Which substance is an Arrhenius base?
A) HNO3
B) H2SO3
C) Ca(OH)2
D) CH3COOH
C) Ca(OH)2
What is the color of the indicator thymol blue in a solution that has a pH of 11?
A) red
B) blue
C) pink
D) yellow
B) blue
The laboratory process in which the volume of a solution of known concentration is used to determine the concentration of another solution is called
Titration
The concentration of a solution can be expressed in
A) kelvins
B) milliliters
C) joules per kilogram
D) moles per liter
D) moles per liter
Molarity!
Equal amounts of ethanol and water are mixed at room temperature to form a solution.
Determine the process that can be used to separate ethanol from the mixture?
Distillation!
Double Jeopardy!
Which statement describes an electrolyte?
A) An electrolyte conducts an electric current as a solid and does not dissolve in water.
B) An electrolyte conducts an electric current as a solid and dissolves in water.
C) When an electrolyte dissolves in water, the resulting solution does not conduct an electric current.
D) When an electrolyte dissolves in water, the resulting solution conducts an electric current.
D) When an electrolyte dissolves in water, the resulting solution conducts an electric current.
Which indicator is blue in a solution that has a pH value of 7.0?
A) bromcresol green
B) methyl orange
C) phenolphthalein
D) thymol blue
Look at Table M - Indicators
pH range and corresponding color
A) bromcresol green
Double Jeopardy!
In a titration, 5.0 mL of a 2.0 M NaOH(aq) solution exactly neutralizes 10.0 mL of an HCl(aq) solution. What is the concentration of the HCl(aq) solution?
A) 1.0 M
B) 2.0 M
C) 10. M
D) 20. M
A) 1.0 M
Which unit can be used to express the concentration of a PbCl2(aq) solution?
A) kelvins
B) kilojoules per gram
C) pascals
D) parts per million
D) parts per million
Which statement describes the components of a mixture?
A) Each component gains new properties.
B) Each component loses its original properties.
C) The proportions of components can vary.
D) The proportion of components cannot vary.
C) The proportions of components can vary.
Which pair of compounds represents one Arrhenius acid and one Arrhenius base?
A) CH3OH and NaOH
B) CH3OH and HCl
C) HNO3 and NaOH
D) HNO3 and HCl
C) HNO3 and NaOH
Solution A has a pH value of 1.0 and solution B has a pH value of 4.0. How many times greater is the hydronium ion concentration in solution A than the hydronium ion concentration in solution B?
A) 30
B) 1000
C) 3
D) 5
pH changes from 1 --> 4 means an increase in 3 pH units
103 = 1000 decrease in H+ ion concentration
B) 1000
Which statement explains why 10.0 mL of a 0.50 M H2SO4(aq) solution exactly neutralizes 5.0 mL of a 2.0 M NaOH(aq) solution?
A) The moles of H+(aq) equal the moles of OH– (aq).
B) The moles of H2SO4(aq) equal the moles of NaOH(aq).
C) The moles of H2SO4(aq) are greater than the moles of NaOH(aq).
D) The moles of H+(aq) are greater than the moles of OH–(aq).
A) The moles of H+(aq) equal the moles of OH– (aq).
What is the molarity of a solution that contains 0.500 mole of KNO3 dissolved in 500 mL of solution?
A) 1.00 M
B) 2.00 M
C) 0.001 M
D) 4.00 M
Molarity = moles of solute/LITERS of solution
Convert 500 mL to L first by dividing the mL by 1000
M = (0.500 mol) / (0.5 L) = 1.00 M
Double Jeopardy!
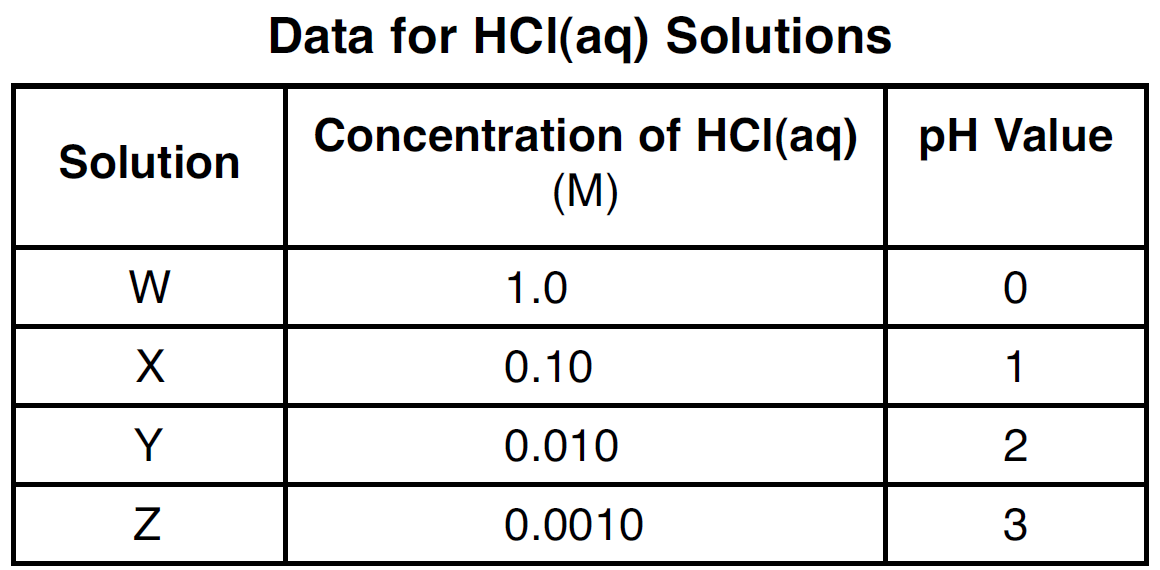
State the number of significant figures used to express the concentration of solution Z.
Two (2) :)
Which two compounds are electrolytes?
A) KOH and CH3COOH
B) KOH and C5H12
C) CH3OH and CH3COOH
D) CH3OH and C5H12
Acids, bases and salts (ionic compounds) are electrolytes; Ions dissolve and are released in water to conduct electricity!
A) KOH and CH3COOH
A sample of seawater has a pH of 8. Determine the new pH of the sample if the hydrogen ion concentration is increased by a factor of 100.
100x greater in H+ concentration means decrease in 2 pH units
8 - 2 = 6
Which equation represents a neutralization reaction?
A) 6HClO --> 4HCl + 2HClO3
B) CH4 + 2O2 --> CO2 + 2H2O
C) Ca(OH)2 + H2SO4 --> CaSO4 + 2H2O
D) Ba(OH)2 + Cu(NO3)2 --> Ba(NO3)2 + Cu(OH)2
Neutralization Reactions:
Base + Acid --> Water + Salt
C) Ca(OH)2 + H2SO4 --> CaSO4 + 2H2O
A solution is prepared using 0.125 g of glucose, C6H12O6, in enough water to make 250. g of total solution. The concentration of this solution is
A) 5.00 x 10-2 ppm
B) 5.00 x 102 ppm
C) 5.00 x 104 ppm
D) 5.00 x 10-4 ppm
ppm = (0.125 g) / (250 g) * 106
500 ppm
B) 5.00 x 102 ppm
At standard pressure, how do the freezing point and the boiling point of H2O(l) compare to the freezing point and the boiling point of 1.0 M KCl(aq)?
A) Both the freezing point and boiling point of H2O(l) are lower
B) Both the freezing point and boiling point of H2O(l) are higher.
C) The freezing point of H2O(l) is lower, and the boiling point of H2O(l) is higher
D) The freezing point of H2O() is higher, and the boiling point of H2O() is lower.
D) The freezing point of H2O(l) is higher, and the boiling point of H2O(l) is lower.
Given the equation representing a reaction at equilibrium:
H2S(aq) + CH3NH2(aq) <--> HS–(aq) + CH3NH3+(aq)
According to one acid-base theory, the forward reaction is classified as an acid-base reaction because
A) H2S is a H+ donor and CH3NH2 is a H+ acceptor
B) CH3NH2 is a H+ donor and H2S is a H+ acceptor
C) HS– and CH3NH3+ are both H+ donors
D) CH3NH3+ and HS– are both H+ acceptors
H2S donates a H+ ion --> HS- = donor
CH3NH2 accepts a H+ ion --> acceptor
A) H2S is a H+ donor and CH3NH2 is a H+ acceptor
Arrange the following solutions (A, B, C) in order of decreasing H+ concentration:
Solution A: pH of 8
Solution B: pH of 4
Solution C: pH of 12
Decreasing H+ ion concentration means increasing in pH units
B, A, C
When 50. milliliters of an HNO3 solution is exactly neutralized by 150 milliliters of a 0.50 M solution of KOH, what is the concentration of HNO3?
Be sure to include the proper units!
MAVA = MBVB
(MA)(50 mL) = (0.50 M)(150 mL)
MA = 1.5 M
What is the molarity of 5.2 liters of an aqueous solution that contains 195 grams of calcium fluoride, CaF2, (gram-formula mass = 78 grams/mole)?
Round your answer to 2 sig figs.
Include proper units.
0.48 M
Compared to the freezing point and boiling point of water at 1.0 atm, a 0.5 M aqueous solution of NaCl at 1.0 atm has
A) a lower freezing point and a lower boiling point
B) a higher freezing point and a lower boiling point
C) a lower freezing point and a higher boiling point
D) a higher freezing point and a higher boiling point
C) a lower freezing point and a higher boiling point
Water has no ion particles dissolved in solution
NaCl(aq) means the Na+ and Cl- ions are dissolved in water. Increasing the # of solute particles means higher boiling point and lower freezing point