The indications for artificial airways.
What are VOPS?
These support airway care but cannot function as true artificial airways.
What are airway adjuncts?
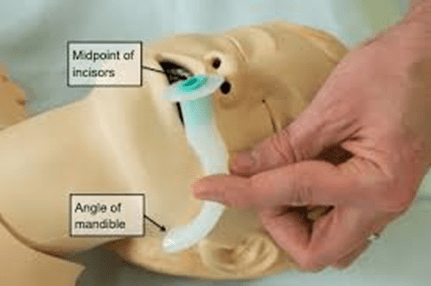
An oral ET tube should be at ____ to _____ at the incisor to be in the correct position.
What is 22 to 24 cm?
This procedure should take no longer than 20 seconds.
What is suctioning?
This is the maximum ET tube cuff pressure ____ that will not cause collapse of the _______________.
What is 30 cmH20 and capillaries?
A stable airway is necessary for a patient to transfer to an LTAC.
What is a tracheostomy tube?
This device helps with suctioning through the nares and reduces trauma.
What is a nasopharyngeal airway or a nasal trumpet?


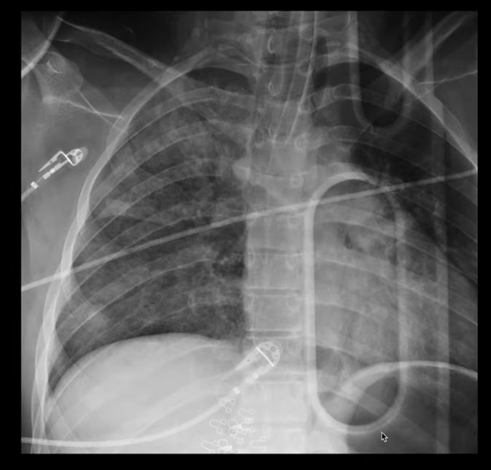
This could happen if the ET tube is advanced too far.
What is a right mainstem intubation?
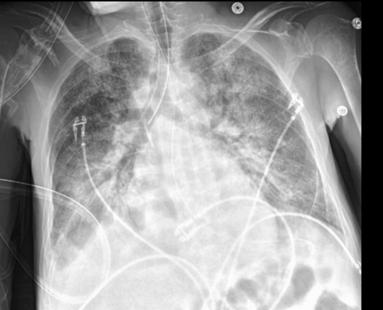
The maximum vacuum pressure used for this procedure in an adult is
What is 150 mmHg?
The ET tube should be rotated from the right side to the middle and then to the left side of the mouth to prevent what?
What is a pressure sore?
This patient experienced a significant CVA and has recurrent aspiration of food and saliva, leading to pneumonias. The reason for this patient's intubation is
What is protection from aspiration?
This serves as a bite block and prevents the tongue from obstructing the airway.
What is an oropharyngeal airway?
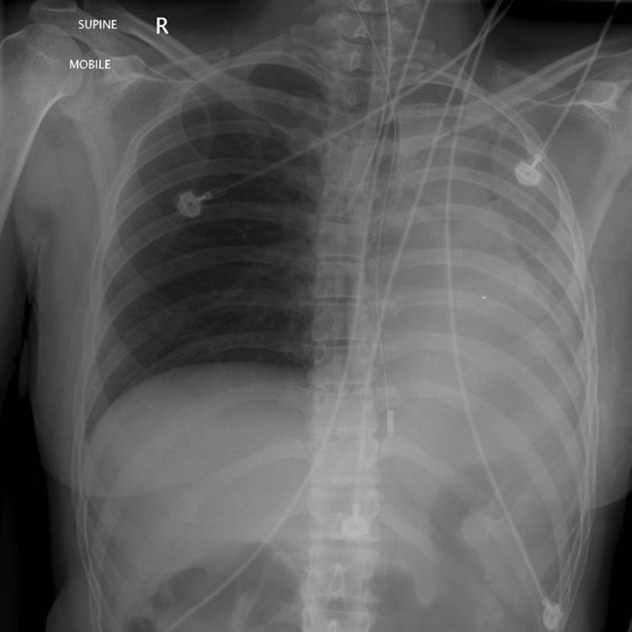
This could occur if a mainstem intubation is not realized for a while.
What is an atelectatic L Lung?
This term indicates a patient is weaned from a tracheostomy tube.
What is decannulation?
This can be prevented by pre-oxygenation and limiting the duration of attempts.
What is hypoxemia?
This patient was just rescued from a fire and has second-degree burns on their face, neck, and chest. Auscultation reveals slight stridor. The reason for this patient's intubation is
What is obstruction?
This airway is used by CFD paramedics and anesthesiologists
What is an LMA?

This indicator is the best practice to ensure the ET tube is in the trachea!
What is the colorimetric capnography
Yellow - YES, Purple - PROBLEM
Excessive pressure or prolonged suctioning can lead to these two complications.
What are hypoxemia and atelectasis?
This serious complication might occur during a tracheostomy procedure if the surgeon pierces the apex of the lung.
What is a pneumothorax?
This patient needs frequent nasotracheal suctioning and has recurrent pneumonias. The reason for this patient's intubation is
What is suction?
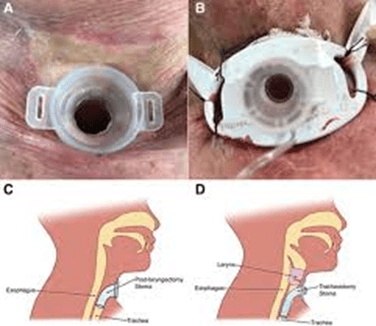
This airway can never heal closed.
What is a laryngectomy?
The patient has just been intubated and the reading on the colorimetric capnograph says .05; the patient's PCO2 is
760 - 47 = 713
713 x .05 = 35.65
What is 36 mmHg?
This procedure is recommended after a seven-day period with an oral ET tube in place when it is determined it will be needed for a longer period duration.
What is a tracheostomy?
This is a rare but lethal complication (if not detected) of ET (or not) intubation.
What is esophageal intubation?