This is considered as the natural pacemaker of the heart
Sino-Atrial Node
What is Troponin and when do we measure its level?
Troponin is a protein found in your muscles, including your heart. When your heart is injured or damaged, troponin is released into your blood.
Measured for any Chest Pain, and 2x for Cardiac Chest Pain
What are the nursing assessments you do while evaluating Neuro-obs?
Vital signs/observations, Limb assessment, GCS, Pupils assessment
Your patient is prescribed with Furosemide 240mg continuous infusion every 12 hours. What is the infusion rate that you will set in your infusion pump (in mls/hr).
Stock: 10mg in 1ml ampoule
2 mls/hr
Discuss the difference between Sepsis and Infection
Sepsis is the body's extreme response to an infection. It is a life-threatening medical emergency.
an infection is simply the presence and multiplication of harmful microorganisms (like bacteria, viruses, or fungi) in the body.
ST Node - AV Node - Bundle of His - Bundle Branches - Purkinje Fibers
Discuss the circulation pathway

How to activate a Stroke call?
Dial 2222 then activate "Stroke Call at Whitley Ward"
What is a medication error and discuss different types of Medication Error that can potentially happen
A medication error is any event that could potentially cause harm to a patient due to a mistake in the medication process.
Types of Medication Errors
- Prescribing.
- Omission.
- Wrong time.
- Unauthorized medication.
- Improper dose.
- Wrong dose prescription or wrong dose preparation.
- Administration errors such as incorrect route of administration, administering the drug to the wrong patient, extra dose, or wrong rate.
What is the Sepsis Six Protocol?
This protocol includes six key actions: giving oxygen, taking blood cultures, administering intravenous antibiotics, starting intravenous fluids, monitoring lactate levels, and monitoring urine output.
What is this rhythm and the key interventions that you have to think about managing it?
Atrial Fibrillation
Mgmt: rate-control, anti-coagulation, chemical and mechanical cardioversion
What is ACS and describe the different types
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a term for a range of conditions caused by reduced blood flow to the heart, most often due to a blocked coronary artery.

What are the signs of Stroke
F - ace (Facial Droop)
A - rms (unilateral weakness)
S - peech (Slurred)
T - ime
What are the oral medications that cannot be crushed?
Capsules, Coated (enteric/film*), timed-release, Cytotoxic, Keppra
Discuss your actions if your patient suddenly have seizure
Immediate Management (during the seizure):
Ensure Safety:Protect the patient from injury by easing them to the floor if standing, clearing the area of hazards, and cushioning their head if possible.
Discuss steps on Rhythm Strip Analysis
Rate, Rhythm, Atrial Activity, P Wave Presence, PR Interval, QRS Interval, Any ST Changes, Axis Deviation, Blocks
Common Management for suspected or confirmed Decompensated Heart Failure
ECG, CXR, NT-Pro BNP, Sats >90%, Diuretics, B-Blockers, , daily Weights, Daily U&Es, Fluid Restriction, HF Medication Optimisation, HF Team Referral
What is stroke, and it's 2 common types?
A stroke happens when the blood supply to part of the brain is cut off, which can damage or kill brain cells.
2 Common Types: Ischaemic and Haemorrhagic
Discuss the infection control screening process needed for all repatriated patients
Candida (3x daily); CPE (1x - weekday / 3x - every alternate day); MRSA; VRE
Difference of DKA and Hyperglycemia Management
Hyperglycemia:Blood sugar levels are higher than normal due to insufficient insulin or the body's inability to use insulin effectively.
Management: Adjusting insulin dosage or oral medication as prescribed; short-acting insulin may be used to temporarily correct high blood sugar.
DKA: A life-threatening complication where the body produces excess acids (ketones) due to severe insulin deficiency, leading to metabolic acidosis and severe hyperglycemia.
Management: Insulin therapy, Fluid replacement, Electrolyte replacement
What is going on with this ECG, what is your priority as a nurse?
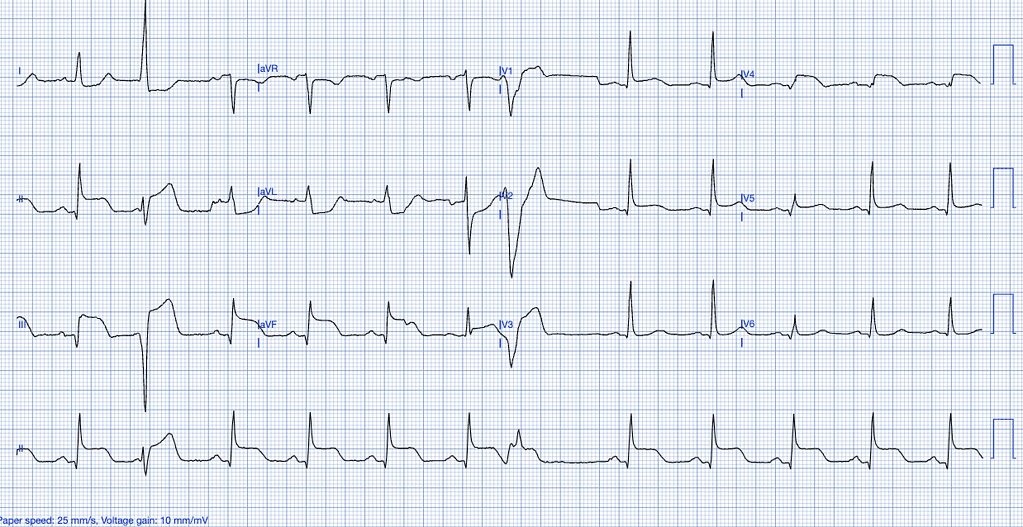
STEMI
Mgmt: Urgent Escalation, Urgent PCI, MONA
Discuss STEMI and ACS Confirmed NSTEMI / UA Treatment Pathway
STEMI: Aspirin 300mg, PPCI Pathway, Cardiac Rehab
NSTEMI: Aspirin 300mg then 75mg OD, DAPT (Ticagrelor 180mg STAT then 90mg BD / Clopidogrel 600mg STAT then 75mg OD)
Give 5 common management for acute stroke patients
Thrombolysis / Thrombectomy
BP control
Anti-coagulation / VTEp
Therapy (Physical,Occupational, Speech & Language)
Nutrition
Discuss post-fall (unwitnessed) management (Including EPR)
DO NOT MOVE PATIENT,ABCDE, Urgent Medical Review, Outreach, Observations, Neuro Obs, Urgent CT Head, Blood Sugar, L/S BP, Datix, NOK, Bed Rails Assessment, Falls Risk Assessment, Post-Fall Care Plan, Clinical Documentation
What is Pulmonary Embolism, and what are the common diagnostic and therapeutic Management
A pulmonary embolism occurs when a clump of material, most often a blood clot, gets stuck in an artery in the lungs, blocking the flow of blood.
Diagnosis: D-Dimer, CTPA
Mgmt: Anticoagulation, Thrombolytics, Oxygen, Surgery