the primary goal of acid-base homeostasis


Maintain a normal pH
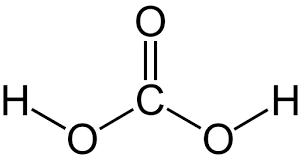
the most significant volatile acid
what is:
Carbonic acid H2CO3
the primary event that leads to a High CO2 and tries to compensate through high HCO-3 which takes place slowly is called
Ph(H+ -hydrogen ion) range: 7.35-7.45
acid <-------7.40------->alkaline(base)
PaCO2 range: 35-35mmHg
akaline<----------40-------->acid
HCO-3 range: 22-26Eg/L
acid<-----------24----------->alkaline
EX: Ph 7.30/PaCO2 50/ HCO-3 30
ph- acid/PaCO2 acid/ HCO-3 alka
what is:
Respiratory acidosis
-Increasing alveoli ventilation will fix this

the organ system that excretes H+ from the body

what is the:
Kidneys
the two points would you use to calibrate an O2 analyzer

what is set at:
21% & 100%
the following are indications for ____
-need to evaluate ventilation(PaO2), acid-base balance(pH & PaCO2), oxygenation status(PaO2 & SaO2) oxygen- carrying capacity of blood(PaO2,HbO2, total Hb, dyshemoglobins)
-to assess the patient's response to therapy or diagnostic test
-monitor severity & progression of documented disease process
-sudden, unexplained dyspnea, acute shortness of breath/tachypnea, cyanosis
-heavy uses of accessory muscles(WOB)
-changes in ventilation settings
-CPR
what is an:
ABG(arterial blood gas)
The driving force behind Bicarbonate buffers is the process of ____
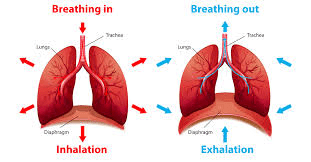
what is: ventilation
the ratio for HCO3- dissolving CO2(this will give you a normal pH balance)
what is:
20:1
the two mechanisms responsible for maintaining a stable pH
what is:
Isohydric buffering
Pulmonary ventilation
the primary chemical event caused by low CO2 levels that could be compensated through low HCO-3 (takes place slowly)
Ph(H+ -hydrogen ion) range: 7.35-7.45
acid <-------7.40------->alkaline(base)
PaCO2 range: 35-35mmHg
akaline<----------40-------->acid
HCO-3 range: 22-26Eg/L
acid<-----------24----------->alkaline
EX: ph 7.60/PCO2 30/HCO-3 20
ph alk/PCO2 alk/HCO-3 acid
what is:
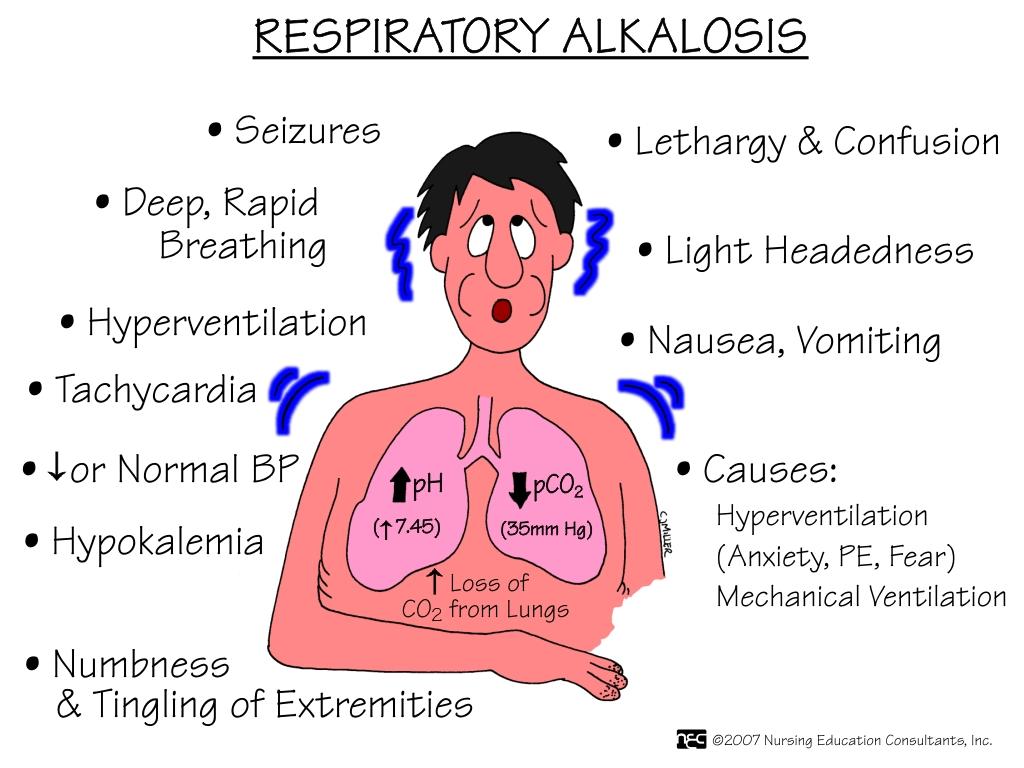
Respiratory alkalosis
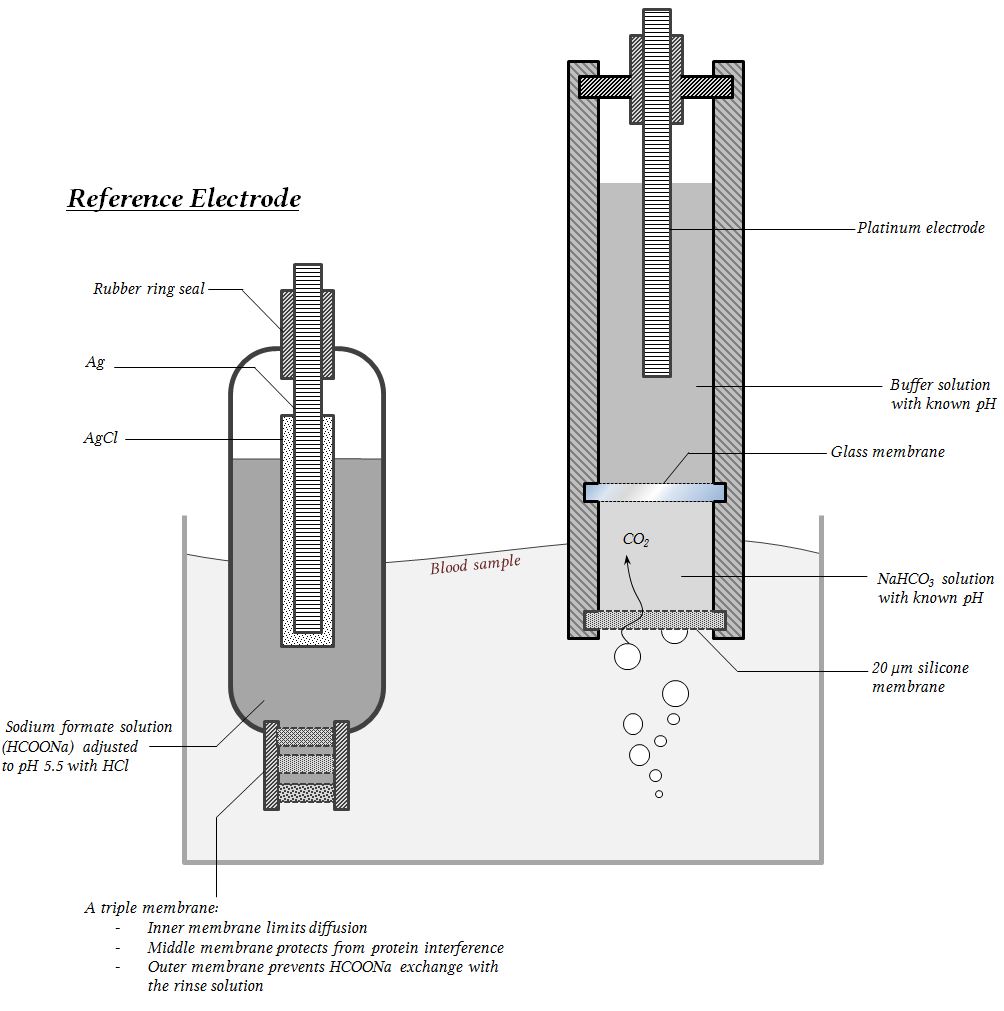
the ___ device is an electrochemical O2 analyzer that slowly measures PO2, not FiO2 concentration, using a gold anode and a lead cathode to generate a chemical reaction that creates current flow across the pole with no external battier source required, but often needs the fuel cell replaced.
what is a:
Galvanic Fuel cell
the 3 values that are measured on the blood gas analyzer

what is measured:
pH, pCO2, p02
when do you do an Allen's test?
what is:
before radial artery puncture ONLY
What is the most important & abundant Non-Bicarbonate Buffer in a closed system?
what is:
Hb
the ratio indication of pH level needed for HCO-3 to dissolve CO2, causing the result to be alkalosis

what is:
> 20:1
the term that matches the following statement:
-the solution that resists large changes in pH upon the addition of an acid or a base
what is a:
Buffer solution
the primary chemical event that is caused by low HCO-3 levels and could be compensate through low CO2(hyperventilation)(works fast)
Ph(H+ -hydrogen ion) range: 7.35-7.45
acid <-------7.40------->alkaline(base)
PaCO2 range: 35-35mmHg
akaline<----------40-------->acid
HCO-3 range: 22-26Eg/L
acid<-----------24----------->alkaline
EX: Ph 7.05/PCO2 20/HCO-3 8
ph acid/PCO2 alk/HCO-3 acid
what is:
Metabolic acidosis

the _____ device that measures FiO2 then uses O2 to produce a reduction-oxidation reaction, by O2 molecules diffusing through the sensor membrane into the electrolyte and polarizing voltage fastly with electricity.
-made of platinum cathode & a silver-silver chloride

what is a:
Clark electrode(polarographic)


the 3 values that are calculated on the blood gas analyzer


what is:
Calculated HCO3-, BE(base excess), Hb
What should you do when doing an arterial blood gas and the pulsatile blood flow stops?
what is:
you should slowly withdraw
the bicarbonate buffer uses the aid of ____ and is then converted to ____, which is excreted during exhalation.
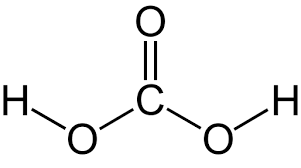
what is:
H2CO3
CO2
the ratio indication of pH level needed for HCO-3 to dissolve CO2, giving an acidosis result


what is:
<20:1
The bicarbonate buffer system for _____ acids takes H+(hydrogen ion) to be buffered by HCO3(bicarbonate ions) and converts it to CO2 and H2O. The CO2 formed is then eliminated in exhaled gas.


what is:
Fixed acids
the primary chemical event that is caused by high HCO-3 levels and could be compensated through high CO2 level(Hypoventilation)(place fast)
Ph(H+ -hydrogen ion) range: 7.35-7.45
acid <-------7.40------->alkaline(base)
PaCO2 range: 35-35mmHg
akaline<----------40-------->acid
HCO-3 range: 22-26Eg/L
acid<-----------24----------->alkaline
EX: Ph 7.49/PCO2 60/HCO-3 40
Ph alk/PCO2 acid/alk
what is:
Metabolic alkalosis
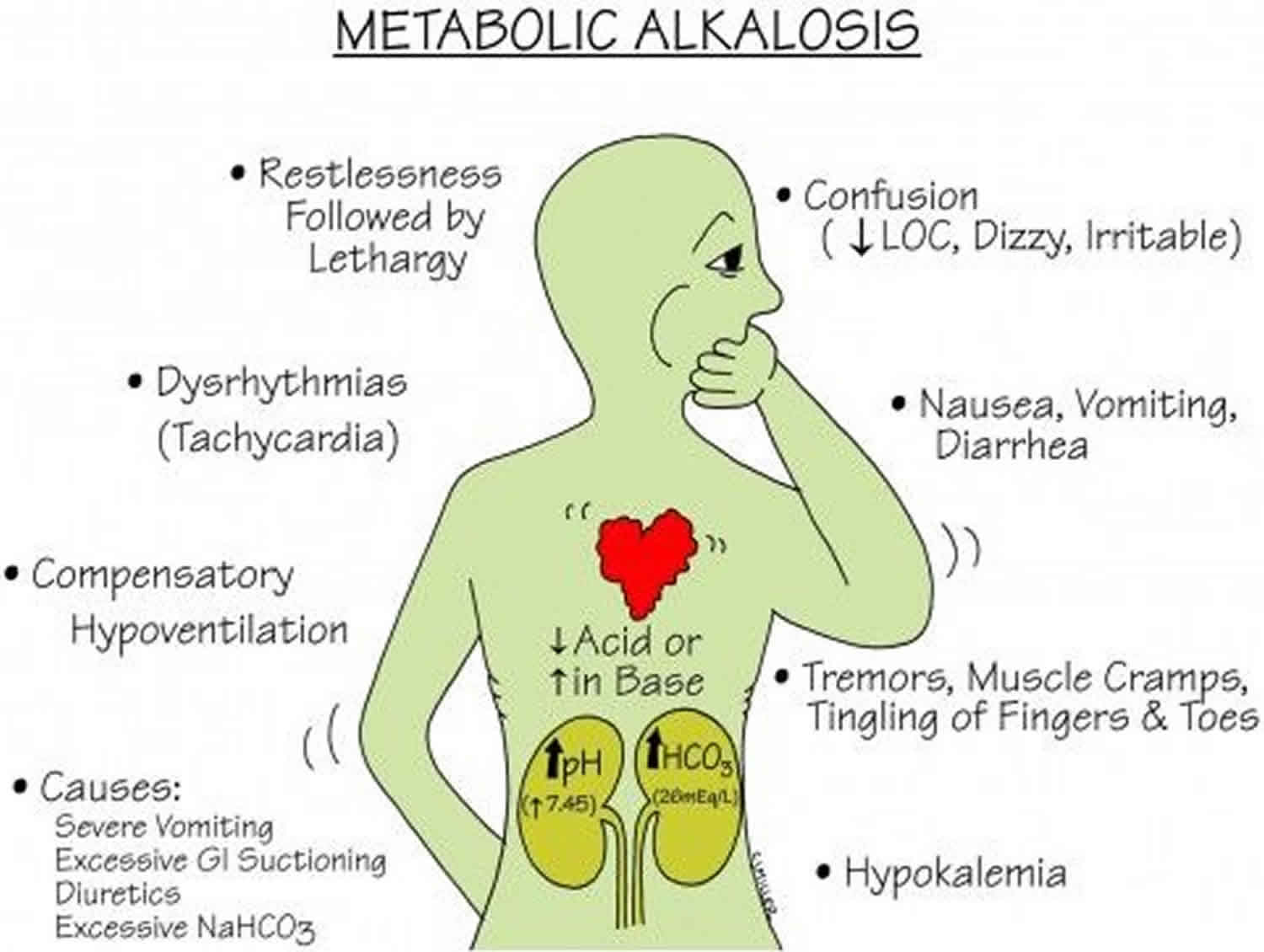
side note: when both respiratory & kidney are experiencing this simultaneously that is a mixed/ combined result
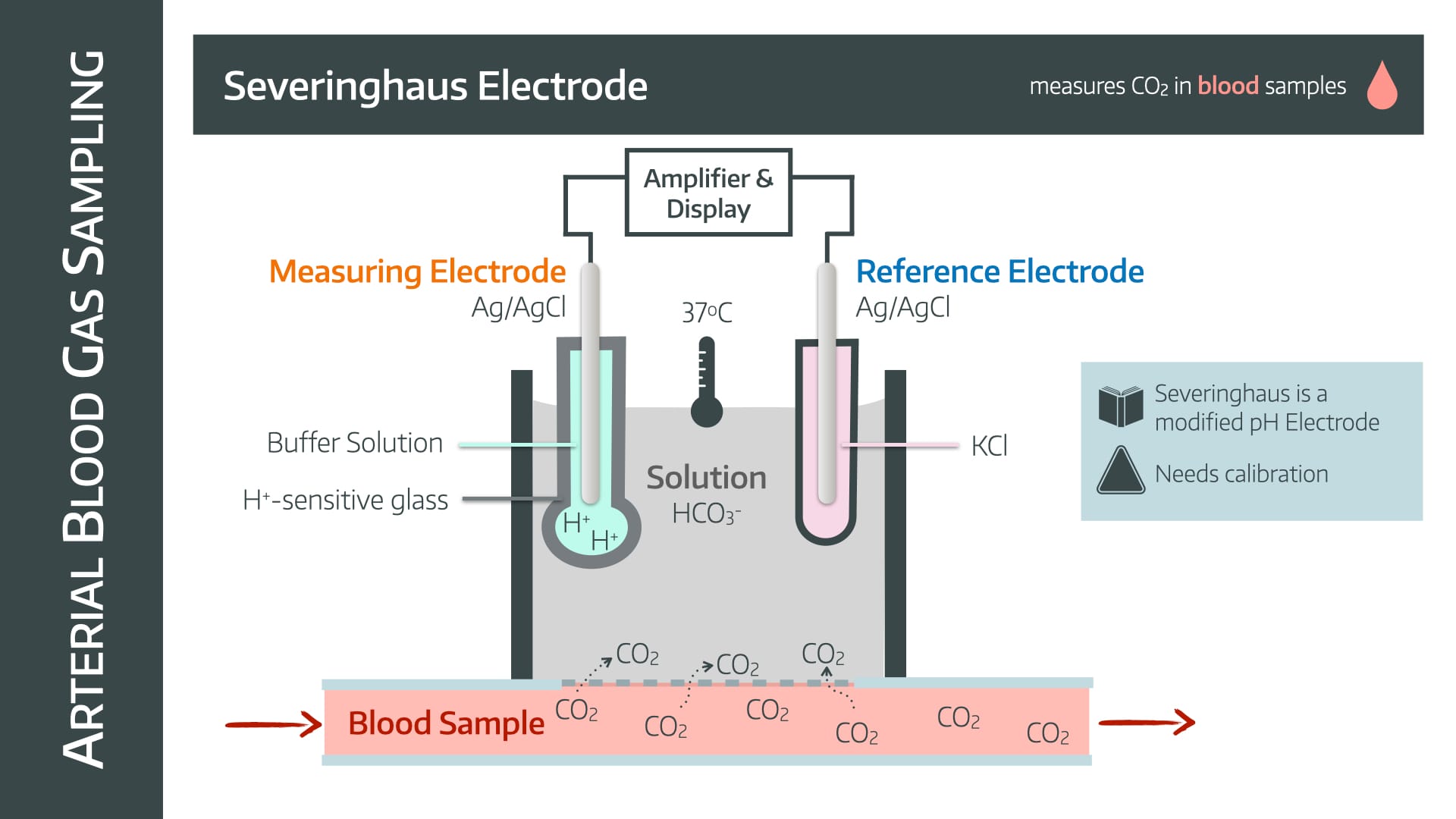
the _____ electrode measures CO2 through sodium bicarbonate, which reacts with the CO2; The reaction changes the pH in the electrode, which corresponds to a change in potential difference, and this is measured. The CO2 is then inferred from the change in pH.
what is: severinghaus
the prevention of the following; air getting into a sample and needle stick injuries is the purpose of ____

what is:
needle capping devices
If a patient was stress hypoventilating during an ABG, what may the results conclude?
what is:
Respiratory Alkalosis
-let the lab know
_____ increases the CO2 removal, causing non-bicarbonate buffers to release H+
what is:
Hyperventilation
-acidosis activates CNS receptors, signaling the need to increase VE(blames kidneys)
the normal arterial blood gas range for pH

what is:
pH 7.35 to 7.45
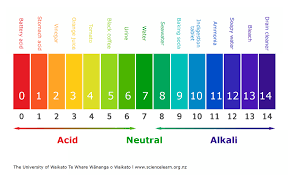
the NON-BICARBONATE closed system takes on the role of buffering when there is no gas to remove acid by ventilation, so H+(Hydrogen ions) bind with phosphates, proteins, and Hb by H2CO3(carbonic acid) donation. The ____ acids are excreted through this process. The source responsible is tissue metabolism producing massive amounts of CO2, which is then hydrolyzed(water molecule added).
-NB can eliminate fixed acids

what is:
volatile acids
-equilibrium with dissolved gas.
-The only one of physiologic significance in the body is carbonic acid(H2CO3-)
the effect H+ has on pH
-Higher H+ concentration: The pH is lower, and the solution is more acidic.
-Lower H+ concentration: The pH is higher, and the solution is more basic
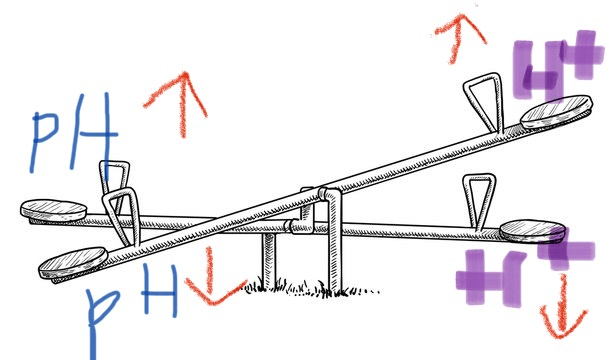
what is: an
inverse relationship
the causes of RT needing to pick an alternative site for an ABG, which of the following would be the reasons:
-Failed Allen's test
-Peripheral vascular disease or infection
-Surgical Shunt
-anticoagulation therapy
Causes: Failed Allen's test, Peripheral vascular disease or infection, Surgical Shunt
NOT a cause- ANTICOAGULATION THERAPY IS NOT A REASON TO CHOOSE A NEW SITE
the cause of a false high on a pulse oximeter
what is: Carboxyhemoglobin (COHb)
the source of arterial blood follow?
what is:
the lungs. An ABG sample tells how well they are working at oxygenating the blood.
the _____ organ system that is the immediate defense against the accumulation of H+ works fast to remove volatile acids
what is the:
lungs
the normal arterial blood gas PaCO2
what is:
PaCO2 35-45mmHg
the open bicarbonate system process is H2CO3 hydrolyzed to CO2. What two components does this system consist of?
The following occurs from them:
-(primary for fixed acids only) is composed of H2CO3 and HCO-3
-uses continuous ventilation to remove CO2
-Carbonic acid is converted to CO2 and removed
what is:
Plasma (35%)
Erythrocyte(18%)

the _____ monitoring gives accurate data by doing an ABG to establish a precise baseline of info. It can cause a greater risk of arteriospasm, air clot or blood emboli, infection, hematoma, hemorrhage, anaphylaxis(anesthetic), pain, decrease in BP & HR(Vasovagal response), trauma to the blood vessel, and arterial occlusion.
-insertion of a device
what is:
invasive
the risks of complications of drawing an ABG are
what is:
Arteriospasm-an involuntary contraction of an artery. It can be caused by manipulation or fresh blood around an artery and can last from minutes to days.
Embolization-stop blood flow to a specific blood vessel
Infection
Hemorrhage -an acute loss of blood from a damaged blood vessel
the ABG sample errors(Preanalytical)
-Decrease in CO2, Increase pH, O2 toward 150mmHG
-CO2 46, O2 40, pH normal low
-Improper cooling, increased CO2, decreased O2 & pH

if you have no recapping device use the single-handed _____ method
what is the:
scoop method
the _____ organ system buffers slowly & thoroughly to remove fixed acids

what is:
the kidneys

the normal arterial blood gas range for PaO2

tip: the grade range you want:)
what is:
PaO2 80-100mmHg
the _____ system uses carbonic acid that is converted to CO2 and removed with a Bicarbonate buffer.

what is:
an open system
the ____ monitoring is an RT's first choice which uses pulse ox, EKG, and heart monitor leads and gives real-time tending to produce ongoing results.

what is:
non-invasive
(just put on skin not under like invasive)

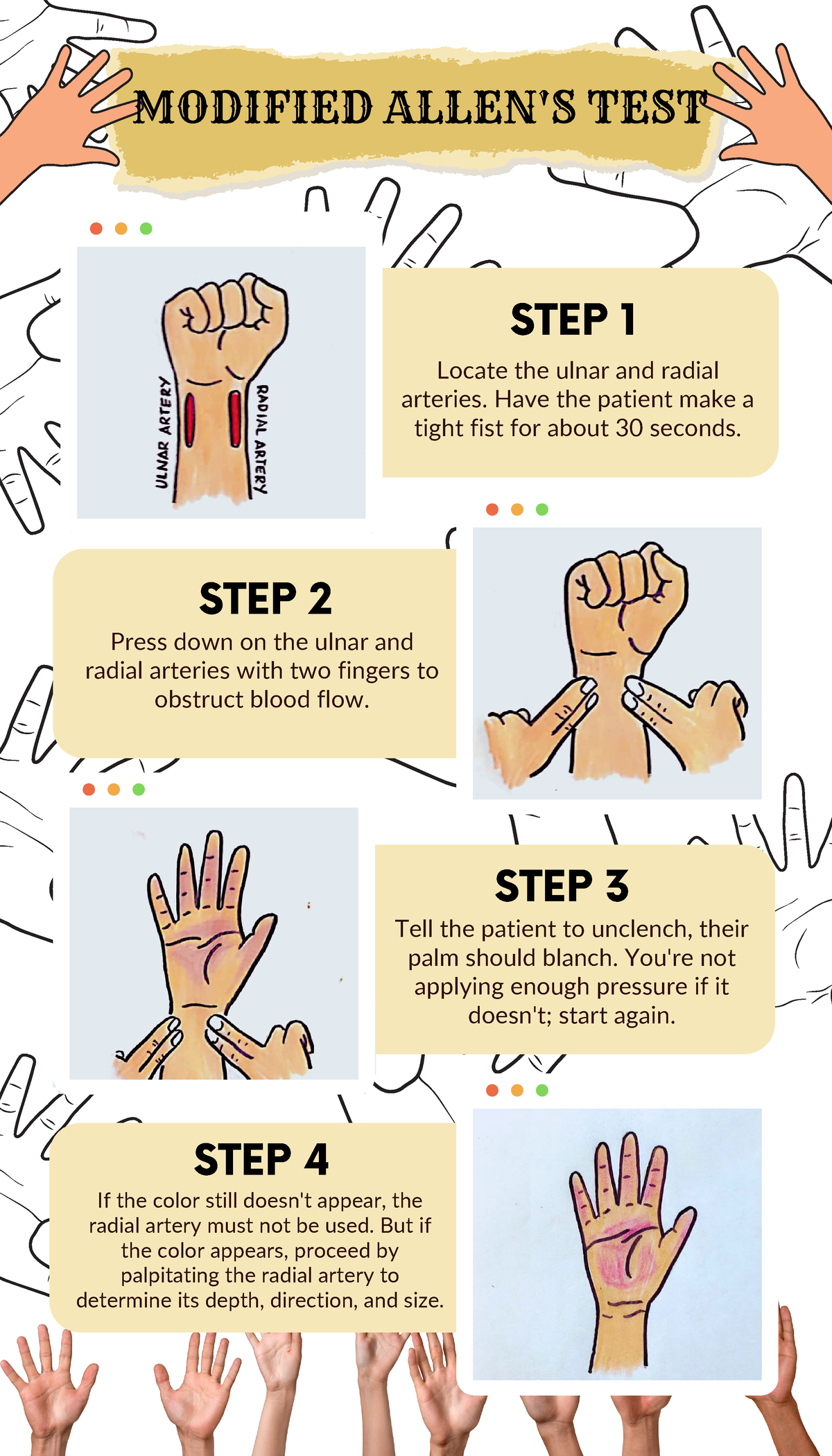
the ____ test that shows collateral circulation when doing a radial ABG to indicate collateral circulation.

what is an:
Allen's test
the hypoxemia normal(range should be 80-100 mmHg)
Mild
Moderate
Severe
what is:
mild: 60-79 mmHg
moderate: 59-40 mmHg
severe <40mmHg
the capnometry measures ___ levels
CO2 (respiratory gases)
_____-_____ allows validation of the reported values on a blood gas report that gives pH, PCO2, HCO-3


what is the
Henderson-Hasselbach
the normal arterial blood gas range for HCO-3

what is:
HCO-3 22-26mEq
the ______system that uses Hb, inorganic & organic phosphates, and plasma proteins to donate a hydrogen ion (H+) and combine with hyperventilation for secretion.
-all components remain in the system
what is a:
closed system
The 3 sites available for drawing an ABG
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/femoral-artery-4/ILbi45NaBS5rfgs14Rw_femoral-artery-4.png)
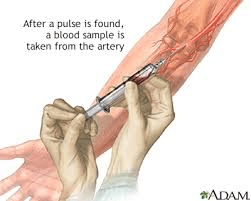
what is the: radial, femoral, brachial

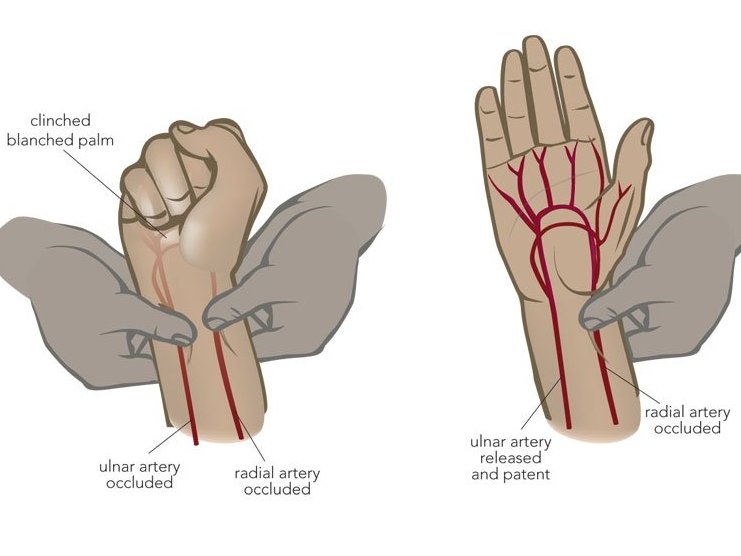
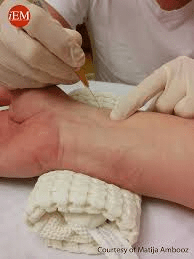
the Allen's test steps in order
1. occlude both radial & ulnar artery
2. have the patient make a fist and open
3. Release the ulnar artery
Blanched hand pinks up in 1-2 seconds if greater than 10 seconds is considered a fail, and another site should be chosen
the following are reasons to use _____ site during ABG(most common)
-is near the surface and easy to stabilize
-collateral circulation usually exists(confirmed with the Allen test)
-No large veins are near
what is the:
radial artery
two ways the body keeps the blood pH constant regardless of how much CO2 is produced
(maintains normal pH even in the face of massive CO2 production)

what is:
Isohydric buffering
Ventilation
Hypoxemia, Hyperventilation, anxiety, fever, pain, stimulants, drugs, and mechanical ventilation are all causes of ____
what is:
Respiratory alkalosis