always expressed as a positive number).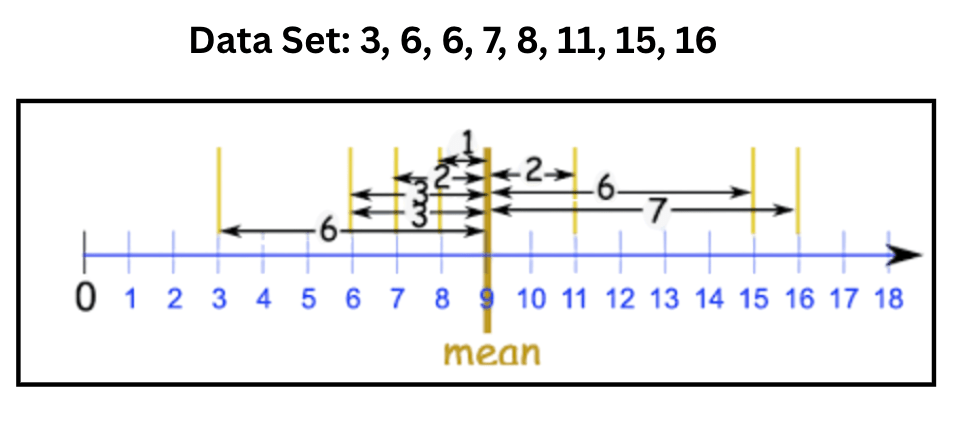
What is the Absolute Deviation?

This is the primary advantage of using a "double" version of a graph rather than two separate ones.
What is comparing two data sets?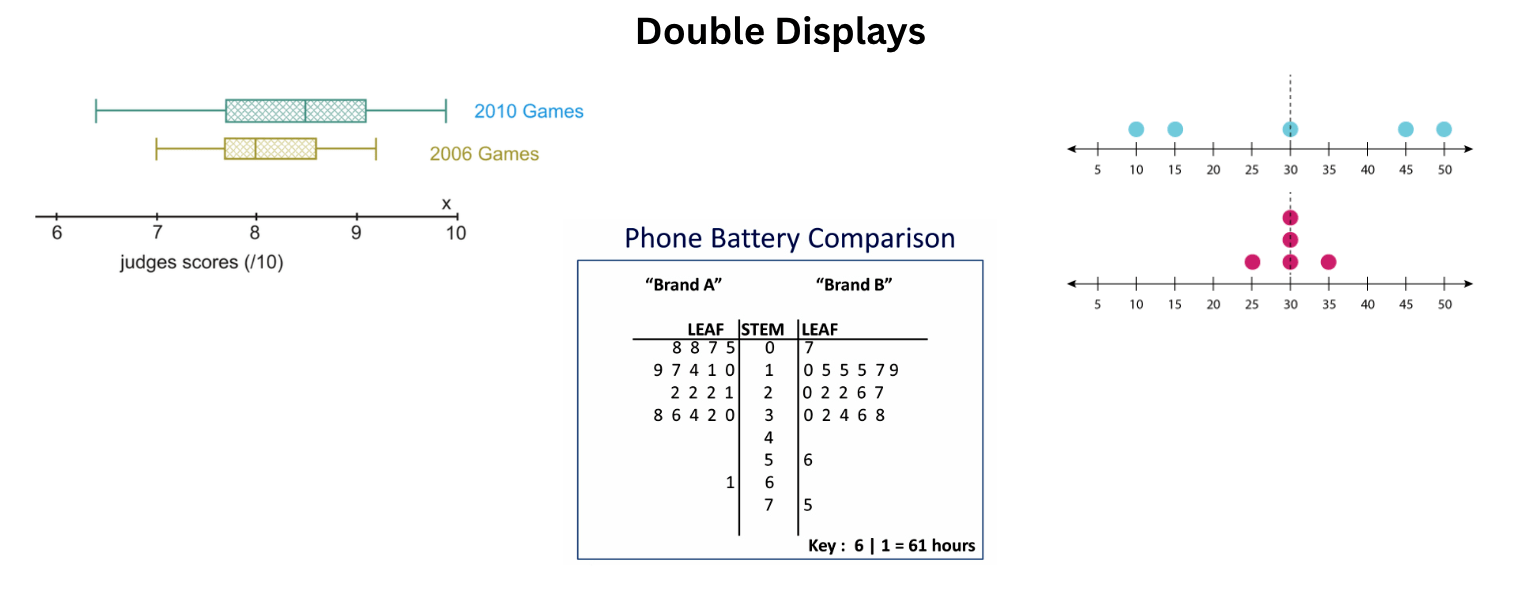
These are the two main steps required after collecting data but before you can interpret it.
What is organizing and modeling data?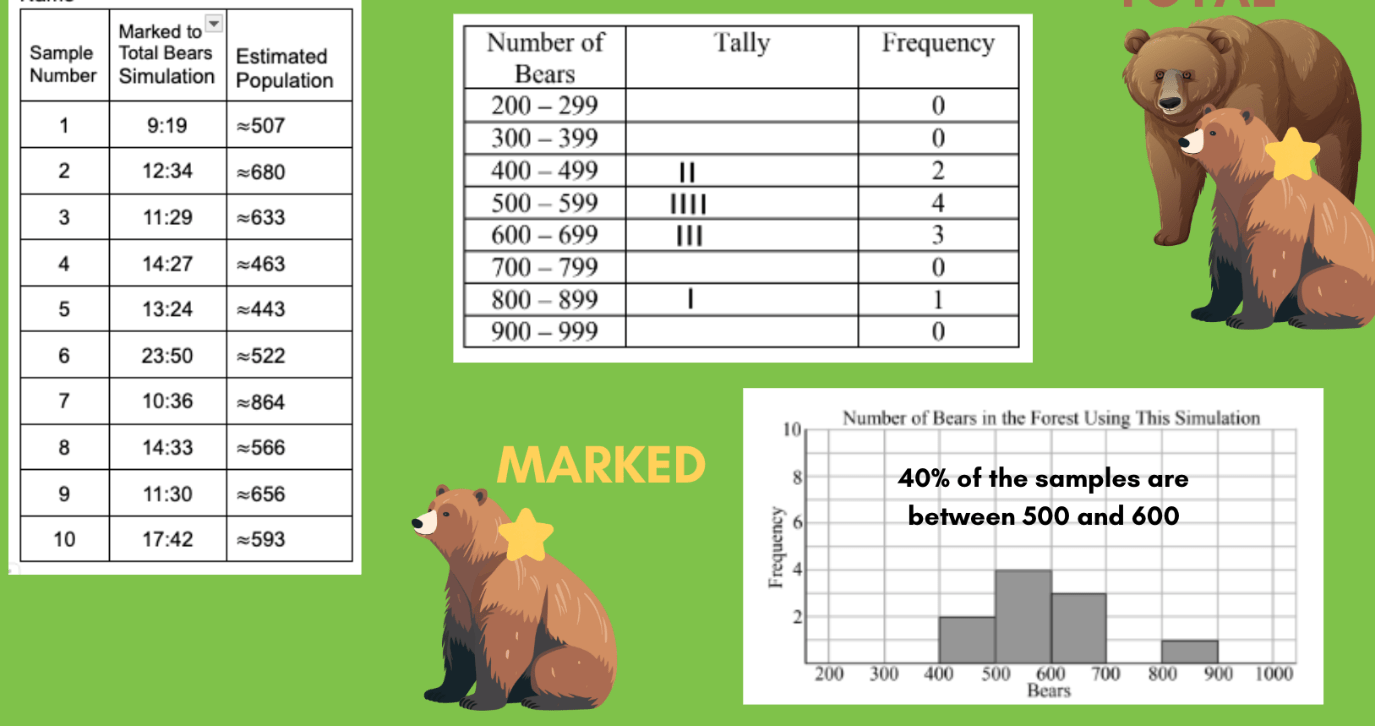
This mathematical statement shows two ratios are equal and is used to estimate a population size based on sample data.
What is a proportion?
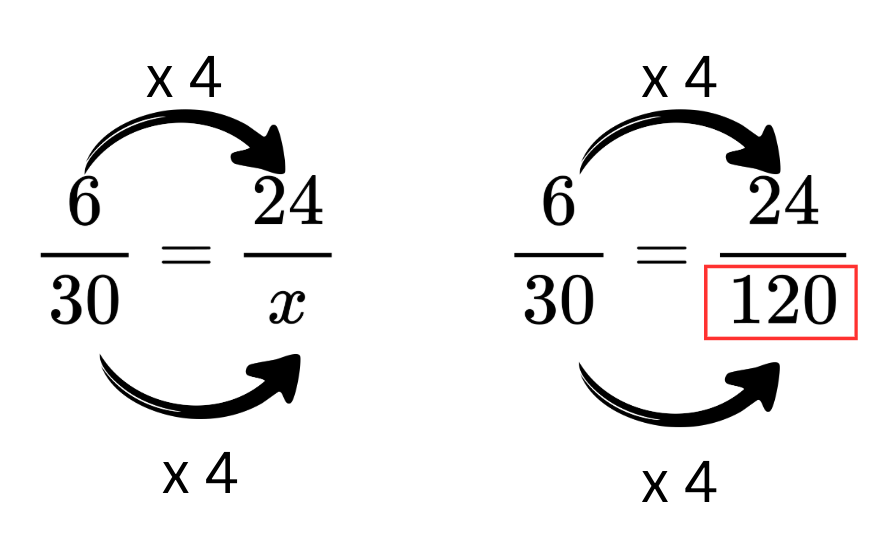
This tool allows a mathematician to look at the centers of two different data sets at the exact same time to see how they compare.
Example: In which Olympics were athletes scores higher on average?
What is a Double Box Plot?
Example: 2010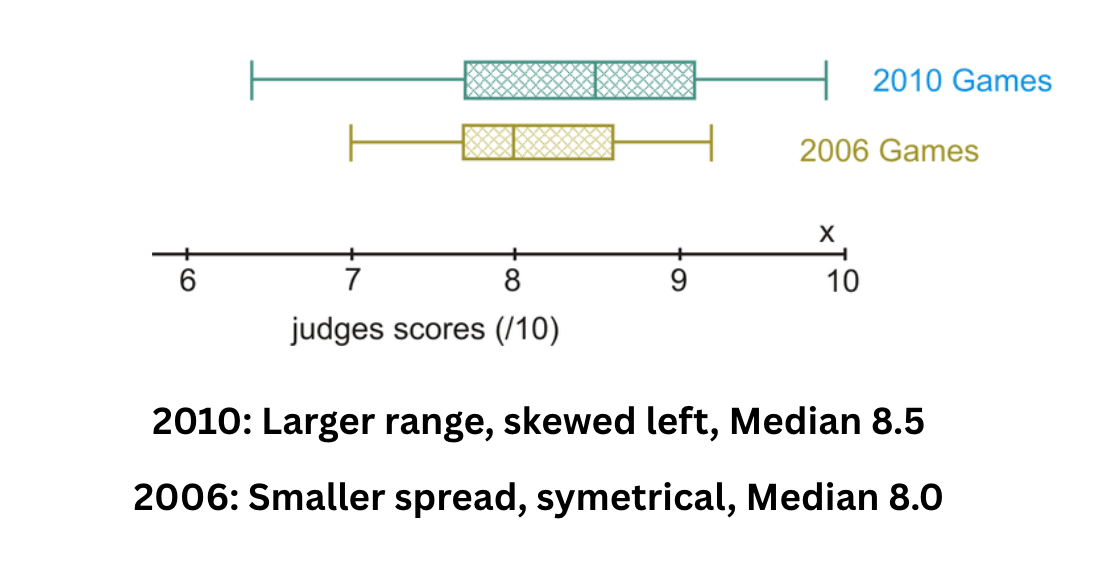
In a real-world context, a high MAD in a set of test scores suggests this about the consistency of student performance.
What is inconsistent or highly varied or spread out?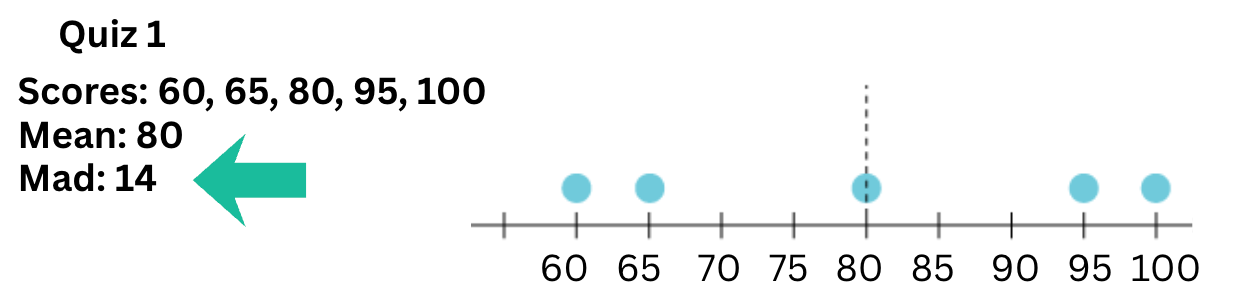
These are the three main things you look for when comparing any two graphical displays: Center, Spread, and this (the overall look of the data).
What is Shape?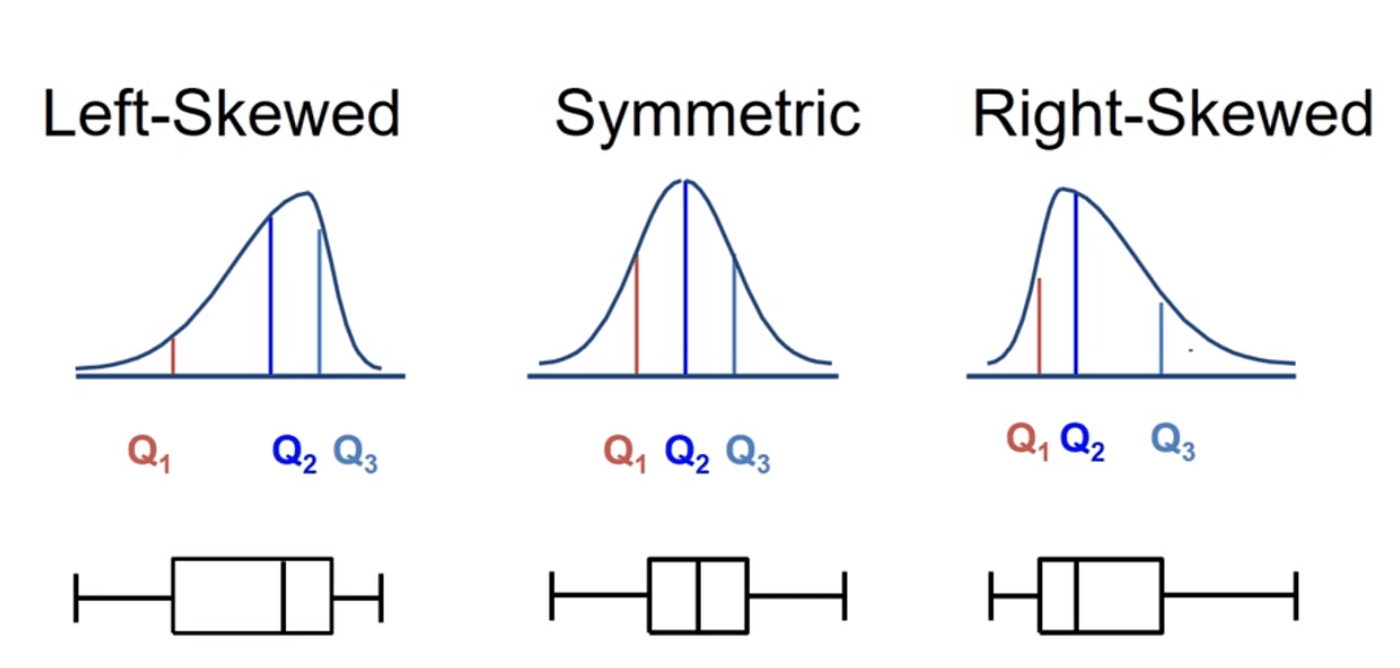
This is the ultimate goal of collecting, organizing, and displaying data in a statistics unit.
Example: Who should Coach Borden take to the championship basketball game?
What is making inferences or drawing conclusions?
Example: Coach should take Maya, because she's a more consistent player.