Also one of the nucleoside bases of DNA, what does the "A" in ATP, one of the most important molecules in biochemistry, stand for?
What is Adenosine?
This element is the most organic element.
What is Carbon?
The name of the first animal to be cloned.
Who is Dolly the Sheep?
What is the IUPAC name of the following compound:
What is 2-Methylbutane?
A tabular display of all known chemical elements, arranged in rows (periods) and columns (groups) by increasing atomic number (number of protons).
What is a periodic table?
This scientist is considered the father of chemistry.
Who is Antoine Lavoisier?
This element is often found in lotions and preparations to prevent sunburn and windburn.
What is Zinc?
The number of bananas eaten to induce radiation poisoning within the span of an hour.
What is 10,000 bananas?
What is the name of the following reaction mechanism:

What is hydrohalogenation?
What is enthalpy?
A thought experiment in quantum mechanics that illustrates quantum superposition by proposing an animal in a closed box, simultaneously both alive and dead, until the box is opened and observed.
What is Schrodinger's Cat?
The highest stable element.
What is Lead?
This scientist credits his use of LSD with helping him visualize the molecular process that led to the invention of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).
What is Kary Mullis?
What is the IUPAC name of the following compound:
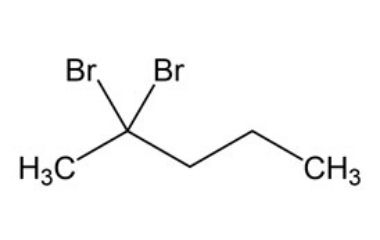
What is 2,2-Dibromopentane?
A fundamental concept in physics and information theory that measures the level of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty within a system.
What is entropy?
Winning for "their synthesis of new radioactive elements," the second woman to win the Nobel Prize for Chemistry was the daughter of two other Nobel Prize winners.
Who is Marie Curie?
A letter not found within the periodic table.
What is J?
What is the name of Walter White's wife in Breaking Bad?
What is Skyler White?
A fundamental organic chemistry reaction where a nucleophile attacks an electrophilic carbon, simultaneously kicking out a leaving group, all in a single, concerted step, leading to inversion of stereochemistry at the carbon center.
What is 2nd Order Substitution Nucleophilic (SN2)?
A thermodynamic potential that measures the maximum amount of reversible, non-expansion work obtainable from a system at constant temperature and pressure.
What is Gibbs Free Energy?
The woman who discovered the structure of DNA and had her work stolen by Watson & Crick.
Who is Rosalind Franklin?
This element was present during the Big Bang.
What is Lithium?
The name for the plastic or metal tube found on the ends of shoelaces.
What is an aglet?
A two-dimensional, planar representation of a three-dimensional organic molecule, specifically designed to display stereochemistry at chiral centers, commonly used for carbohydrates and amino acids.
What is a Fischer Projection?
It is stated that if a dynamic equilibrium is disturbed by changing conditions (concentration, pressure, or temperature), the system shifts its equilibrium position to counteract the change and restore balance
What is Le Chatelier's Principle?