During mitosis a _____ cell undergoes division, producing a ______ cell.
body... daughter
The purpose of mitosis is to produce
what is identical somatic cells.
Genetic mutations in the G checkpoints of mitosis could result in a
What is a tumor.
A solute moving down its concentration gradient, from high to low solute is known as
Passive diffusion
When _______ levels are low, glycolysis is the only avenue for ATP production.
What is oxygen
Which phase of mitosis is depicted in the diagram?
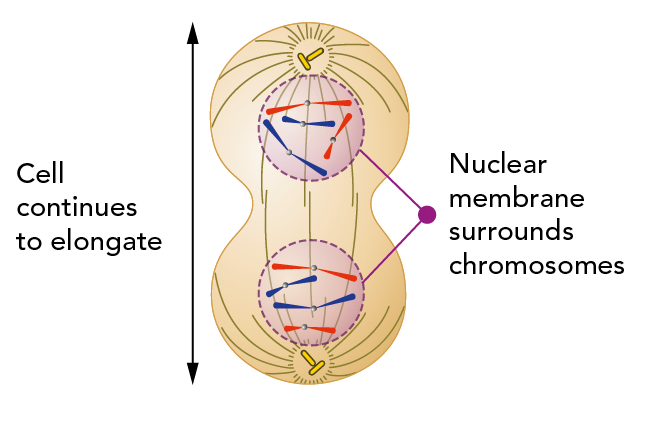
What is telophase
An organism has a diploid number of chromosomes of 10. How many chromosomes would be found in their somatic cell?
Somatic = 10 (diploid)
What would be an advantage to asexual reproduction?
rapid reproduction
The diagram below depicts two substances that are separated by a permeable membrane. This solution is considered to be

What is at equilibrium
This diagram depicts the

what is the electron transport chain.
90% of a cell's life is spent in
What is Interphase
The G1 and G2 checkpoints of interphase are responsible for
What is checking the original and duplicated DNA for errors.
What protein structures in the cell are responsible for organizing the chromosomes during cell division?
centrioles and spindle fibers
CO2 and O2 are able to diffuse through the cellular membrane because

what is small and do not carry a charge.
Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in the
what is the inner membrane of the mitochondria
The two reasons for mitosis are
What is for organism growth and tissue repair
In Mitosis, which 2 phases have duplicated chromosomes and which two phases have single, unduplicated chromosomes?
Duplicated - prophase, metaphase
Unduplicated - anaphase, telophase
The process below describes
Chromatin condenses
- Nuclear membrane breaks down
- Mitotic spindle fibers forms
What is prophase
The Boston Marathon is held on a hot summer day. One of the runners forgot their electrolyte supplements and is forced to hydrate with pure water. At the end of the marathon the runner has a severe headache and then has a seizure. Blood work shows that their cells are
what is swollen and lysing
C6H12O6 -------> 6CO2 is an example of a reduction or oxidation reaction?
What is oxidation
Mitosis begins with a _________ cell and ends with a _______ cell.
What is a diploid... diploid
Metaphase, the second step of mitotic phase, can be described as
the process of organizing DNA so that it can be precisely divided between the two cells.
During the majority of a cells life its DNA is uncondensed. This is so _______. During prophase the DNA condenses and organizes into chromosomes. This is so ___________.
What is so MRNA can translate DNA.
What is so DNA can be divided accurately.
When a patient needs an IV at the hospital, this liquid must be
what is isotonic
These molecules act as H+ acceptors and donators in all stages of cellular respiration.
What are NADH and FADH