A scientist used a model to predict the path of a hurricane. The hurricane followed a similar paht but did not follow the exact path that was predicted. How does this example demonstrate a limitation of models?
A. Models cannot be used to predict events
B. Models can be used to predict weather events before the event occurs.
C. Models cannot account for how every factor may suddenly change.
D. Models can only be used to show physical structures,not events such as hurricanes.
C. Models cannot account for how every factor may suddenly change.
Erosion is the process by which soil and sediment are moved by wind, water, or gravity. Erosion occurs naturally, but it can be accelerated by human activity. Which of these human activities least contributes to soil erosion?
A. urban sprawl
B. planting trees
C. surface mining
D. deforestation
B. planting trees
Describe the Law of Conservation of Energy.
The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, only transformed into a different type of energy.
Describe how natural selection can either lead a species to evolve or become extinct.
The species that are most well adapted to their environments will most likely be able to live long enough to reproduce and pass beneficial traits to offspring. If a population of organisms is not well suited for their environment, they will not be able to survive, possibly leading to extinction.
Define the following terms:
1 - Autotroph
2 - Heterotroph
3 - Herbivore
4 - Carnivore
5 - Omnivore
Is a fungus/mushroom an autotroph or a heterotroph?
1 - Autotroph: uses energy from sunlight to produce its own food
2 - Heterotroph: consumes other organisms in order to gain its energy
3 - Herbivore: consumes only plants
4 - Carnivore: consumes only meat/animals
5 - Omnivore: consumes both plants AND animals
Fungi/mushrooms are heterotrophs (remember: they are decomposers!)
The advancement of the electron microscope has assisted scientists in studying microrganisms and cells. The image below is a micrograph of a hydrothermal worm.

What statement best explains why technology is essential to science?
A. Technology provides scientists tools to use in the laboratory.
B. Technology changes rapidly.
C. Technology is limited to computers
D. Technology improves a scientist's ability to make observations
D. Technology improves a scientist's ability to make observations
What are the three categories of rocks present in the rock cycle, and what is necessary to create each of them?
Igneous rock - intense heating
Metamorphic rock - intense heating AND pressure
Sedimentary rock - weathering, erosion, and deposition of sediment, pressed together
Describe how heat flows between objects. Give an example.
Heat flows from warmer objects to cooler ones.
Ex: heat moving from a hot stove to a cool pan, heat moving from a hot curling iron to a cooler hand, heat moving from a warm body to a cooler chair, etc.
Describe individual 4, generation II:

Affected female
Part of a desert food web is diagrammed below.
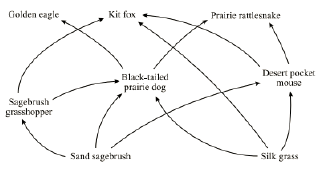
What do the arrows in this food web show?
Define the following terms and name the organisms from the food web shown that describe them:
1 - Producers
2 - Primary consumers
3 - Secondary/Tertiary consumers
4 - Decomposers
The arrows show the flow of energy from what is consumed to what is consuming.
Producers - use sun's energy to produce their own food. Ex: silk grass, sand sagebrush
Primary consumers - consume only producers. Ex: sagebrush grasshopper, black-tailed prairie dog, desert pocket mouse
Secondary/Tertiary consumers - consume other consumers. Ex: golden eagle, kit fox, prairie rattlesnake
Decomposers - consume dead/decaying organisms. Ex: trick question, none shown here! but examples include things such as mushrooms, earthworms, etc
Jae testing the effect of pressure on the volume of a gas. She performed her experiment three times and recorded her results in a data table. Mateo read her procedures, and completed the same experiment so he and Jae could compare their results. Identify the repetition in this scenario.
Repetition (when a scientist conducts multiple trials) occurred when Jae performed her experiment three times.
Describe the Law of Superposition. How does this provide evidence for how Earth has changed over time?
The Law of Superposition states that the youngest layers of the Earth (and youngest fossils) are found towards the surface, getting older as you move further downwards.
As you move lower under the Earth's surface, the types of fossils that may be observed changes, showing that different types/versions of organisms lived during different times in Earth's history.
Describe the energy transformations occurring in the following scenarios:
1 - a person riding a bike
2 - a battery powering a flashlight
3 - a roller coaster moving from the top of a hill to the bottom of a hill
1 - chemical energy to mechanical energy
2 - mechanical energy to electrical energy to light energy
3 - potential energy to kinetic energy
Define mitosis.
Mitosis is the process of asexual reproduction where there is one parent present which creates an offspring that is an exact copy of itself.
Part of a desert food web is diagrammed below.

What would happen to the Sagebrush grasshopper population if the Black-tailed prairie dog population were to decline? Why?
The Sagebrush grasshopper population would increase because they would have less predators.
What is the difference between a scientific theory and a scientific law?
What is the major similarity?
A Theory explains many related ideas and observations.
A Law describes how events may occur under specific conditions (usually mathematically).
Both are supported by large amounts of evidence.
Describe the following tectonic plate boundaries, and what types of land forms/events each is responsible for:
Convergent, Divergent, Transform, Subduction Zones
Convergent - two plates moving towards one another, responsible for mountain building
Divergent - two plates moving away from one another, creating rift vallys
Transform - two plate sliding past one another, causing earthquakes
Subduction Zones - one plate being subducted (pushed under) another plate, creating volcanoes
1 - Name the types of waves in the Electromagnetic spectrum.
2 - How is the Electromagnetic spectrum organized, from left to right? (Hint: two factors)
3 - Which type(s) of wave(s) are we able to see?
1 - Radio waves, Microwaves, Infrared radiation, Visible light spectrum, Ultraviolet, X-rays, Gamma rays
2 - Decreasing wavelength, increasing frequency
3 - Visible light spectrum ONLY
Define meiosis.
Meiosis is the process of sexual reproduction where there are two parents present, and the offspring contains 50% of its inherited traits from each parent, creating a unique and genetically diverse offspring.
Draw faces to represent each of the relationships listed below:
1 - Mutualism
2 - Commensalism
3 - Parasitism
4 - Predation
What is the difference between parasitism and predation?
1 - happy face, happy face
2 - happy face, meh face
3 - happy face, sad face
4 - happy face, sad face
In parasitism, the parasite wants to keep the host alive for as long as possible, giving it an ongoing meal/home
In predation, the predator kills the prey for food.
Name and define the three types of variables needed in a scientific experiment. How many of each will an experiment have?
Independent variable - the factor that is changed/manipulated by the scientist (ONLY ONE)
Dependent variable - the factor that changes as a result of the manipulation of the independent variable (one or more)
Controlled variable - the factors that remain constant (the same) throughout the experiment (as many as possible)
Name and describe the layers of the earth.
Crust - thinnest layer, made of mostly granite and basalt, broken up into tectonic plates
Mantle - thickest layer, mostly made of magma, convection currents responsible for movement of tectonic plates
Outer core - second thickest layer, liquid nickle and iron, responsible for Earth's magnetic field
Inner core - most dense layer, solid nickel and iron
Describe the rate of speed that the following types of waves travel through the three states of matter:
1 - Light waves
2 - Sound waves
1 - Fastest through gases, medium through liquids, slowest through solids
2 - Fastest through solids, medium through liquids, slowest through gases
If you cross Tt x Tt in a Punnett Square, where the allele for a tall plant (T) is dominant, what are the genotype and phenotype probabilities? Must use proper vocabulary!!
genotypes:
TT (homozygous dominant) - 25%
Tt (heterozygous) - 50%
tt (homozygous recessive) - 25%
phenotypes:
Tall plants - 75%
Short plants - 25%
Describe the relationships in the following scenarios:
1 - a lion hunts a zebra
2 - a flea lives on a dog
3 - a bird builds a nest in a tree
4 - a fish cleans the mouth of a moray eel
1 - predator-prey
2 - parasitism
3 - commensalism
4 - mutualism