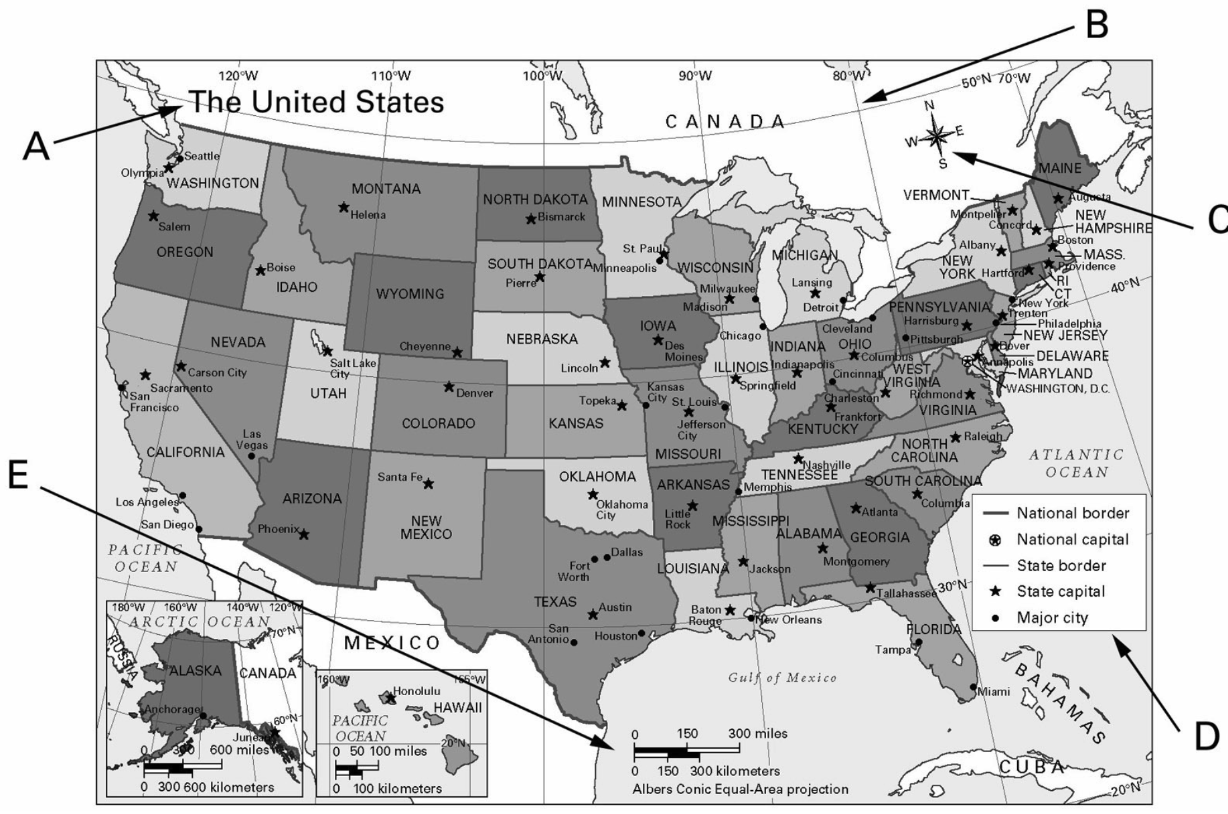
1. What do geographers use to find the absolute (exact) location of any place on Earth?
Latitude & Longitude (global grid)
6. What part of the Earth is most likely changed by physical processes?
The crust
11. The cracking of rocks caused by freezing and melting water is known as what?
Weathering
16. An area with one or more features that sets it apart from others is referred to a what?
a region
2. What does a map's scale compare?
The distance on a map to the distance on Earth
7. What two natural forces wear down mountains?
Glaciation and Erosion
12. Which of Earth's spheres made up of land or rock, above or below water.
the Lithosphere
17. What is the latitude of Menzies?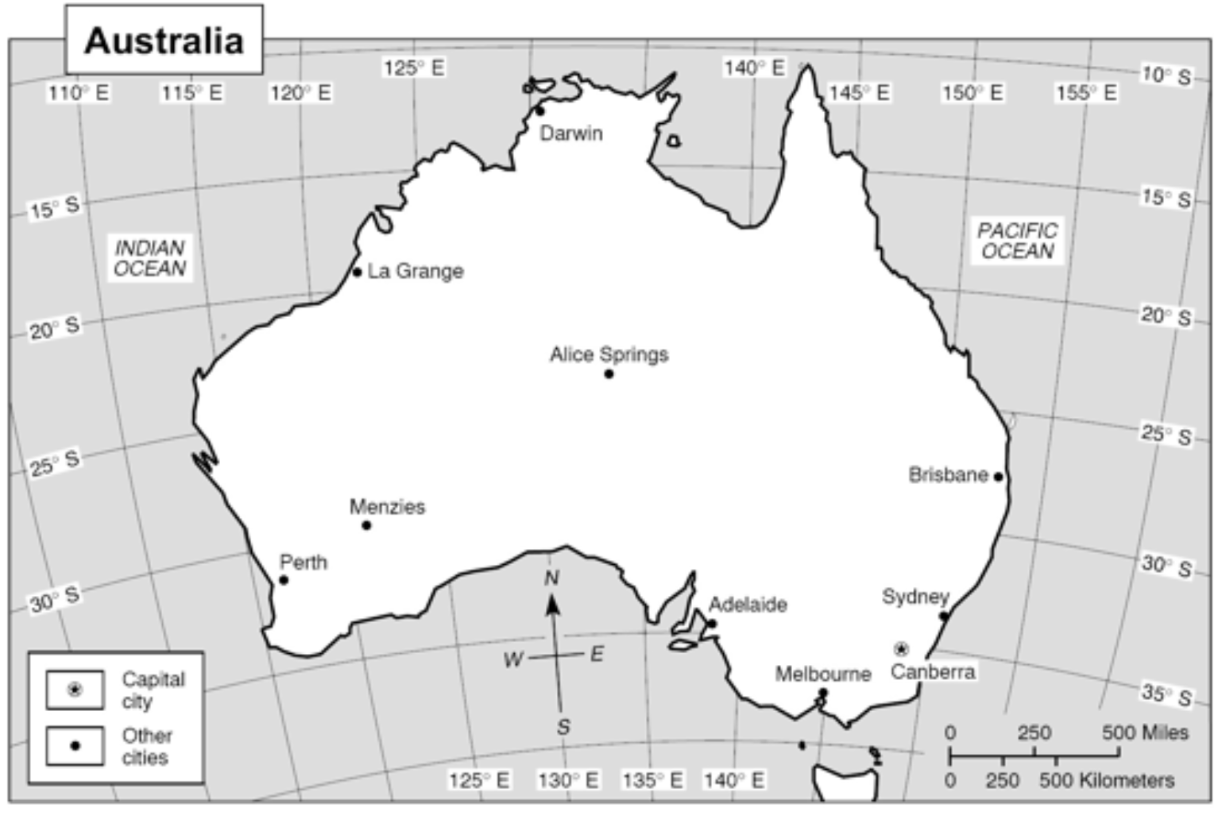
30º S
3. What is the reason why flat maps cannot represent the exact size or shape of Earth’s features?
Distortion
8. What process formed the Himalayan Mountains?
the collision of tectonic plates
13. Which layer of the Earth is made up of magma?
the mantle
18. What landform is represented by the letter D?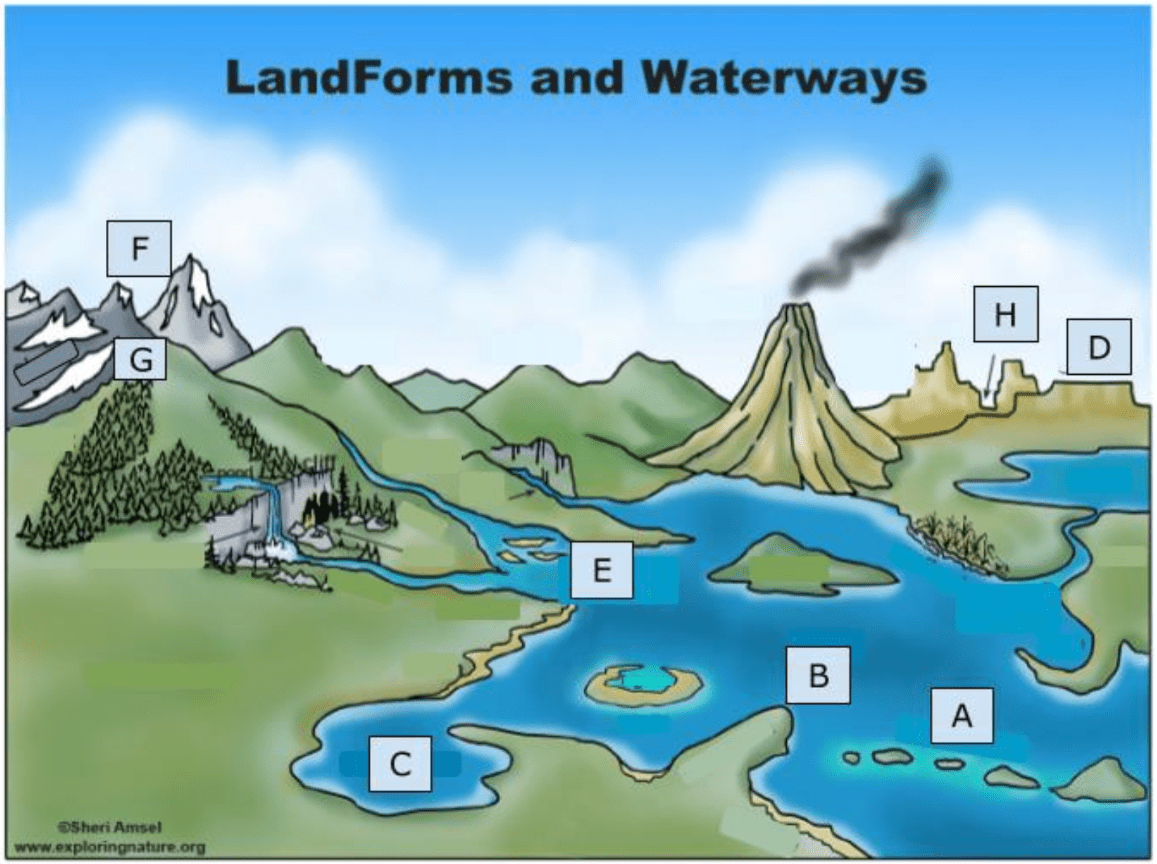
Plateau
4. What's the main advantage of this type of map?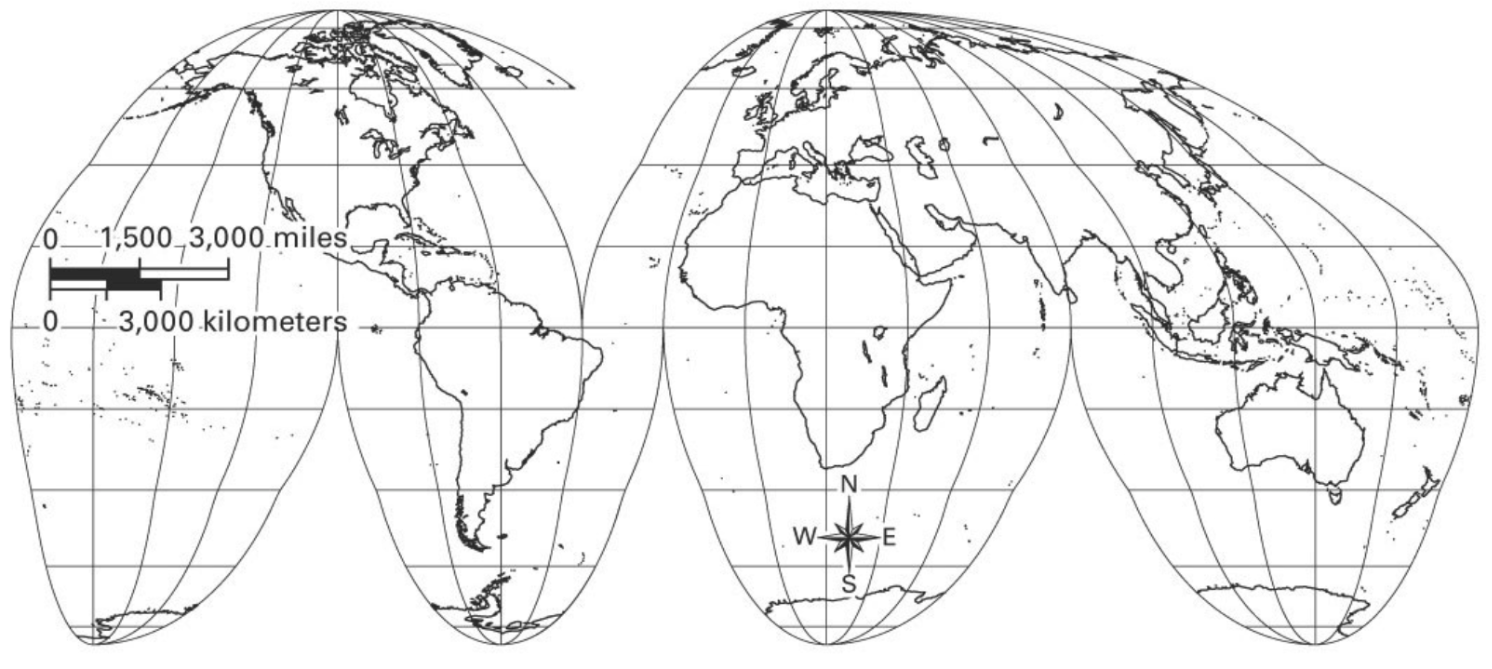
It shows the size and shapes of continents more accurately.
9. What is the major cause of earthquakes?
movement of tectonic plates
14. What are the four spheres of the Earth?
Lithosphere, Hydrosphere, Atmosphere, Biosphere
19. What landform is represented by the letter C?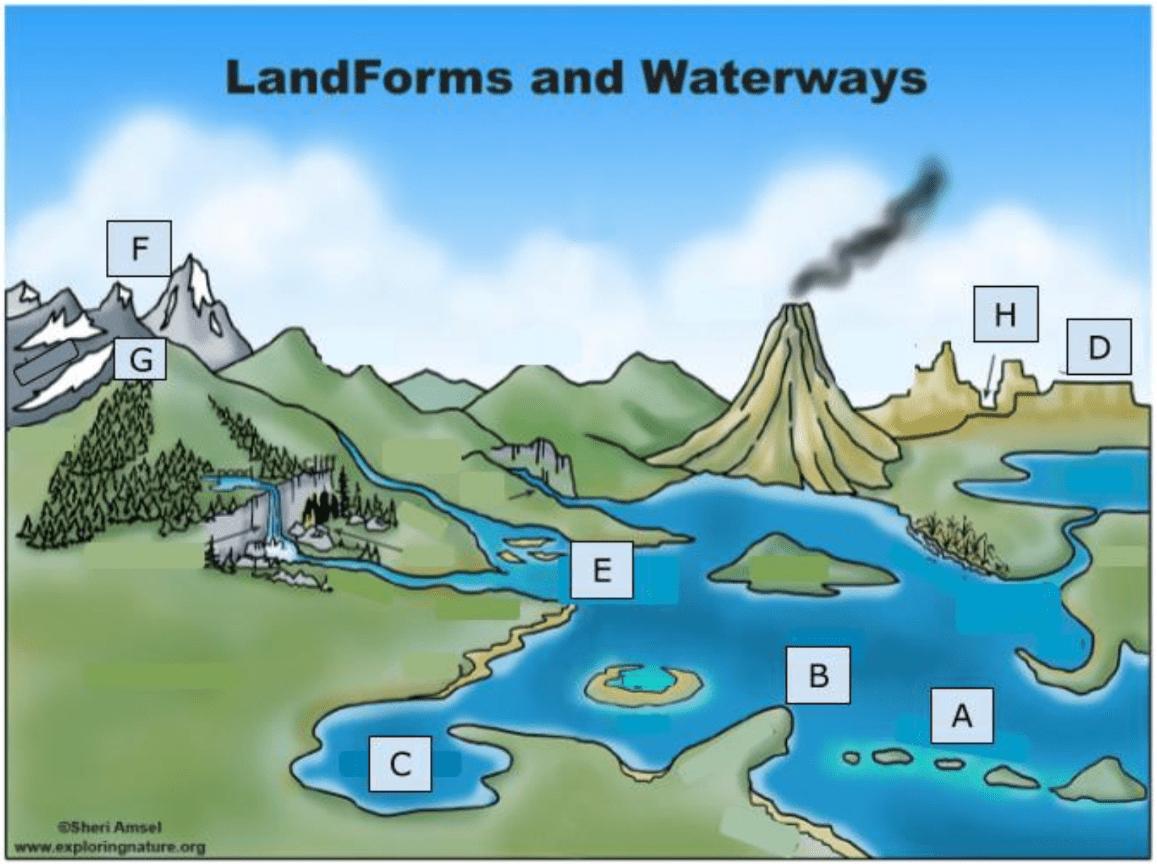
Bay
5. A map that shows you population density os what kind of map?
Thematic map
10. The Ring of Fire surrounds which ocean?
Pacific
15. What is the name of the horizontal line that sits at 0º?
The Equator
20. What two letters are representing the Title and the Legend?