What is heat?
The energy transferred between objects that are different temperatures
This cannot be created not destroyed, but it can be transformed.
energy
Copper, diamond, and gold are considered good _____.
conductors
Convert 150 K to Celsius. (round to the nearest hundredth)
-123.15 C
0 kelvin is also known as what?
absolute zero
This kind of heat transfer goes through the vacuum of space.
radiation
Why do clothes keep us warm?
wool and cotton are good insulators which means they keep heat in.
Convert -273.15°C to Fahrenheit. (round to the nearest hundredth)
-459.67 F
q = m X Cs X ???
temperature change (delta T)
Thermal energy can also be transformed to do ___ like using it to heat water to create steam which in turn makes pistons or wheels move.
work

What's this picture an example of?
thermal expansion and thermal conduction
Convert 400°F to Kelvin. (round to the nearest hundredth)
477.59 K
What is an example of something with high heat capacity?
water
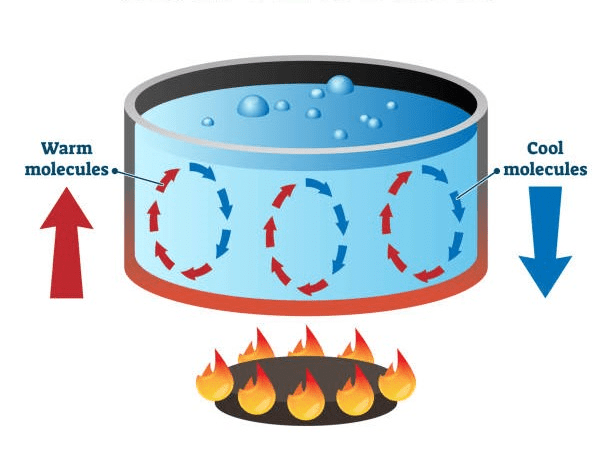
Explain what is happening and what this process is called?
cycles created from warm particles and a heat source. Heated up particles rise and cooler particles taking it's place. The warm particles that rose cool down and the cold particles get warmed up and rise. Convection currents
Anytime one form of energy is converted to another, some of the original energy always gets converted into ???
thermal energy
A 500 g sample of water (Cs = 4.18 J/g°C) is heated from 20°C to 80°C. How much heat energy is required?
125,400 J
What unit do we use to measure thermal energy?
Joules (J)
If you take a metal fork and place the end of it over a fire, what do the particles do and why?
vibrate due to increase in temperature
provide an example of an object and what is it's "waste byproduct?"
lightbulb and thermal energy
chainsaw and sound energy
A 3.5 kg sample of an unknown metal absorbs 25,000 J of heat energy and increases in temperature from 30°C to 90°C. What is the specific heat capacity of the metal? (round to the nearest hundredth)
0.12 J/g°C