The knee is _______________ to the ankle.
proximal
What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands?
Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, while exocrine glands release their secretions through ducts onto body surfaces or into the digestive tract.
What are the 4 shapes of bones
Short, Flat, irregular, long
What are the functions of the muscular system?
movement
posture
organ volume
Temperature Regulations
Protection
a layer of cells at the back of your eyeball that converts light into nerve signals.
Retina
This is a type of metabolism that builds up complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy input.
Anabolism
What are the three layers of skin? (from superficial to deep.)
Epidermis
Dermis
Hypodermis (Subcutaneous)
this is the long shaft of the bone
diaphysis
What are the 4 characteristics of muscle tissue?
elasticity, excitability, extensibility, contractility
What are the 3 broad functions of the nervous system
Sensory
Integration
Motor
A loop that is a normal biological response in which the effects of a reaction slow or stop that reaction.(bring it back to normal)
negative feedback
What are the 4 principle tissue types?
Epithelial
Connective
Muscular
Nervous
What are osteoblasts?
cells that form new bones and grow and heal existing bones
What is the thin myofilament called and the thick myofilament called in muscle fibers?
Actin is thin
Myosin is thick
part of your nervous system that lies outside your brain and spinal cord.
peripheral nervous system
What body cavity is the spinal cord in?
Dorsal or vertebral
Which type of muscle is B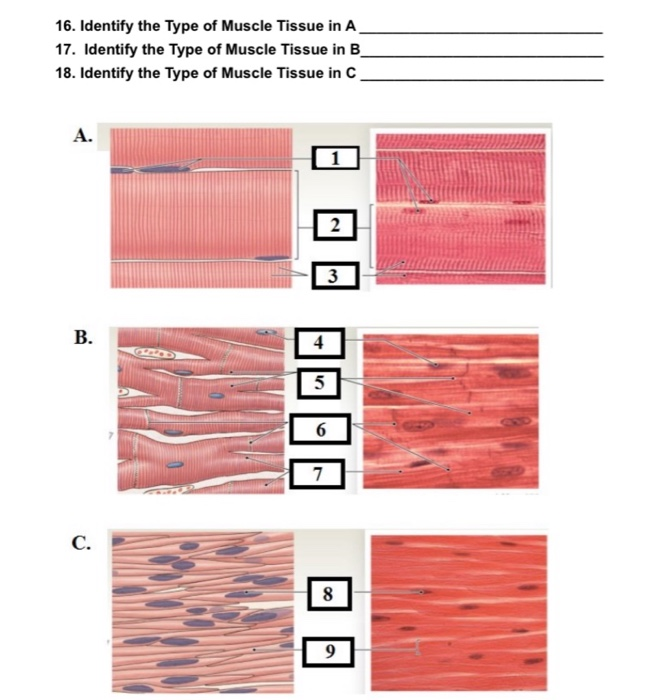
cardiac
What is compact bone?
bone where osteocytes are tightly packed together.
What are the four roles of muscles
prime mover -provides the primary force
Antagonist - opposes or reverses the action of another muscle
Synergist - assist the prime mover
Fixator - stabilizes a joint or bone to allow another muscle (agonist) to function effectively during a movement.
What does microglia do?
brain, responding to infections, injuries, and other pathological events by undergoing "activation
List the 6 levels of organization in order from simplest to complex
Chemical
Celular
Tissue
Organ
System
Organism
what are the 4 basic types of membranes
mucous- line the body cavities and openings that open to the outside
serous - body cavities that don't open to the outside
synovial - Line the joints
cutaneous - skin
What are the 5 functions of the skeletal system?
support
blood production
mineral storage
protection
Movement
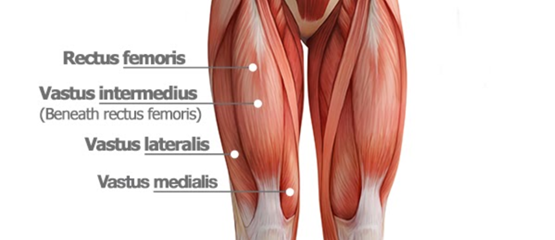
What 4 muscles make up the Quadriceps?
What are the components of a reflex arc?
receptor
sensory neuron
interneuron
motor neuron
effector