What did Democritus call his theoretical "can't be cut" object?
an atom
what group type is the largest across the periodic table?
transition metals
Label each image.
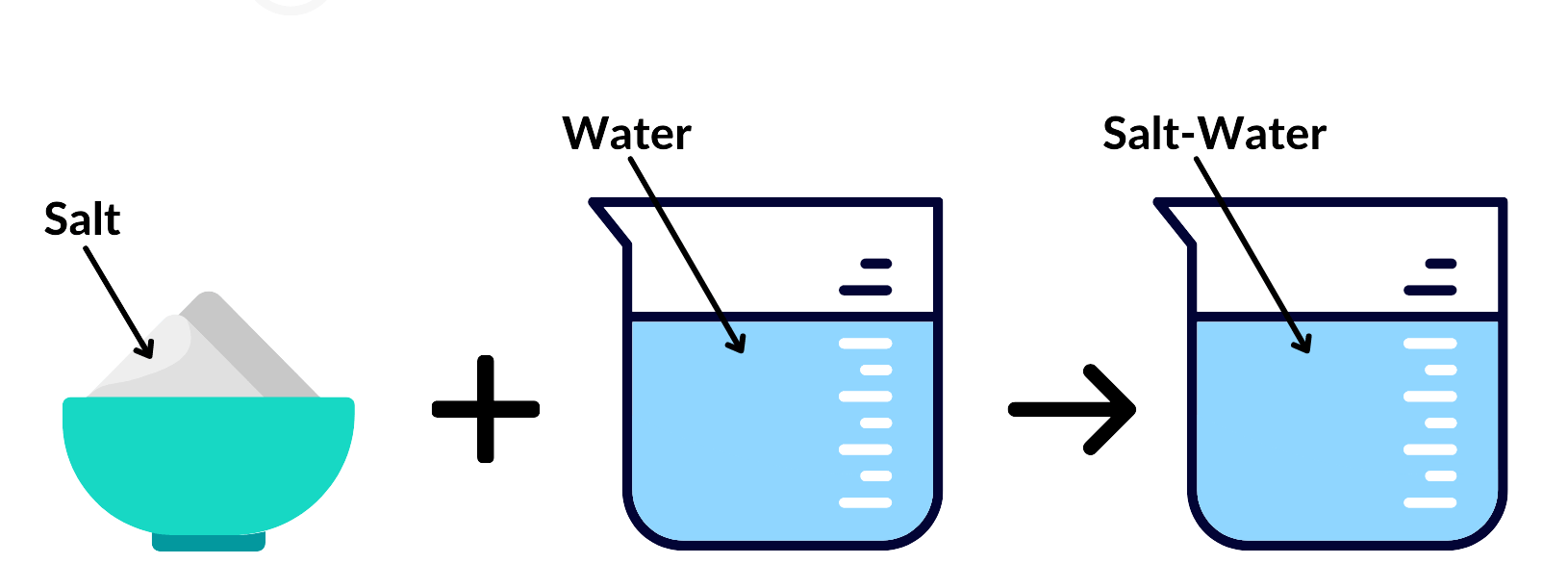
salt = solute. water = solvent. salt-water = solution
What is an atom's nucleus made out of?
protons and neutrons
What are the three kinds of ions and what is the difference between them?
neutral = no charge. anion = negative charge (more electrons than protons). cations = positive charge (more protons than electrons).
In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev created the first what?
periodic table
What's the other name for groups and why?
families because they all have similar chemical behaviors.
What is baking soda made out of?
sodium, hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen
What are the three parts of an atom and what's their amu?
* bonus 100 for saying what amu stands for*
proton and neutron = 1 amu. electron = 0 amu
* atomic mass unit*
____ is the rounded to the nearest whole number version of _____.
mass number , atomic mass
In 1897, J.J. Thomson theorized and drew one of the first accepted models of an atom. What was it called?
plum-pudding model
Name 5 different periodic table groups/categories.
alkali metal, alkali earth metal, transition metal, halogens, noble gases, boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen, lanthanoids, and actinoids
Name two properties of nonmetals.
dull, poor conductors of electricity and heat, brittle, unmalleable.
What gives an element it's identity?
the number of protons
Give me the P, N, and E of arsenic-68?
P = 33, N = 35, E = 33
John Dalton wanted to know why elements form compounds so in 1803, he published his atomic theory. Describe two of the three.
1. All substances are made up of atoms that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed.
2. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike and atoms that are different have to be different.
3. Atoms join other atoms to make new substances.
Give me the category/group name of these 4 elements in order.
Tin, Bromine, Radon, Fermium
carbon, halogen, noble gases, actinoids
What's the main difference between mixtures and compounds.
mixtures are not chemically combined.
What's the name of the "tracks" the electrons follow?
electron orbits
We call unstable isotopes this.
radioactive isotopes
in the early 1900s, Rutherford made a groundbreaking discovery about the structure of atoms. What was it?
That atoms had a dense nucleus rather than being empty spread particles.
Of the 4 corners of the periodic table, which one has the biggest atomic radius and shows the most metallic characteristics?
bottom left
name and describe the three type of solution concentrations.
isotonic= balanced. hypertonic=more solutes "high concentration." hypotonic = more solvent "diluted."
While electrons may follow a track, these "tracks" make up the what?
electron cloud
Which isotope has more electrons and by how much? Carbon-9 or Lithium-11
carbon by 3.