any method of determining whether an event or object is older or younger than other events or objects.
Relative Dating
The trace or remains of an organism that lived a long time ago, most commonly preserved in Sedimentary rock.
Fossil
The process of determining the exact age of a rock or other material.
Absolute Dating
Which formed first: rock layers or faults (large cracks)?
rock layers
The graphic organizer that contains divisions of Earth's history is known as
The Geologic Time Scale
A principle that states that younger rocks lie above older rocks if the layers have not been disturbed.
Superposition
Most often, fossils are formed in this type of rock.
What is sedimentary rock?
The use of radioactive decay to determine the age of a rock.
Radiometric Dating
A gap in the sequence of sedimentary rock layers caused by erosion..
unconformity
How is the geologic time scale divided into eras and periods?
According to changes in the fossil record/types or organisms alive/extinctions (BIG changes)
What is a fault?
A crack in rock layers as a result of movements in Earth's crust.
______ fossil is found in the rock layers of only one geologic age and that is used to establish the age of the rock layers.
Index
Give a scenario that would require the use of Carbon-14 rather than Uranium-238 when absolutely dating.
- still have organic material available
- "specimen" suspected to be relatively young
Based on the model, what must have occurred between layers A and B? 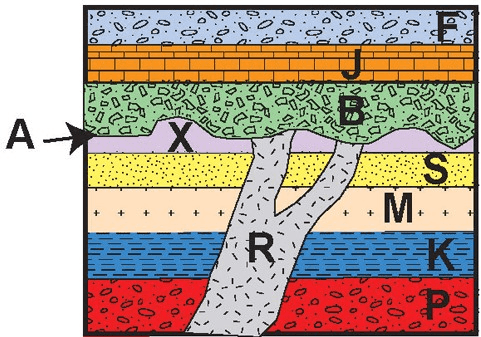
What is erosion?
True or False? Explain your answer. Humans were dominant for most of geologic time.
False. If you tried to squeeze Earth's 4.6-billion year history into a 24-hour day, modern humans don't even appear until less than a second before midnight!
This geologic principle of relative dating states that an intrusion, disturbance, fault, etc... that cuts through layers is younger than the layer.
Law of Cross-cutting
What is the relative age of a rock?
age of a rock compared with the age of other rocks in terms of younger or older, but not giving a date or time period
The amount of time it takes for half of the mass of a radioactive substance to decay into daughter product.
Half-Life
This is when magma hardens in rock layers and overwrites any pre-existing rocks.
What is an intrusion
How old is Earth?
4.6 billion years
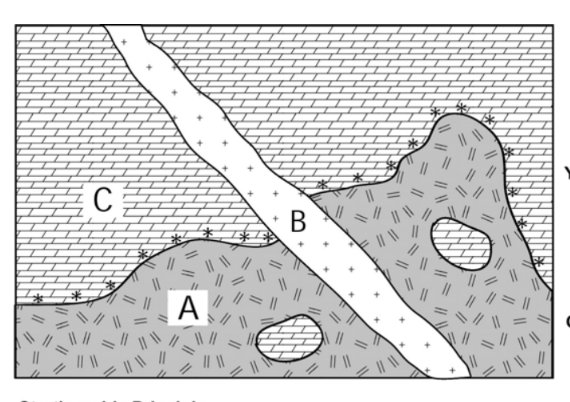 According to the law of inclusion, which layer is oldest?
According to the law of inclusion, which layer is oldest?
Layer C (since material C appears inclusions within layer A, it must have formed prior to layer A)
Which letter represents the best index fossil: A, B, C, or D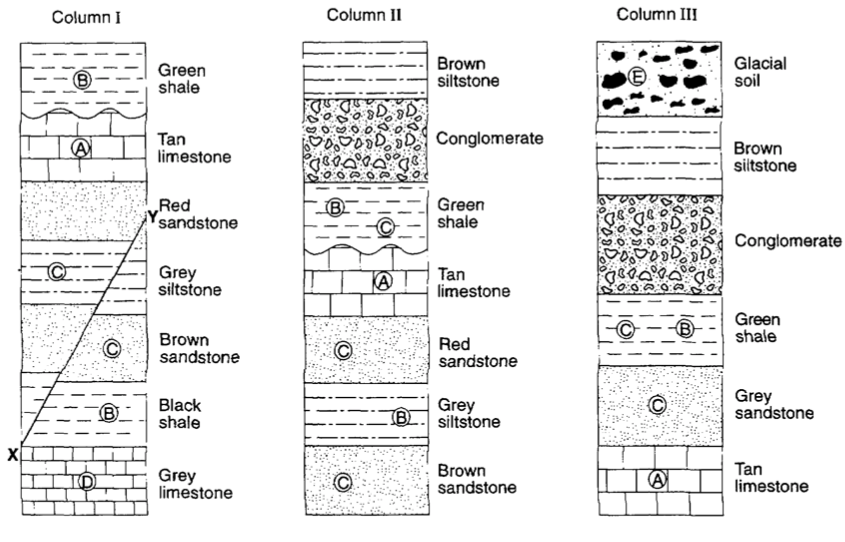
A
You find a rock with 56 total grams of Uranium-238 and lead. If there are 7 grams of Uranium left in this sample and Uranium-28 has a half-life of 4.6 billion years, how old is this sample?
13.8 billion years old
(after 1st half-life - 28 g of U238, 4.6 byo
after 2nd half-life - 14 g of U238, 9.2 byo
after 3rd half-life - 7 g of U238, 13.8 byo)
Put the rock layers and events in order from oldest to youngest

P -> K -> M -> S -> X -> R -> A -> B -> J -> F
It states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
What is the principle of uniformitarianism?