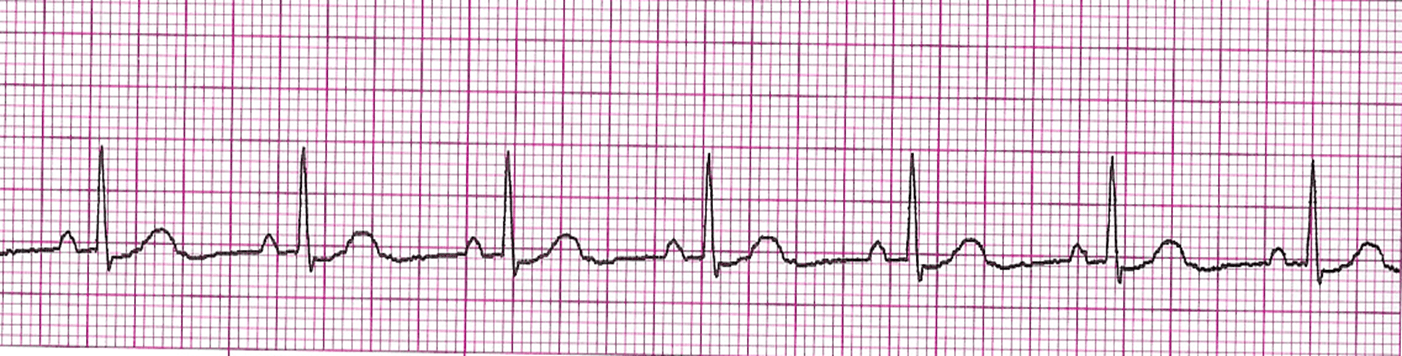
What is Normal Sinus Rhythm
This is how many Heart Failure affects
What is millions of people
You do this STAT on arrival if the patient had an intervention.
What is an EKG
The first step when an acute change in neurological status is noted
What is call a Rapid Response
You must monitor this vital sign after giving your patient NTG
What is BP
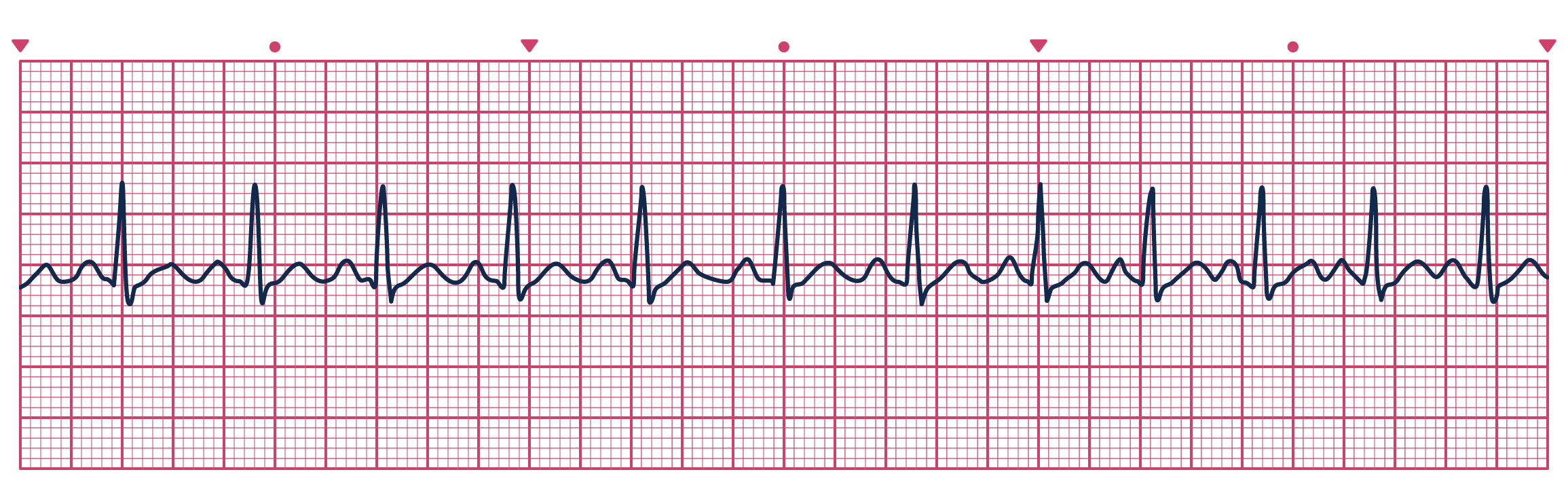
What is Sinus Tachycardia
Risk/Contributing Factors
HTN, MI, DM, Thyroid dysfunction, Infection, non-compliance with diet and/or meds
These are the labs that need to be drawn 3 hours after the procedure
What is CBC and potassium
The "A" in BE FAST
What is Arms
You must check this if a patient has a syncopal event when trying to stand
What is Orthostatic VS
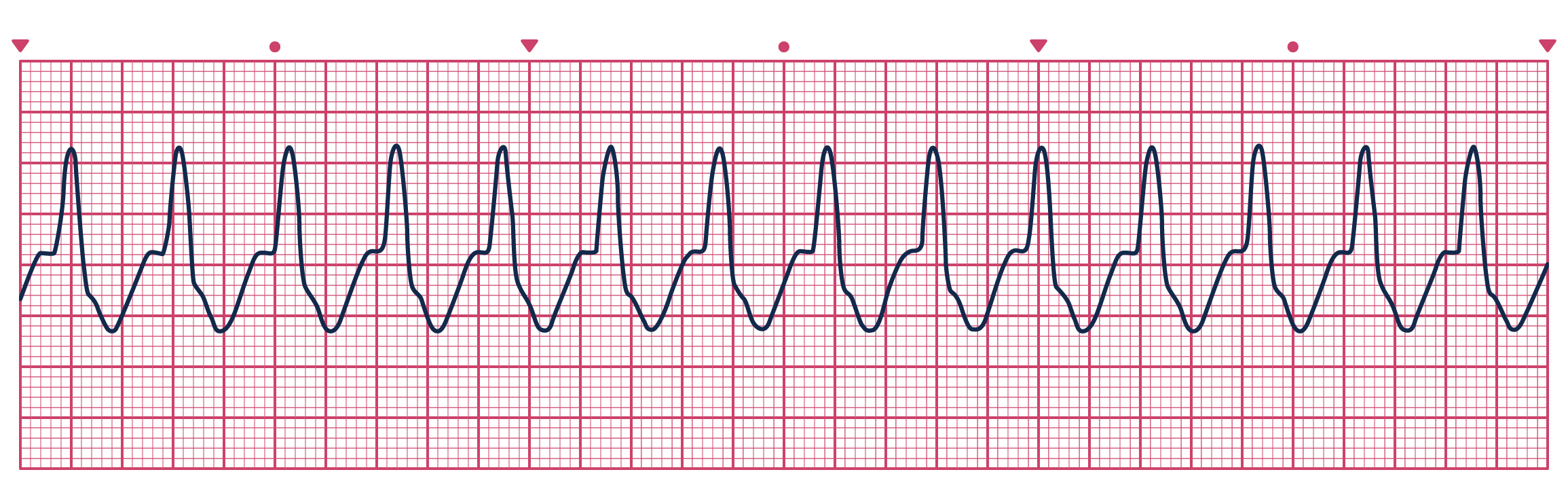
Ventricular Tachycardia
The "r" in HFrEF
What is reduced
This is done the first time you ambulate a patient
What is orthostatic vs
This dot phrase is used when preparing for discharge
What is .DCSTROKE
This is a common medication to "fix" a preload problem
What is NS or IV fluids
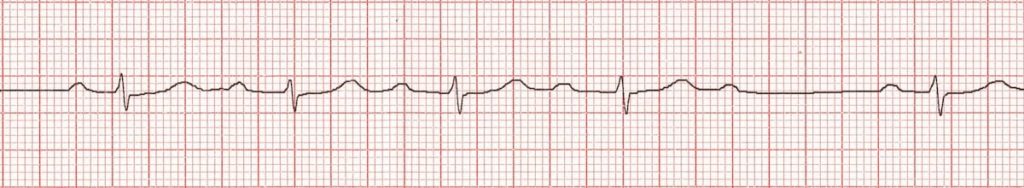
What is 2nd Degree type 1
This type is a "filling" problem
Diastolic Heart Failure
The amount of time there can be no BP or labs done on affected arm for radial access
24 hours
This is the window of eligibility for the use of Alteplase
What is 4.5 hours
What is AV pacing
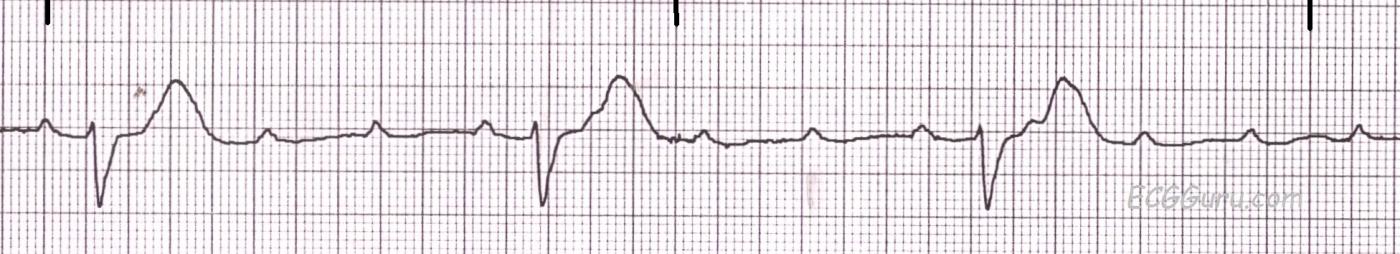
What is 3rd degree heart block
This type is a Pump problem
What is Systolic Heart Failure
This is who you call for after hours complication
Cardiology
Frequency of NIHSS to be documented
On arrival, At time of transfer, Or any change in neuro condition
The max dose of potassium you can give a patient at one time.
What is 40 mEq