The patient meets Bradycardic criteria at a HR of _____ so long as they are symptomatic.
< 60
You are the first arriving crew to an apneic and pulseless patient. What is the correct compression:ventilation ratio without other assistance?
30:2
Patient presents with expiratory wheezing, respiratory distress, and uses home O2 at 2L routinely. What is the MOST likely medical h/x they are exhibiting an exacerbation of?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder
When is Preeclampsia regarded as Eclampsia?
Seizure Onset
A baby was just delivered at 39 weeks. At < 1 minute they have no muscle tone and a strong cry. What is the most appropriate action?
Warm, dry, stimulate.
# of IV sites minimum to obtain on a severe burn patient, and why?
2, need for massive volume resuscitation.
Act out the 2 types of Posturing
Decorticate and Decerebrate
Most appropriate medication given for volume support with Bradycardia and most other protocols.
Normal Saline Fluid Bolus
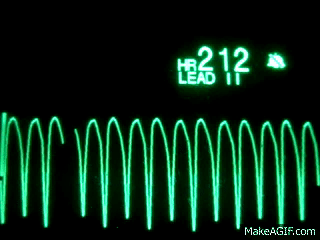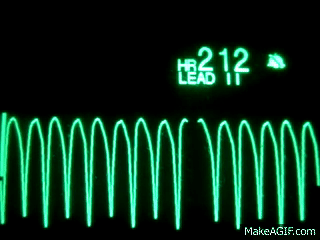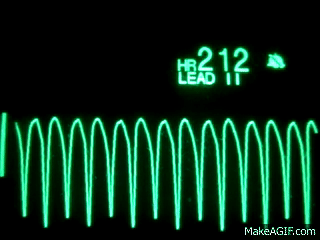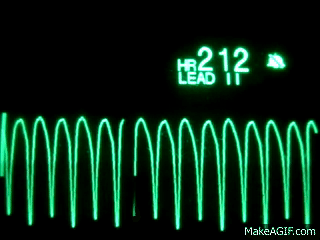
Name this rhythm: 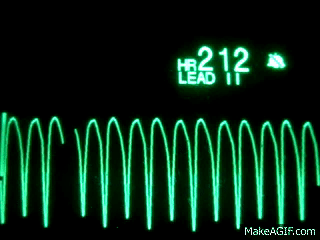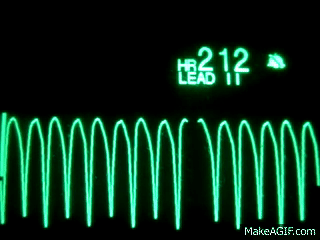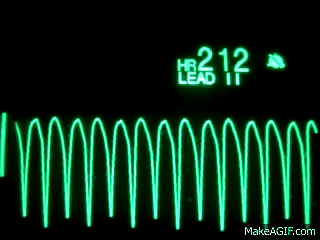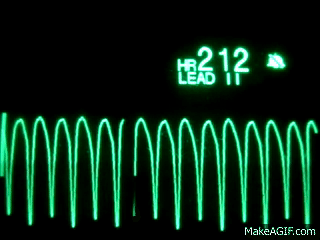
Ventricular Tachycardia
Primary beta-agonist for bronchoconstriction (First Line Medication, not O2)
Name:
Dose:
Route:
Times it can be repeated:
Albuterol, 2.5 mg - 5 mg, Nebulized, can repeat indefinitely for Paramedics
Your patient is 29 weeks OB. They exhibited a rapid onset of headache, blurred vision, and weight gain. What condition needs to be ruled out?
Preeclampsia
1 minute following delivery, the baby has an APGAR of < 8. You have not performed any interventions yet. Their heart rate is 56 and they exhibit agonal breathing. What is your first intervention?
Assisted Ventilations
Your patient experienced a thermal burn and exhibits hoarse voice and blackened nares. They are normotensive and exhibit no stridor. How would you best manage this airway?
RSI / OTI
Key performance indicator of a head trauma patient in the pre-hospital setting.
GCS
First line medication for a stable and symptomatic patient exhibiting bradycardia (not volume support).
Name:
Dose:
Routes:
Atropine, 1 mg, IV/IO
To shock this rhythm when it does not have an associated pulse, what are the correct initial and repeat Joule settings?
200, 300, 360
For all patients exhibiting primarily respiratory pathology, what is the primary medication we can use to reduce pulmonary secretions.
Name:
Class:
Dose:
First Medication to give in presence of tonic/clonic activity with an OB patient.
Name:
Dose (IM Route):
Versed, 5mg
Name the two appropriate interventions for post-delivery hemorrhage (in absence of shock)
Fundal Massage and Oxytocin
What types of burns are calculated in a TBSA for tretment?
Partial & Full Thickness
Your patient presented with a sudden onset of altered mental status with BP 230/84, HR 46, and RR of 8 and highly irregular.
1) Name the associated syndrome and most appropriate primary impression.
2) Primary 2 numerical goals when ventilating this patient.
Cushing's Triad from suspected Head Bleed / ^ Intracranial Pressure
ETCO2 35-45, SPO2 100%
Endstage Sympathomimetic option(s) for a symptomatic and potentially unstable patient with notable bradycardia and hypotension.
Medication:
Dose Range:
Titration Goal:
Epinephrine 1-10 mcg/min, titrated to SBP > 90
OR
Dopamine 2-20 mcg/kg/min, titrated to SBP > 90
First Line Sympathomimetic in any cardiac arrest rhythm.
Name:
Dose:
Repeat every:
Last line medication to attempt to manage bronchoconstrictive/reactive pathologies.
Name:
Dose: 2g
Given over ____ Minutes:
Magnesium Sulfate, 2g, 10-20 minutes
Medication to administer for Eclampsia, not currently exhibiting tonic/clonic activity.
Name:
Dose:
Administration time (in minutes):
Magnesium Sulfate, 2-4g, over 2-3 minutes
First action to consider with a patient exhibiting crowning at 32 weeks gestation, per NCOEMS
Rapid Transport
You have a burn victim with 40% TBSA from a thermal burn. They are stable but being heavily resuscitated with volume support, and have been successfully RSI'd.
You are 5 minutes away from your local Emergency Department (General), and 35 away from the closest burn center. What is the most appropriate destination?
Burn Center
Your patient exhibits a barrel chest appearance and pursed lip breathing, with audible wheezing. What is the MOST accurate condition that will cause this?
Emphysema
Endstage Sympathomimetic option(s) for a symptomatic and potentially unstable patient with notable bradycardia and hypotension.
Medication:
Dose Range:
Titration Goal:
Epinephrine 1-10 mcg/min, titrated to SBP > 90
OR
Dopamine 2-20 mcg/kg/min, titrated to SBP > 90
List your 10 H's & T's for Reversible Causes
Hypovolemia, Hypoxia, Hydrogen Ions, Hypothermia, Hypo/Hyperkalemia, Tension Pneumothorax, Tamponade cardiac, Toxins, Thrombosis, Pulmonary, Thrombosis, Coronary
Your patient is exhibiting Hypertension, Bilateral Rales, and Wheezing.
Most likely Pathology:
3 Interventions/Meds that can be given:
CHF
Nitro, CPAP, Albuterol
Your patient denies any knowledge of being OB. She has been exhibiting vaginal hemorrhage for 2 hours and is showing obvious signs of shock. Most appropriate intervention for this patient (not including volume support) would be:
Name:
Dose:
Administration Time:
Transexamic Acid, 1-2g, over 10 minutes
Describe the maternal position for Labor.
`Supine` or `Semi-Fowlers` with head flat or elevated per mothers choice. Maintain `flexion` of both knees and hips. Elevated `buttocks` slightly with towel.
Volume to give in first 8 hours and later 16 hours for an approximately 70 kg pt w/ 30% TBSA
4200 over 8h
4200 over 16h
4mL x 70kg x 30 (%) = 8400
Name the failed airway criteria.
Inability to maintain SPO2 to at least 90% during/after 1 attempt, AND/OR anatomy would not allow for further attempts, AND/OR 3 unsuccessful attempts by most experienced provider on scene.