What nerve is highlighted
 ^
^
Medial Pectoral Nerve
Name this muscle
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13075/pasted_image_0.png)
Infraspinatis
Which of the following is innervated by the radial n?
A) Biceps Brachii
B) Coracobrachialis
C) Triceps Brachii
D) Deltoid
C) Triceps Brachii
Why can you ulnar deviate more than radially deviate?
Styloid process of radius is longer than styloid process of ulna
What plane and axis is abduction of the shoulder joint.
Coronal plane and Anteroposterior axis
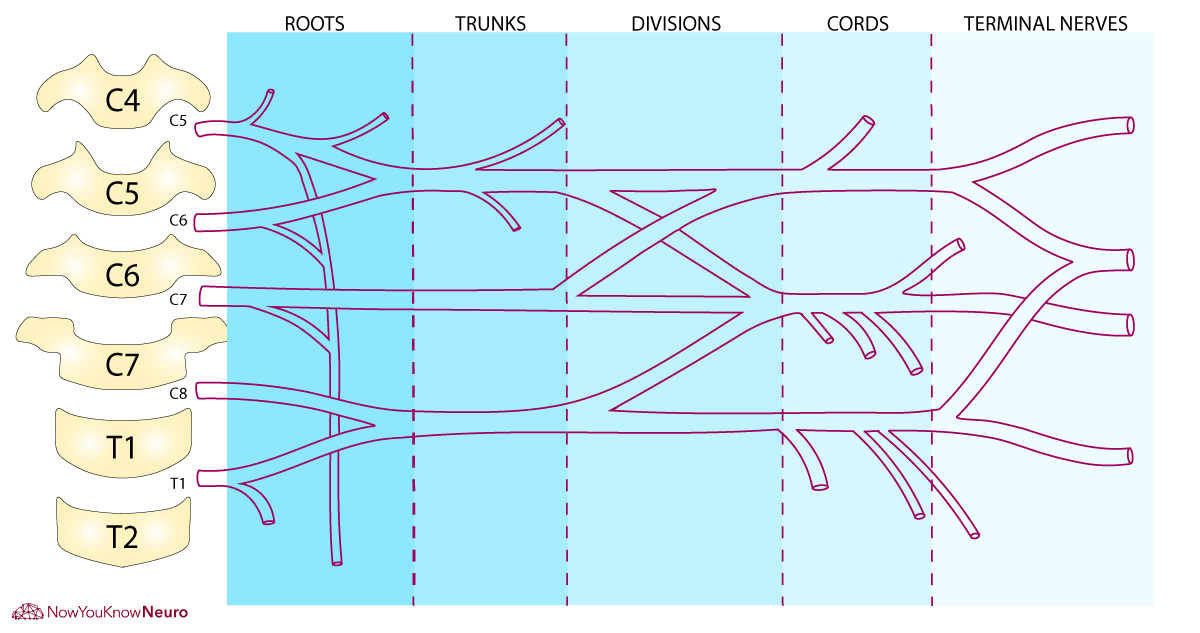
Why is there a C8 cord and where is it located?
There is a C8 nerve because the cervical vertebrae roots all originate above the vertebrae, while thoracic vertebrae roots originate below vertebrae.
The C8 root is below C7 vertebrae and above T1
Which of the following is NOT a rotator cuff muscle?
a) Teres minor
b) Teres major
c) Subscapularis
d) Infraspinatis
Teres Major
You are explaining bicipital tendonitis to a patient. Using anatomical terminology, describe the location of the long head of the biceps tendon and why it is prone to inflammation.
The long head of the biceps tendon originates on the supraglenoid tubercle and travels in the shoulder joint.
Inflammation from irritation during shoulder movements from transverse humeral ligament repeated friction and compression with acromion hood.
Does the radius turn over the ulna at distal or proximal end
Distal
What makes a synovial joint a synovial joint?
Give one example of a synovial joint
Synovial membrane, synovial cavity, and synovial fluid
Which terminal nerves create "the M" of the brachial plexus
Musculocutaneous, Median, and Ulnar nerves
A patient presents with difficulty initiating shoulder internal rotation. Which muscle is likely affected?
Subscapularis
You are palpating a patient’s anterior upper arm and want to differentiate between the biceps brachii short head and coracobrachialis. Describe the landmarks and movements you would use to identify each muscle.
Biceps Brachii inserts onto radial tuberosity; Elbow flexion
Coracobrachialis inserts medial aspect halfway down humerus ; adduction and shoulder flexion
What are the four most superficial forearm flexors?
Pronate teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor carpi ulnaris
What bone is this and what is the protrusion coming off of it called?

Hamate and hook of hamate
Your patient has an injury to the Posterior Cord, name 4 nerves which may be affected?
Upper Subscapular n., Thoracodorsal n., Lower Subscapular n., axillary n., radial n.
What is the origin, insertion, nerve innervation, and action of the teres minor
O: Halfway down lateral border of scapula
I: Greater tubercle
N: Axillary n.
A: External rotation & act with other RC muscles
What is the origin, insertion, nerve innervation, and action of the anconeus
O: Lateral Epicondyle of the humerus
I: lateral surface of olecranon and posterior ulna
N: Radial n.
A: elbow extension
A patient has difficulty performing pronation of the forearm. Using your anatomical knowledge, identify two muscles involved in pronation and their innervations.
Pronator Teres: Median n.
Pronator Quadratus: Anterior Interosseous nerve from median n.
Describe isometric vs isotonic contractions and their respective types
Isometric: Muscle length remains the same but muscle tension is generated
Isotonic: Muscle length changes with production of movement
- Concentric: Contracting muscle that shortens under force
- Eccentric: Contracting muscle that lengthens under force
An injury at the musculocutaneous nerve could have come from which root?
Bonus: Which muscles/ actions may be hindered?
C5, C6, and C7
Elbow flexion, shoulder flexion, shoulder adduction
Biceps Brachii, Brachialis, Coracobrachialis
Name the two coracoclavicular ligaments
Conoid and Trapezoid Ligaments
What is the arterial blood flow from heart to upper arm (5 arteries)
Bonus: What 2 muscular structures help separate the regions?
Brachiocephalic artery -> Subclavian artery -> Axillary Artery -> Brachial Artery
Anterior Scalene helps separate the Subclavian and Axillary arteries
Pectoralis Minor helps separate the Axillary and Brachial arteries
A patient presents with difficulty flexing the distal phalanx of the index finger. How would you use your understanding of forearm anatomy to determine whether the lesion is at the anterior interosseous nerve or a more proximal median nerve injury?
Flexion of the distal phalanx of the index finger is performed by the flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) to the index, innervated by the anterior interosseous nerve
If you asked a patient to make a fist and their hand looked like the image on the left upon attempting to flex the digits of the hand... what nerve do you think is involved?
Bonus: What muscle?
Median Nerve
Flexor Digitorum Profundus