What is Colonization?

Acquisition and exploitation of territory by a foreign power for its own economic and political benefit.
List at least 3 countries involved in African Imperialism.

Great Britain
France
Portugal
Germany
Belgium
Italy
What is cultural transformation?

Since culture is dynamic and ever changing , culture can be shifted, changed and transformed. This can happen in a variety of ways, such as outside influences, generational gaps, and can have a positive or negative impact on the culture community.
What was happening between European countries that transformed the political geography of Africa in between late 19th century and 1914?

Scramble for Africa: Competition with one another to gain more land / power
Advancement in weapons and medicine that lead Europeans to explore and take over African land
The Berlin Conference: Dividing up land between imperialist powers.
Name 2 countries in North Africa.
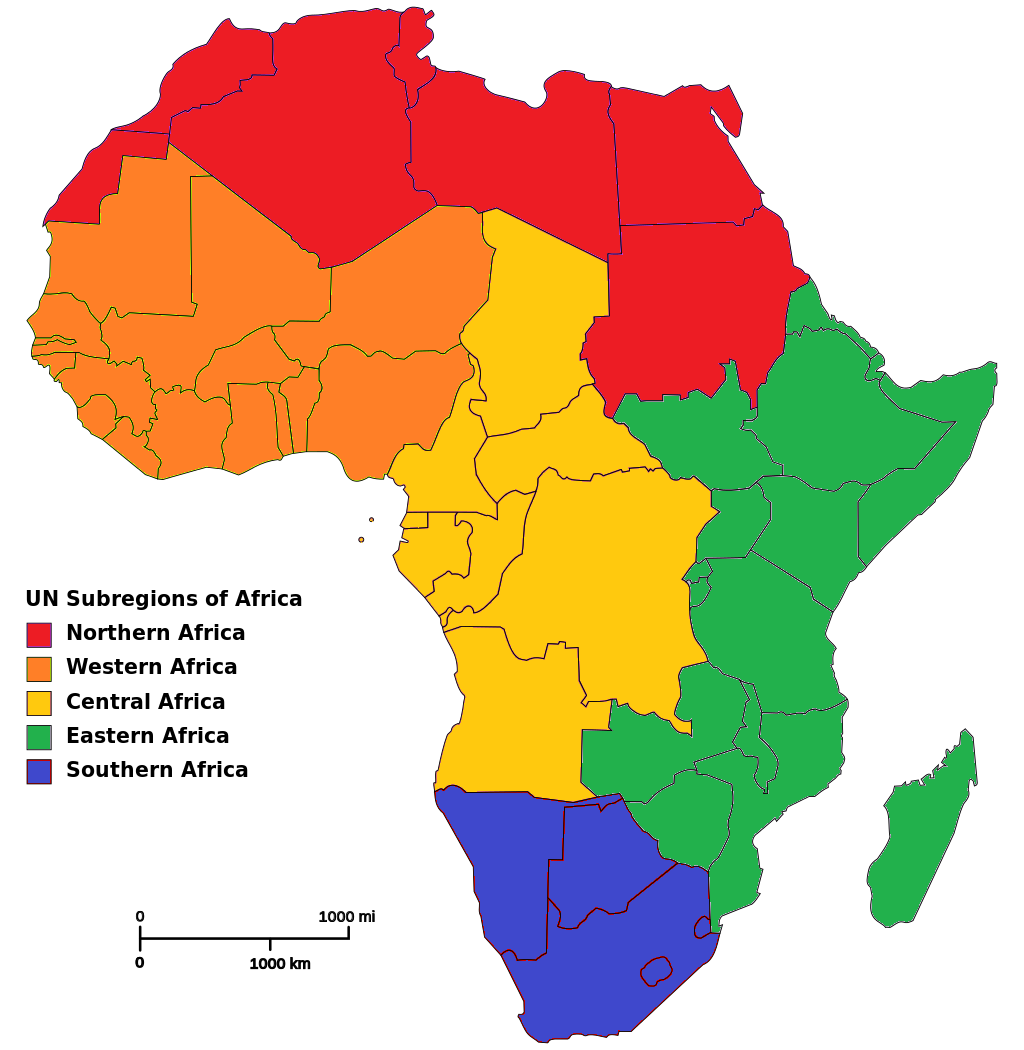
Algeria
Tunisia
Morocco
Western Sahara
Libya
Egypt
Sudan
What is Imperialism?

The policy of extending the rule of a nation though increasing its power by gaining control over other areas of the world.
What is an economic advancement that fueled European motive for colonization of Africa.
Industrial Revolution
Need for raw natural resources (Coal, Oil, Metals)
Advancement in guns, medicine, railroads
Use advancements to exploit = Cheap human labor
What was one way the Europeans transformed African societies' culture?
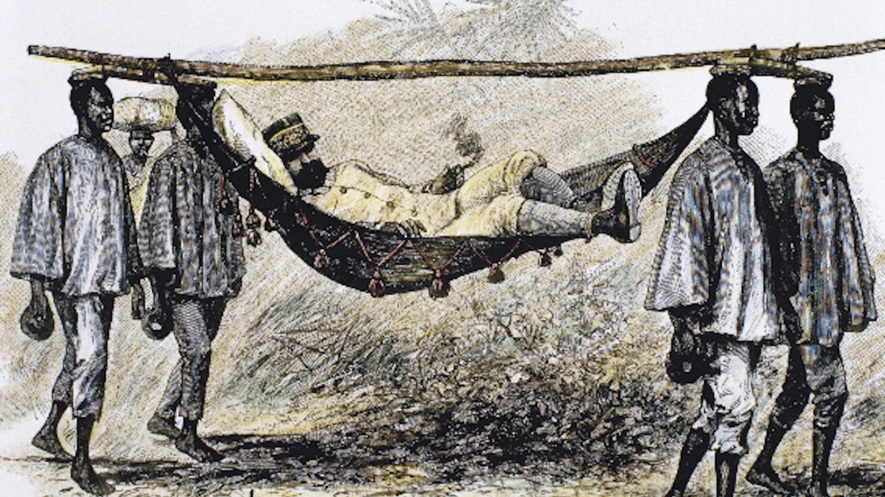

New ruler
Had to pay taxes
Residential schools were made
Cut down trees making many dry seasons
Different clothes
Religion alters
Some younger Africans turned on their culture / influenced to join European culture
Food was deprived
Name the only two territories that remained independent after 1900.

Liberia and Ethiopia
Name 2 counties in South Africa.
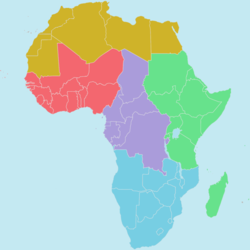
South Africa
Botswana
Namibia
Lesotho
Swaziland
Describe what the Scramble for Africa was.
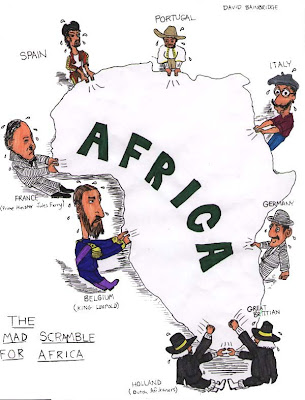
It was the occupation, division, and colonization of African territory by European powers.
What was an political motive for European colonization?
European Nationalism: Pride for country
Compete with other European Nations
Set up Military & Naval bases
Political Power move to set up colonies
More people under country's political rule.
What aspects of colonialism history did the European historical account leave out?
European powers exploited Africa’s natural and human resource for own economic benefit, set up own systems of government, denying Africans the ability to their their own political and economic affairs. And then they argued that they brought morality and development for Africa.
Thy glossed over violence, racist and destructive aspects of colonial rule and left out stories of African resistance.
In the late 19th century what parts of the Africa continent did Europeans claim?
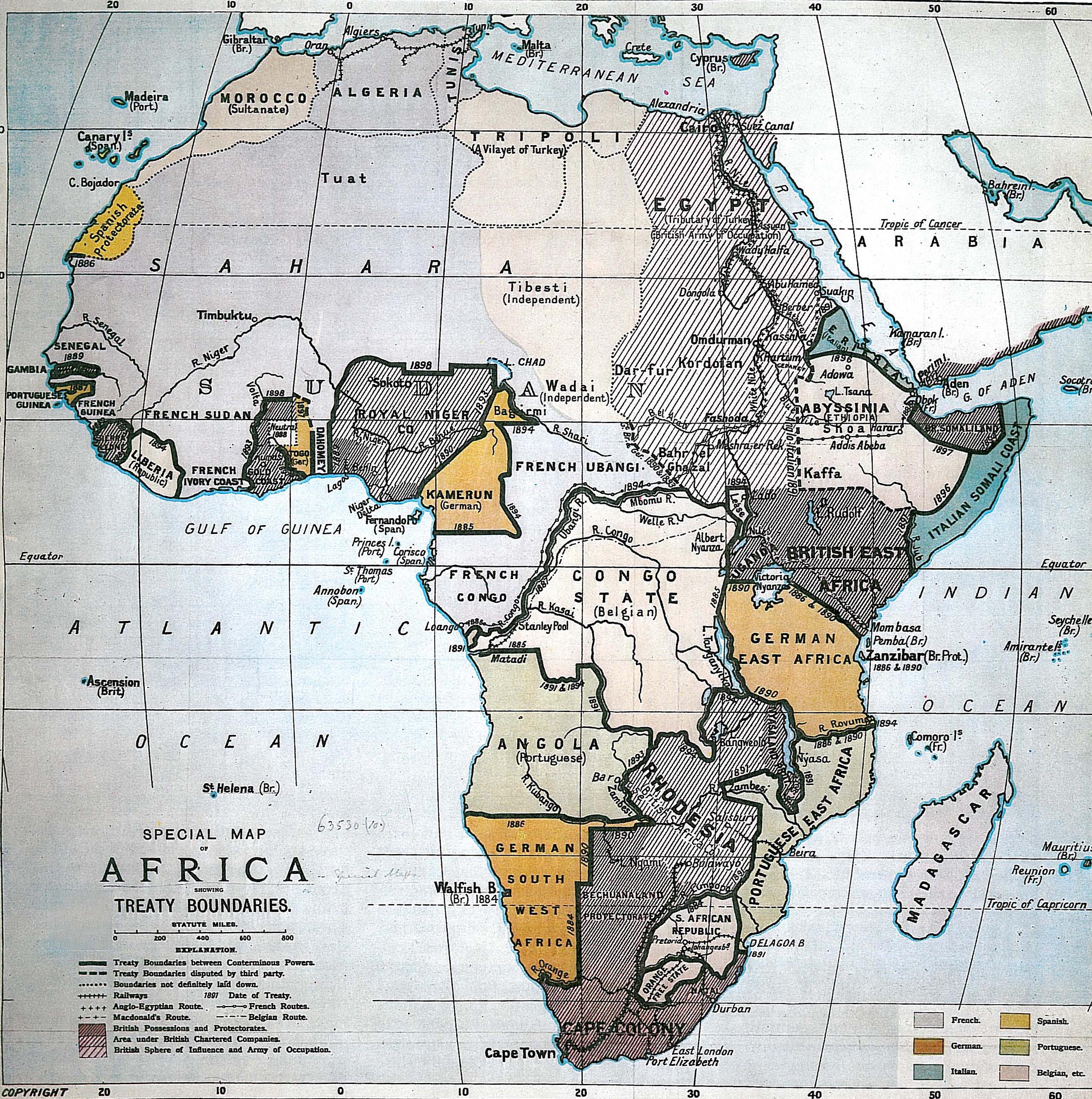
North Africa was controlled by the French.
Great Britain had some land in West & South Africa.
Portugal has land in South and East Africa.
Name 2 counties in West Africa.
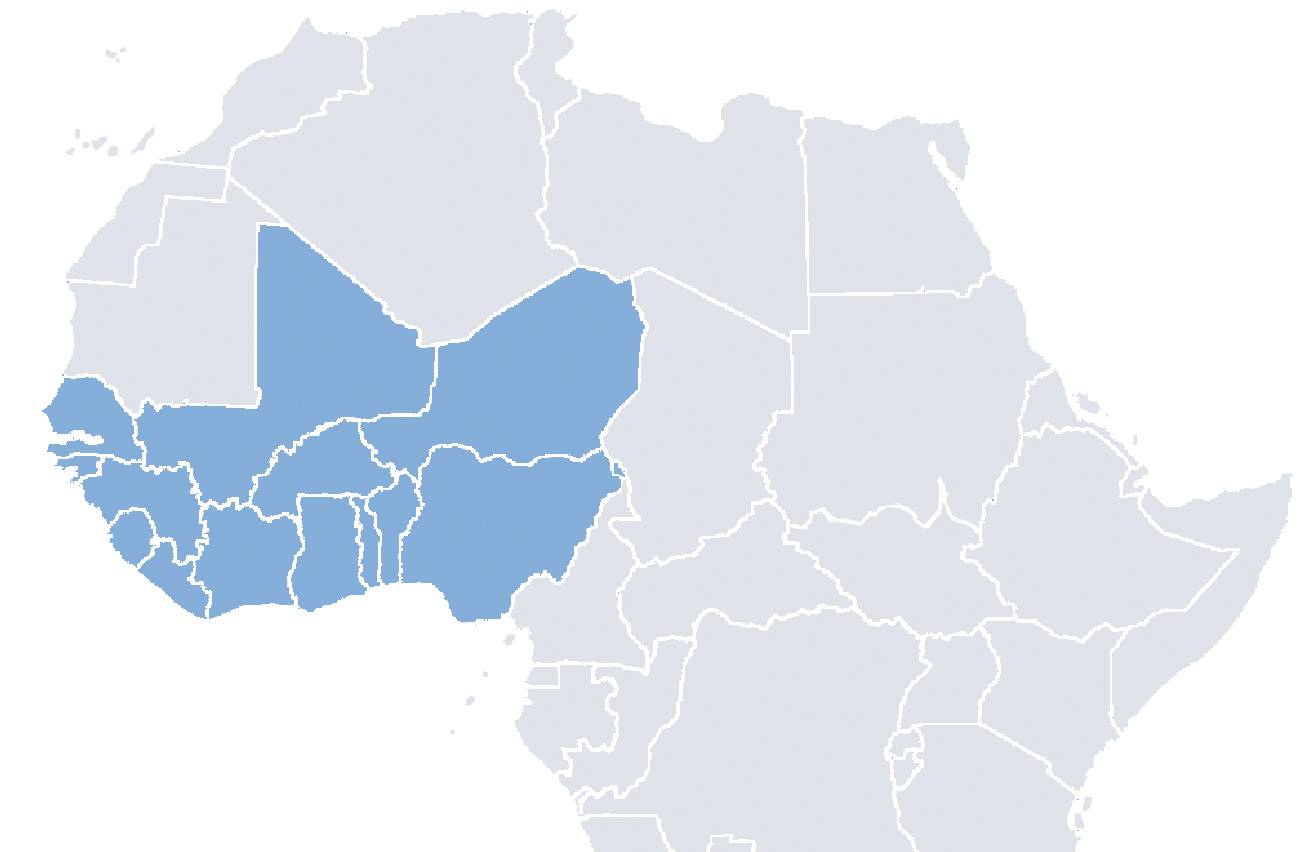
Nigeria
Ghana
Benin
Togo
Mali
Burkina Faso
Mauritania
Ivory Coast
Liberia
Sierra Leone
Guinea
Guinea Bissau
Gambia
Senegal
Niger
What was the purpose of the Berlin Conference?

Not a single African was present and many Europeans involved in the Berlin Conference had never been to Africa.
What was the European's cultural motive for imperialism?

To set own governmental instructions
Teach English
Spread Christian Religion
Believed white was the superior race and imperialism was their calling of power
What are some ways Africans resisted imperialist powers?

Diplomacy to convince Europeans to withdraw.
Alliances with Europeans hoping for respect.
Discouraged European interest in Africa.
Used guerrilla war to attack European forces.
After 1914, how did Europeans change the way the African Map looked?

During the Scramble for Africa, European imperialist powers divided the continent, created new boundaries and took control of the majority of Africa.
Name 2 countries in East Africa.
South Sudan
Burundi
Comoros
Djibouti
Eritrea
Ethiopia
Kenya
Madagascar
Malawi
Mozambique
Rwanda
Seychelles
Somalia
Tanzania
Uganda
Zambia
Zimbabwe
What were the two countries that had the largest imperialist power and claimed the most territory?
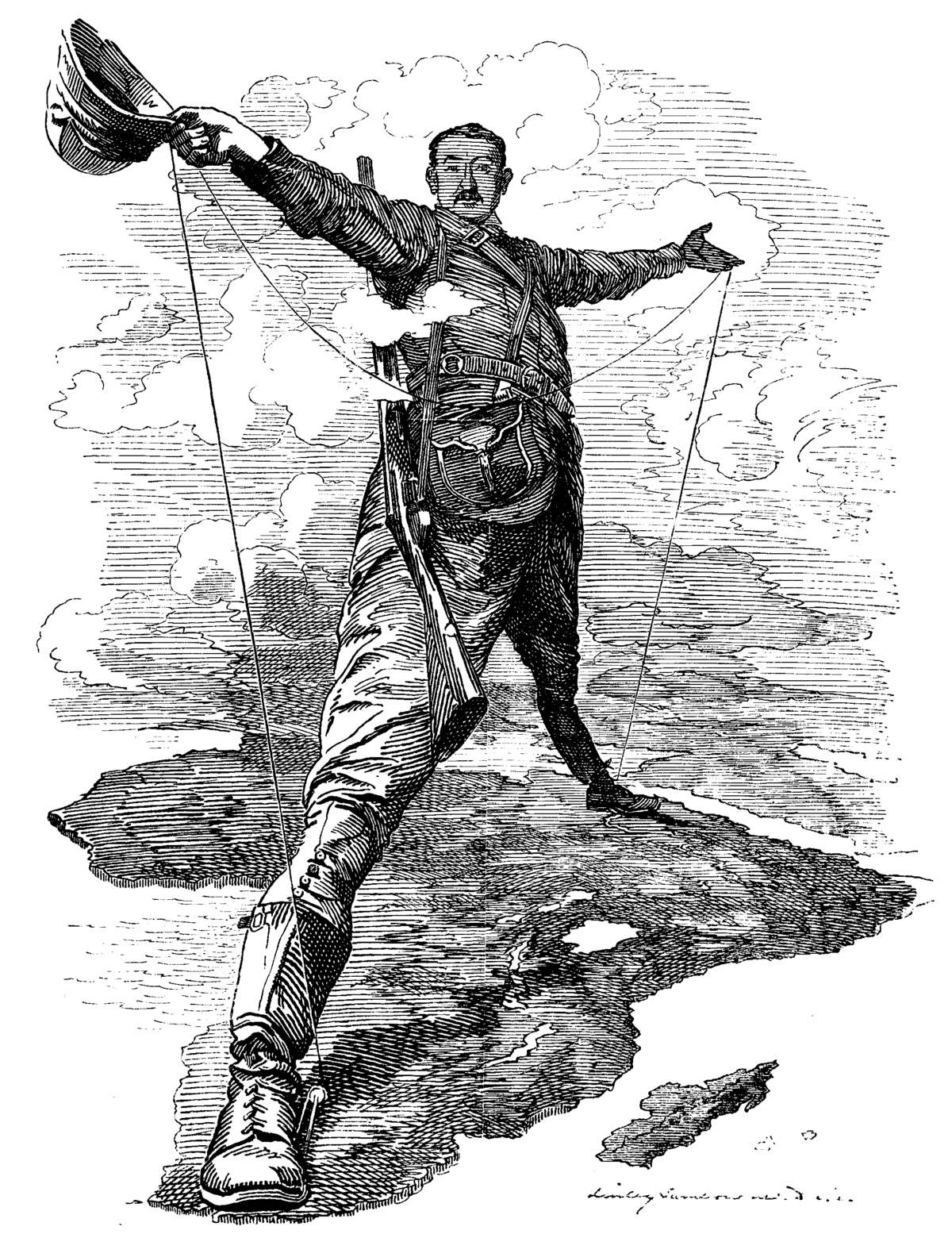

Great Britain and France
What was the "White Mans' Burden"?
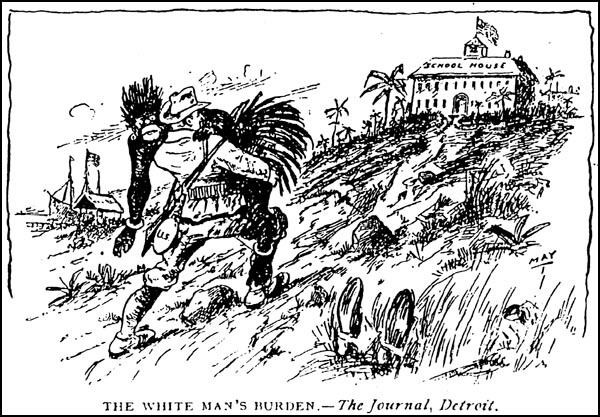

"The White Man's Burden" (1899) is a poem written to justify imperialism. It proposes that the "white race" is morally obligated to rule the "non-white" peoples of planet Earth, and to encourage their progress (economic, social, and cultural) through settler colonialism, which is based upon the Roman Catholic and Protestant missionaries displacing the natives' religions.
A poem backed up racist viewpoints and stated that it was the white man's responsibility to educate foreign lands. Labeled Africans (also Filipinos and other people of color)) as "Half-Devil, Half Child"
How did Europeans change the political / economic structure of the African societies?

Creating country boundaries randomly
Forcing labor, exploiting resources
Dividing Africans into two groups: those cooperating with Europeans and those not.
Divide some societies into different countries and placed multiple societies in one country.
How did the boundaries of colonial territories shaped the boundaries of countries on the continent today?
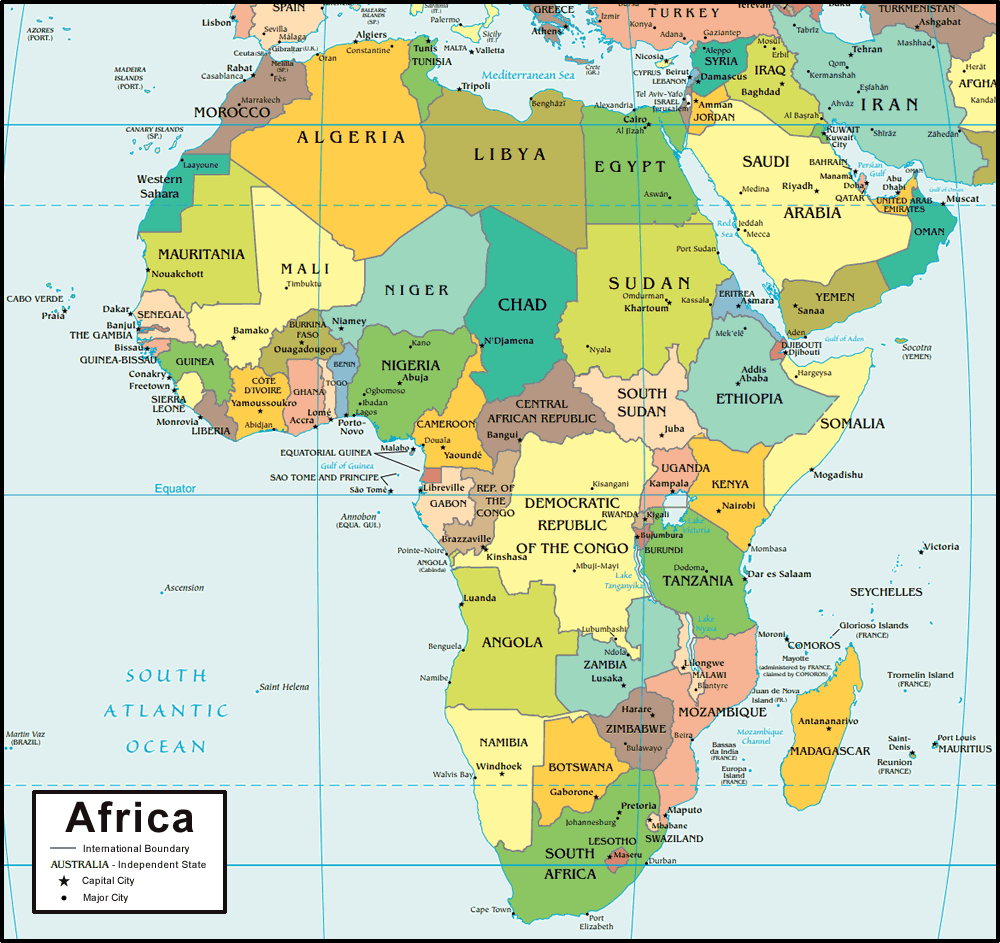
Colonial territory boundaries are very similar to the boundaries of Africa today.
Name 2 countries in Central Africa.

Angola
Cameroon
Central African Republic
Chad
Congo
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Equatorial Guinea
Gabon
Sao Tome and Principe