This bone is fractured.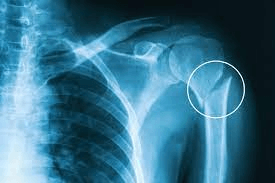
What is the proximal humerus? (double points for saying proximal)
The bony projection highlighted in red.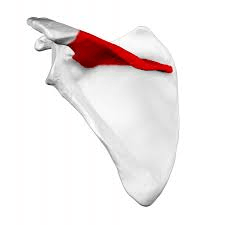
What is the spine of the scapula?
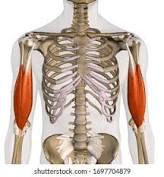
What is the biceps brachii?
This injury occurs with direct contact or FOOSHING. Causing deformity, pain and swelling to the clavicle.
What is a clavicle fracture?
movement of the thumb across the palm of the hand
what is opposition?
The joint highlighted in red. Found on all 5 phalanges. AKA the punching knuckles.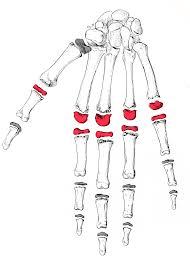
What is the metacarpal-phalangeal articulation?
This projection is highlighted in red and is the connection point for the clavicle.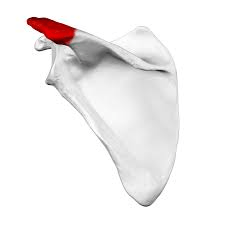
What is the acromion?
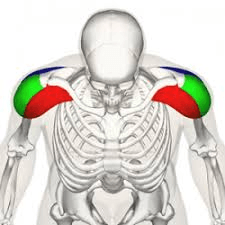
What are the deltoids?
This injury occurs with a direct hit to the tip of the finger.
What is an interphalangeal dislocation?
movement /rotation of a shoulder away from the midline.
What is external rotation?
This bone has been surgically repaired.
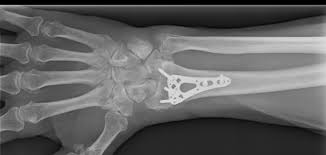
What is the distal radius? (double points for saying distal)
The projection on the tip of your elbow, distal end of the ulna.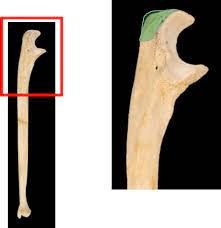
What is the olecranon (process)?
This muscle causes external rotation and abduction.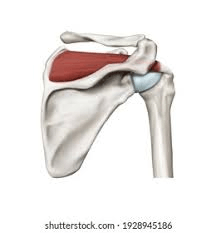
What is the supraspinatus?
This injury occurs with overuse, throwing overhead, and presents with pain in the extensor forearm muscles. This is also known as little league elbow or golfers elbow.
What is medial epicondylitis?
complete displacement of a bone from its joint.
What is a dislocation?
This joint is circled.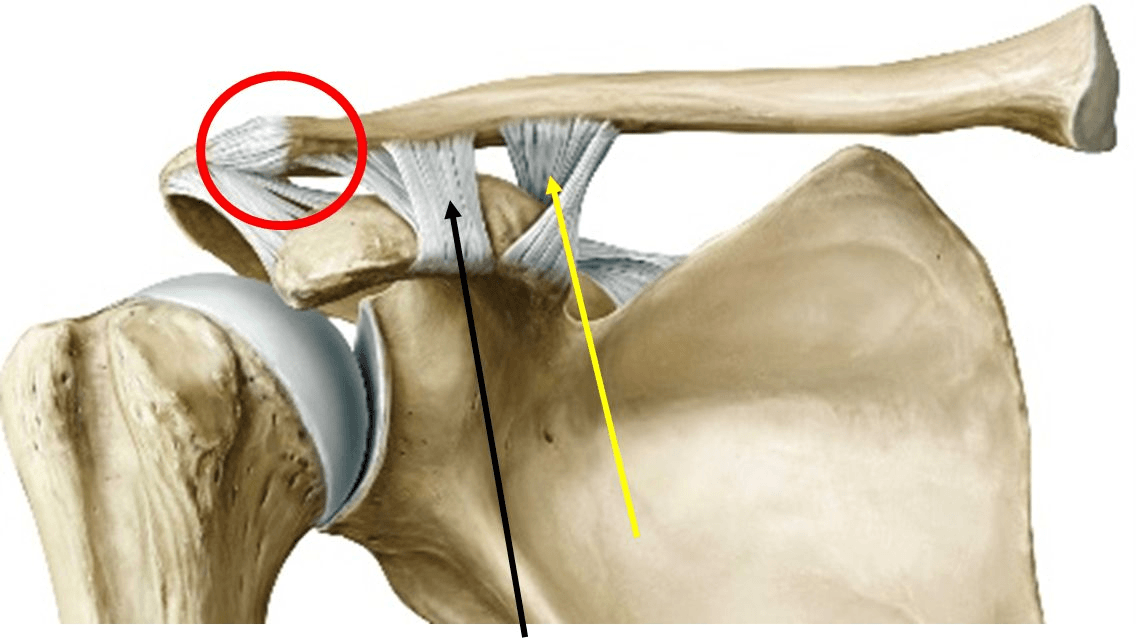
What is the acromioclavicular articulation?
This is an anterior view. The highlighted red projection is a connection point for short head of the biceps muscle.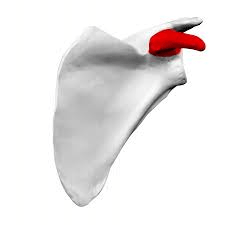
What is the coracoid process?
This muscle causes external rotation and helps stabilize.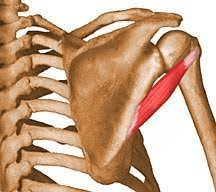
What is the teres minor?
This injury occurs with forced external rotation and abduction. The treatment is to splint and refer to physician asap.
What is a glenohumeral dislocation?
Tissue that connects bone to bone.
What is a ligament?
This joint is dislocated. AKA the knocking knuckles.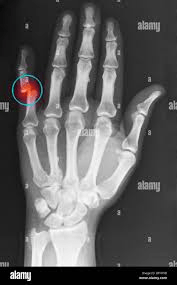
What is the proximal interphalangeal articulation?
There are two of these. The bumps on the distal humerus that allow for the flexors and extensors to connect.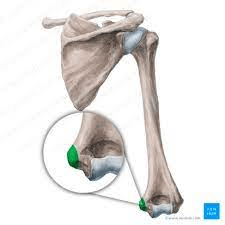
What are epicondyles? Medial and lateral epicondyles.
This muscle causes external rotation and helps with stability.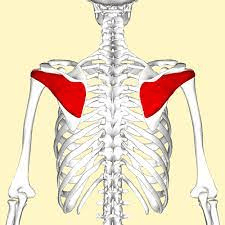
What is the infraspinatus?
This injury occurs with overuse athletes, poor posture and muscle imbalances between the pecs and the back. Treatment is correcting poor posture.
What is impingement syndrome?
Excessive movement beyond anatomical position.
What is hyperextension?
This joint is highlighted in green and is commonly dislocated.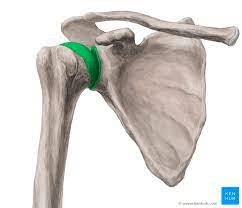
What is the glenohumeral articulation?
The distal end of the ulna. This patient has an oversized one.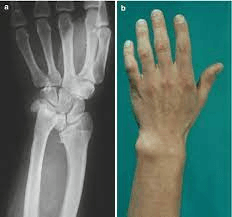
What is the styloid process?
This muscle causes internal rotation and helps with stabilization.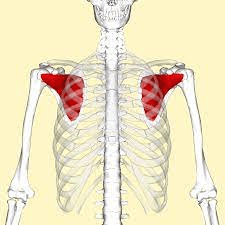
What is the subscapularis?
This injury occurs with a direct hit, hitting the tip of the shoulder or fooshing. Pain is on the tip of the shoulder and damages a ligament. With grade 2 and 3, there will be obvious deformity of the distal clavicle.
What is an acromioclavicular sprain or AC joint separation?
Decreasing the angle between two bones or bending a joint.
What is flexion?