When a probe fails to find a suitable goal, the search ends with no penalty to the derivation.
What is fallible Agree?
The agreement is only with the subject
What is subject agreement?
The pair that participates in an Agree relation
What are the probe & goal?
Anaphors across languages typically cannot trigger "normal" (i.e. phi-covarying) agreement.
What is the Anaphor Agreement Effect (AAE)?
Nothing can escape this chunk of structure except through its head or specifier.
What is a phase?
One goal, two (or more) probes.
The agreement is with the subject or object, whichever happens to be nominative.
What is case-discriminating agreement?
This constraint prevents an element from moving or Agreeing across another element of the same category.
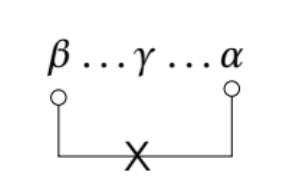
What is Relativized Minimality?
This phenomenon seen in Basque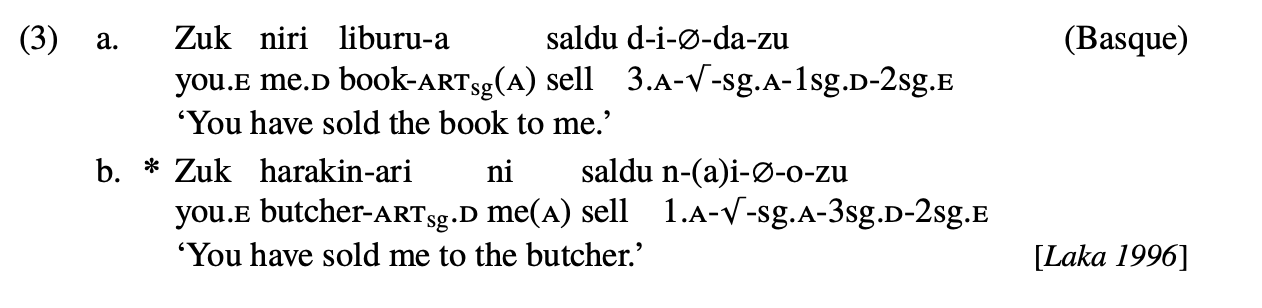
What is the Person Case Constraint (PCC)?
This is the atom of syntax.
What is a syntactic feature?
The probe searches in its c-command domain and if it fails to find a matching goal, it expands its search space and searches upward.
What is cyclic Agree or cyclic expansion?
Agreement reflects features of both the subject and the object.
What is object agreement?
The requirement that the goal in an Agree relation bear at least one unvalued/unchecked feature.
What is the Activity Condition?
The phenomenon seen in this minimal triple in Basque:
What is allocutive agreement?
The rule that prevents a phrase XP from having more than one head.
What is endocentricity?
The probe is specified for two things:
1. The features it can copy
2. The features that terminate its search
What is Interaction/Satisfaction?
Agreement reflects the features of the subject in intransitives and of the object in transitives
What is an ERG-ABS agreement pattern?
Faux-Icelandic:
a. The boys.DAT was/*were bored.
b. [The computers.NOM] are/*is ugly.
c. Finds/*Find [the student.DAT] [the computers.NOM] ugly.
(= The student finds the computers ugly)
What is defective intervention?
The kind of matrix verb agreement shown for Hindi below:

What is long-distance agreement?
The operation underlying the examples in (a) & (b):
(a) Mary seems to be expected to appear smart.
(b) Who did Ali tell Rahman that Saurav saw Meena meet?
What is successive cyclic movement?
The probe searches for, and is satisfied by, a proper subset of the features on the goal.
What is relativized probing?
A-bar extraction of the subject bleeds subject agreement.
What is anti-agreement?
Two probes Agree jointly with a common goal.
What is a shared probe?
The kind of phenomenon seen in Washo below: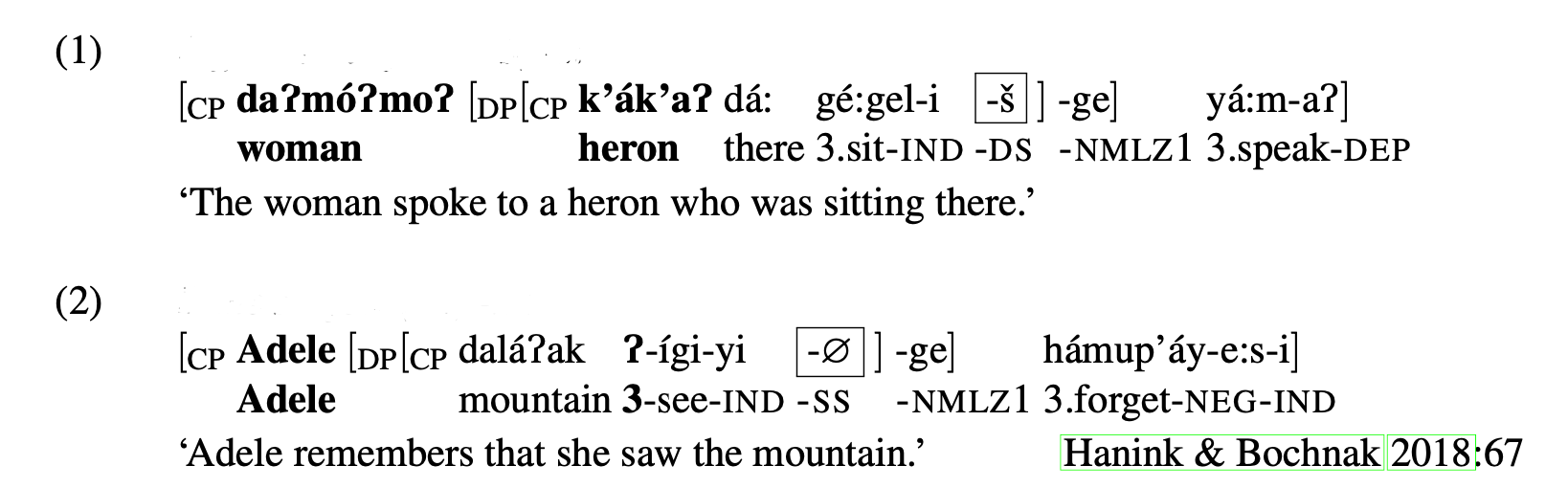
What is switch reference?
It is a maximal projection and so is its mother, but not its sister.
What is a specifier?