The Primary Imaging Feature of an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
What is >3 diameter
Label A
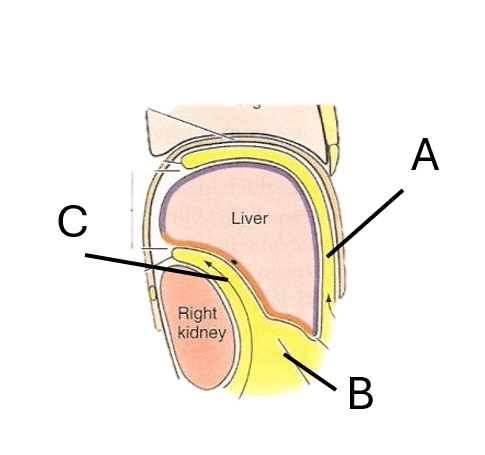
What is Subphrenic space
Congenital extension of the liver anteriorly and inferiorly to the right kidney
What is the Reidel lobe
What are the parts of the Pancreas?
What is the Head/Neck, body, and Tail
Where is a Klatskin tumor commonly located?
What is junction of the right and left hepatic ducts
This vessel runs posterior to the neck of the pancreas and anterior to the uncinate process
What is the Superior Mesenteric Vein
Label c
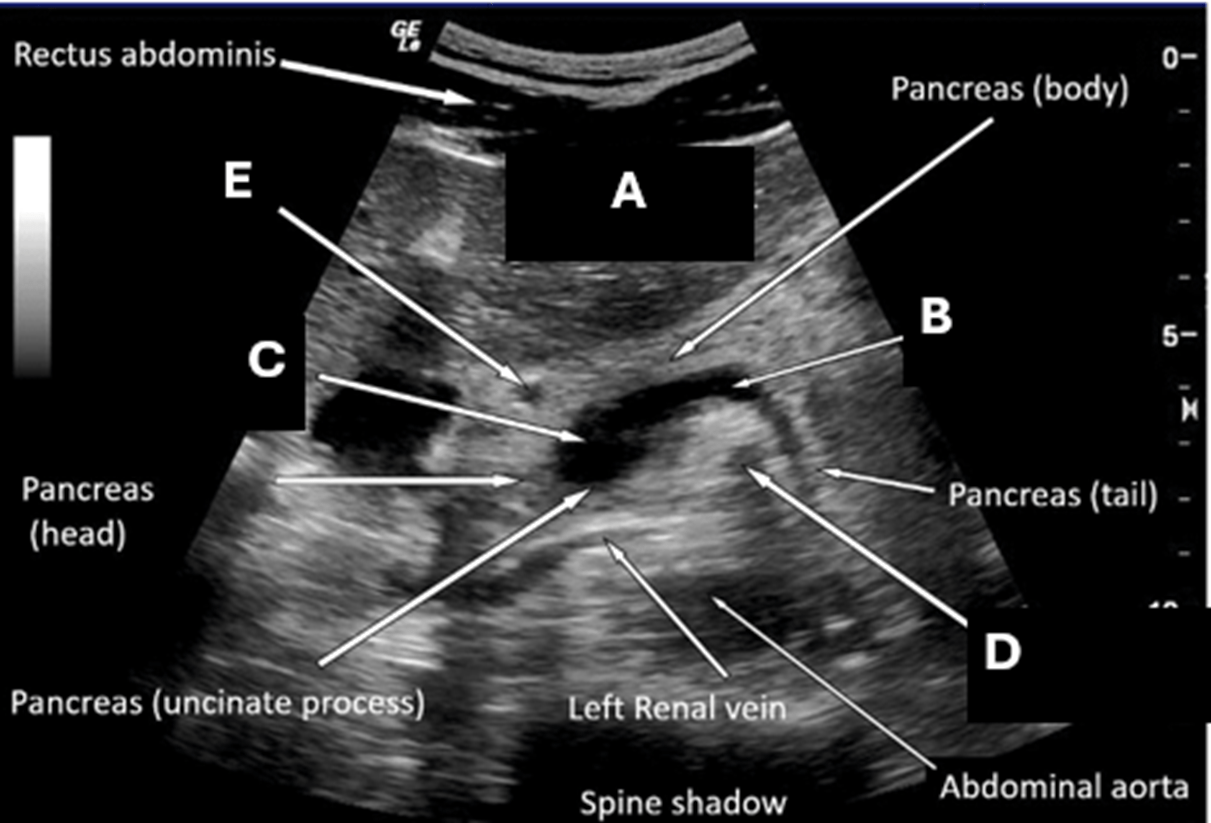
What is the superior mesenteric and splenic vein confluence
The measure of an adult liver is considered to be enlarged if
AP diameter is >15 cm
Diameter of the head should not exceed?
3mm
Non-shadowing, low amplitude echoes located in the dependent portion of the gallbladder
What is Biliary Sludge
A specific pattern seen in arteries distal to a stenosis or blockage
What is Tardus-Parvus Waveform
Label B
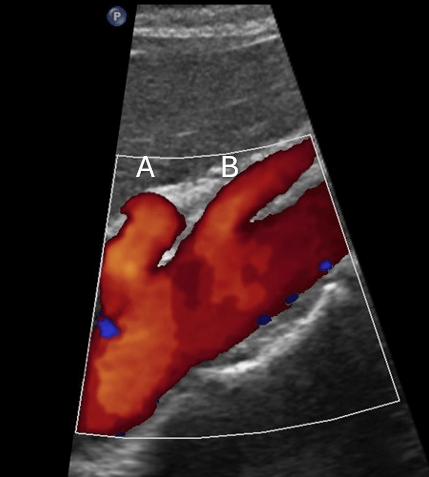
What is superior mesenteric
Will a Cavernous hemangioma display a propagation speed artifact?
No.
What is anterior to the portosplenic confluence
What is the Pancreas Neck
Label A-D
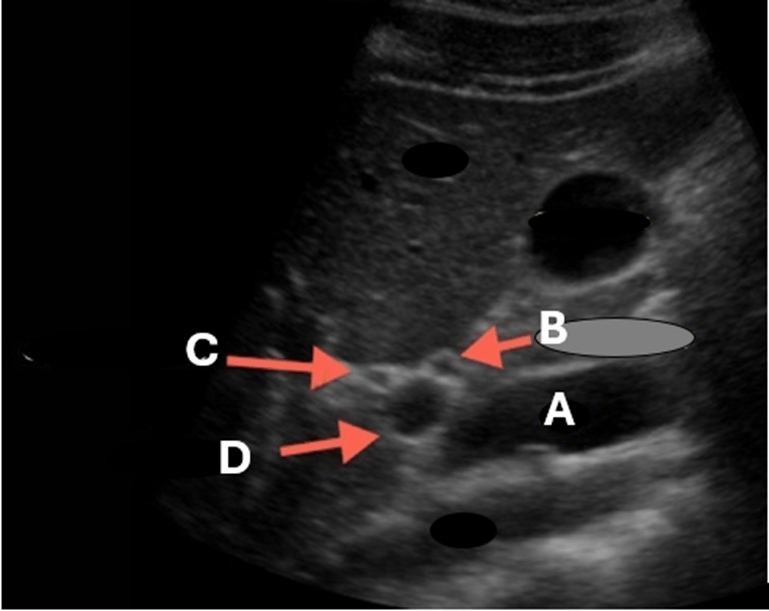
A- IVC
B- Hepatic Artery
C- Common Bile Duct
D- Main Portal Vein
IVC Doppler Waveform is normally
What is Phasic flow with respiration
Left Arrow points to?
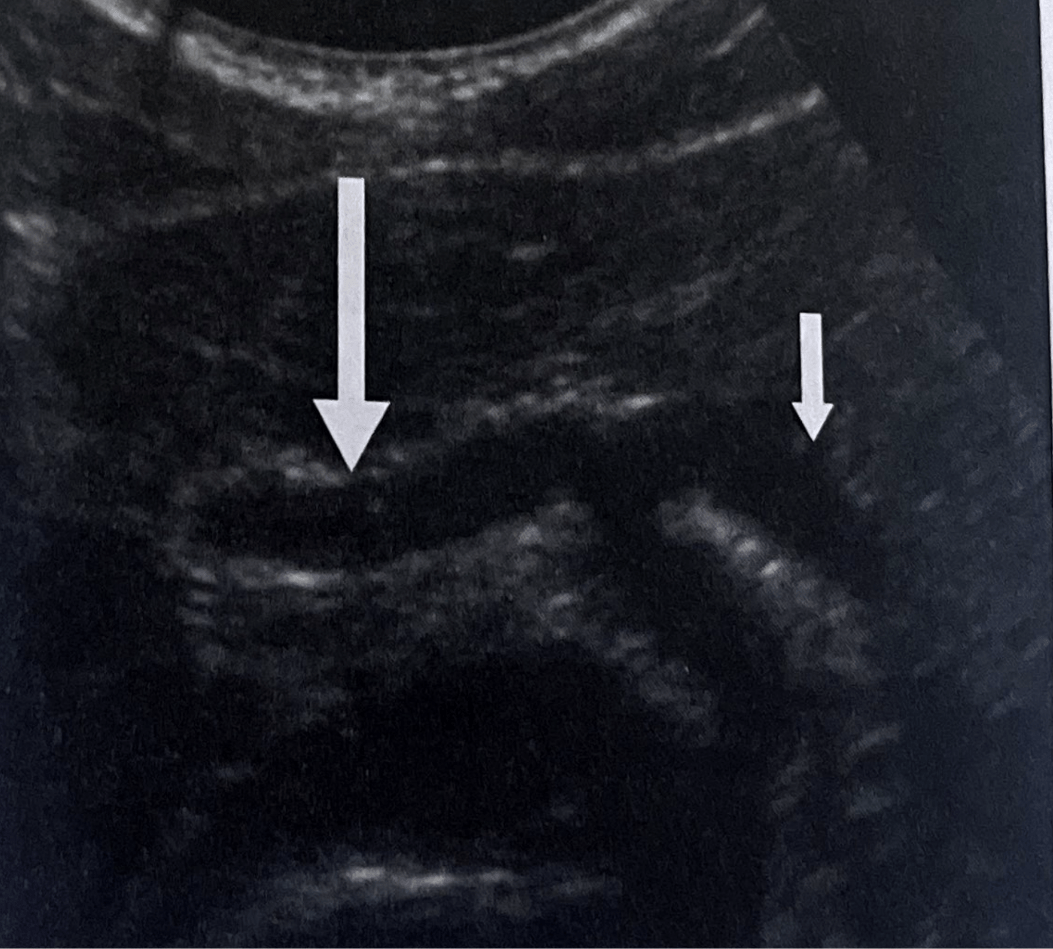
What is Hepatic Artery
Wheel within a wheel is associated with?
What is candidiasis
What is most commonly located in lesser sac abdominal recess?
What is a Pseudocyst
A patient presents with a 2 day history of RUQ tenderness, elevated LFT’s. The sonogram of the gallbladder demonstrates cholelithiasis and hydrops
What is acute cholecystitis
The origin of the
Common hepatic artery?
What is gastrodoudenal artery
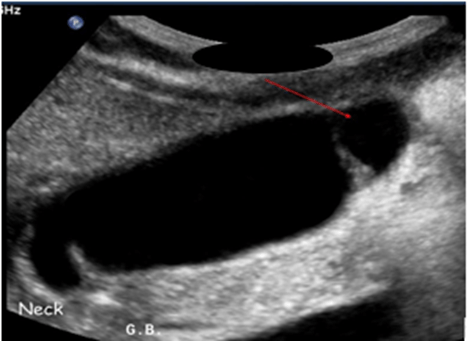
What is phrygian cap
IVC dilation is not a secondary sign of
What is the Santorini
The secondary secretory duct of the pancreas
Patient presents with a 2 day history of RUQ tenderness, elevated LFT’s. The sonogram of the gallbladder demonstrates cholelithiasis and hydrops
What is biliary obstruction