pH below 7.35
Acidosis
p. 4
7.35 to 7.45
pH
p. 3
Critical to homeostasis and optimal cellular function.
Normal acid-base balance
p. 4
Results from abnormal bicarbonate loss or excess of nonvolatile acids in the body?
Metabolic Acidosis
p. 4 and 5
You may notice a decreased LOC, irritability and altered mental status or impaired memory and/or personality changes - What is the concept
Cognition.
p. 7
pH above 7.45
Alkalosis
p. 4
75-100 mmHg (book says 80 to 100 mmHg)
PaO2
p. 10
Substances that prevent major changes in pH?
Buffer systems:
p. 4
Excess of bicarbonate in relation to amount of hydrogen ions
Metabolic Alkalosis
p. 5
Identify patients at risk for acid-base imbalances.
Diabetes, Crohn's disease, Chronic kidney disease, chronic lung disease.
p. 7
Reflects acid-base balance through out the entire body and is the gold standard for assessment.
Arterial Blood Gasses (ABG's)
p. 9
35 to 45 mmHg
PaCO2
(Carbon dioxide)
p.10
Name the three major buffer systems.
Bicarbonate-Carbonic acid
Phosphate Buffer system
Protein Buffers
Primary change is in concentration of carbonic acid and CO2 is retained.
Respiratory Acidosis
p. 5
patients may experience respiratory distress may require intubation or a hypoxemic patient may require supplemental oxygen.
Airway Management
p. 12
paO2 level <80 mmHg
Hypoxemia
p. 10
24 to 28 MeQ/l
HCO3
(bicarbonate)
p. 10
Regulates carbonic acid by eliminate or retaining CO2.
Patients with chronic lung disease may have high serum CO2 levels
The respiratory system
p. 4
Primary change is in concentration of carbonic acid, CO2 is lost.
Respiratory Alkalosis
p. 5
Name some ways that we can promote health within our patients.
Maintain fluid balance, monitor chronic conditions, Nursing focused is on patient teaching related to nutrition and adherence to prescribed medications and treatment regimens.
p. 7
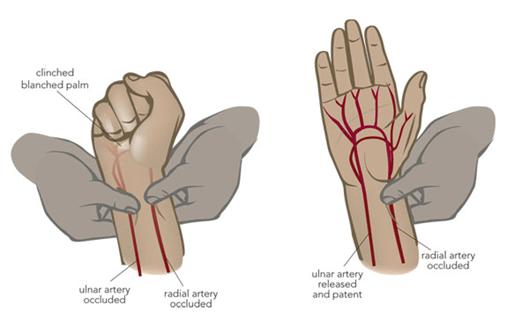
Allen test: to measure ulnar patency
p. 9
-3 to +3
Base Excess (BE)
p. 10
Responsible for long term acid-base regulation.
Renal System
p. 4
Name the risk factors for acid-base imbalance.
Critically ill, Hydration status, chronic conditions
p. 6 for the table
p. 7
Name the independent interventions a nurse can do when it relates to acid-base imbalances.
Thorough patient history, daily weight, I/O, Assessment of respiratory and renal function, Maintain patient airway, Vital signs, O2 saturation, Assessing LOC and neurological status, Prompt reporting of changes in condition.
p. 11