the three phases of drug action?



what is:
Drug administration
Pharmacokinetic Phase
Pharmacodynamic Phase
the following are the benefits of what:
-Smaller doses than systemic administration
-The quick onset of drug
-Delivers to the targeted organ
-Systemic side effects minimal
what is:
using inhaled aerosol for respiratory issues

the type of effects occurs when this receptors are stimulated
vasoconstriction
what is:
Alpha 1
the indication of the following event should be treated with:
-the breakup of mucus (thinning out) aids mucus ciliary escalator
what is:
Mucolytic
the muco-active agent that is specifically for
CF (cystic fibrosis); helps reduce recurrent infection

what is:
Dornase Alfa
the folllowing treats what
Pentamadine (Nebupent); uses Respiragard II


what is:
Pneumocystis jiroveci

the equation to find dose(mg)
what is:
dose(mg)= vol(mL) x conc (mg/mL)
the phase that describes the time course and distribution of the drug in our body is based on:
"what the body does to the drug"
-absorption
- distribution
-metabolism
-& elimination(primary source is kidney)
what is the:
pharmacokinetic phase (receptor)
the brand name for this drug is Proventil & Ventolin
Drug Class: Beta-Adrenergic, SABA(short-acting beta agonist)
receptors: Very mild Beta 1, Beta 2(beta 2 agonist most active part)
Dosage: SVN 2.5mg & MDI 90ug/puff, 2-4 puffs
frequency: TID or QID
Use for reversible airway obstruction
side effects: tremors(most common), headaches,tachycardia, worsening of V/Q ratio, insomnia, nervousness
what is:
Albuterol Sulfate
the combined anticholinergic bronchodilator and beta-agonist bronchodilators
Brand names combined: Proventil, Ventilin, Atrovent
usage: patients for COPD receiving regular treatment who require
names for this combined in MDI & SVN
frequency 2 puffs Q4 or QID
what is:
MDI-Combivent & SVN-Duoneb
Dosage:
combivent- MDI= albuterol 90mcg/ atrovent 17mcg
DouNeb- SVN= albuterol 2.5 mg/ Atrovent 0.5mg
the aerosol medication that matches the following:
Brand name: QVAR
Drug class: inhaled steroid (pink/green)
what is:
Belcomethasone
the phases of drug action that:
-How the drug is made available to the body
-Aerosol, IV, IM, patch

what is:
-Drug administration
the type of medication would you use to limit the systemic effects
what is:
Fully ionized – Ipratropium Bromide
the type of effects occurs when this receptors are stimulated
increased heart rate & contractility

what is:
Beta 1
the indication of the following event should be treated with:
Inflammation
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chest-pain-common-potential-causes-1745274_FINAL-ecbc2bd3b0f0401c8cfd77840901720f.jpg)
what is:
steroids
the muco-agents that specifically treat
viscous mucus; breaks the disulfide bond into a sulfhydryl bond.
what is:
Mucomyst (acetylcysteine)
the following treats what:
- Ribavirin (Virazole); uses SPAG


what is:
Respiratory Synovial Virus

the equation for volume(mL)
what is:
Volume(mL)= dose (mg) /(divide by) conc (mg/mL)
the aerosol drug has little or no side effects, and does not absorb across lipid membranes, so is not absorbed in the bloodstream, having little to no effects on the parasympathetic system (what term is this)
-RTs use this to limit systemic distribution transformation(stays in lungs)
what is:
fully ionized aerosol (most common Ipratropium Bromide aka Atrovent)
the aerosol medicine that matches the following:
brand name: xopenex
drug class: Beta-Adrenergic, Noncatecholamine
Receptors: less beta 1, more Beta 2
patient type: cardiac patient
Dosage: SVN: 0.63mg/ 1.25 mg & MDI: 45ug/puff, 2 puffs Q4-6hours
what is:
Levalbuterol
the term found in caffeine causes bronchodilation
what is:
methyl-xanthines
the aerosol medication that matches the following:
Brand name: Pulmicort
Drug Class: inhaled steroid
Dose: SVN 0.25mg and 0.5 mg in 2 mL NS
MDI: 90mcg and 180mcg
administered via Pari-Neb
what is:
Budesonide
the phase of drug action that:
-What the body does to the drug
-Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination
-Fully ionized have little to no systemic effects (Atrovent)
what is:
Pharmacokinetic Phase

the folllowing are parts of what term
-Lung availability/total systemic availability
-Higher the number the better the lung deposition (greater efficiency)
what is:
L/T ratio

the type of effects occurs when this receptors are stimulated

what is:
Beta 2
the indication of the following event should be treated with:
-Upper airway edema or during bronchoscopy to stop bleeding

what is:
Ultra-Short-acting catecholamine
the following reduce oropharyngeal impact and helps with hand & breath coordination, what are they used with
Reservoir devices
One-way spacers
Valved holding chambers
what is:
-a MDI
the term defined by suspension of solid or liquid particles in gas
what is:
aerosol
the following are procedures for what device
-shake device
-release one or more sprays in the air, will mix the drug propellant
-attach spacer/ holding chamber
- spray inhale slowly, and continue to inhale
-hold your breath for 5-10 seconds
-after have the patient rinse their mouth (steroids cause thrush)
what is:
a MDI
the drug is lipid soluble, diffuses across the cell membrane, and into bloodstream, causing systemic side effects
what is:
nonionized aerosol
the aerosol medicine that matches the following:
Brand name: Serevent
Drug Class: Beta-Adrenergic, LABA, Noncatecholamines
Receptor: Primarily Beta 2
Uses: Maintenance therapy; nocturnal asthma
-not a rescue inhaler
Dosage strength: MDI 25ug/puff (micrograms/ BID 2 puffs), DPI 50ug/puff
duration: 12 hours (BID)
side effects: mild tremors, headache, insomnia, nervousness, nausea
what is:
Salmeterol
the aerosol that affects respiratory secretions
-Acetylcysteine(Mucomyst)
-Dornase alfa(Pulmozyme)
what is:
Mucoactive drug
the aerosol medication combination that is mixed with LABAs:
fluticasone propionate/salmeterol (advair diskus/ advair HFA)
Budesonide/formoterol fumarate HFA(Symbicort)
Mometasone furoate/ formoterol fumarate HFA (Dulera)
fluticasone furoate/ vilanterol (breo Ellipta)
what is:
Combination inhaled corticosteroids and LABAs
the drug action phase that:
-What does the drug do to the body
-The combination of a drug with a matching receptor causes drug effects

what is:
Pharmacodynamic Phase
the receptors for pharmacologic control located(3 parts)
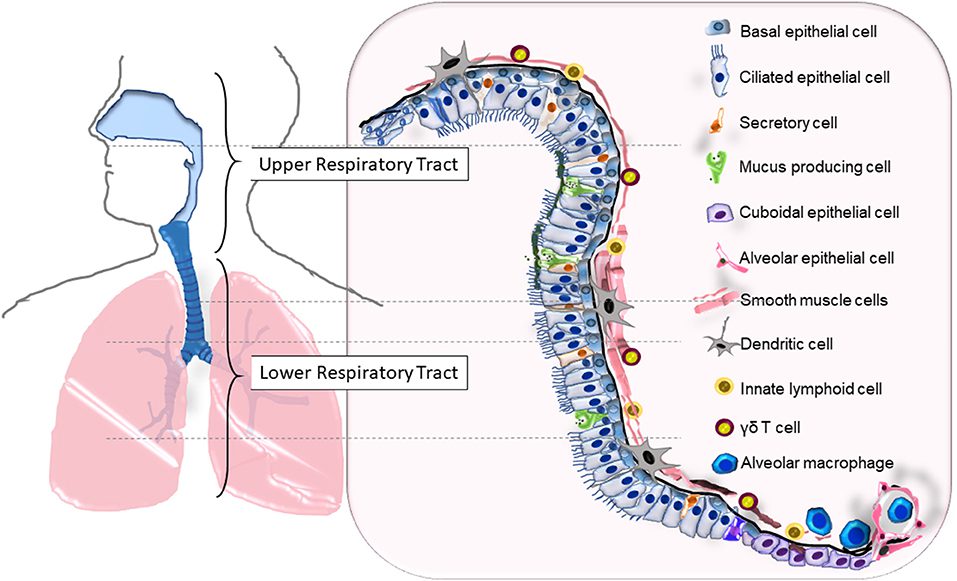
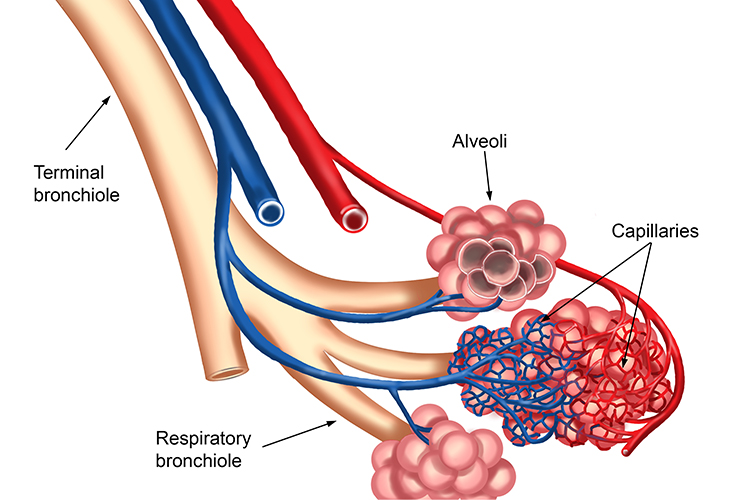
what is:
Smooth muscle, secretory cells, and blood vessels (in bronchioles)
the type of effect occurs when this receptor is stimulated
-Bronchoconstriction, increased mucus production
what is:
Muscarinic 3(M3)
the indication of the following event should be treated with:
-Reversible airflow obstruction

what is:
Adrenergic bronchodilator
the mocu-active agents used specifically for sputum induction

what is:
Hypertonic saline
the following effect:
Size of particles, physical characteristics of the airways, shape, and motion of the particles
what is:
deposition of aerosol
the following is the procedure for which the device
- assemble the apparatus
-load dose(should come already loaded) sometime extra dosage counted but just for practice/clearing
-exhale slowly to the functional residual capacity
-seal lips around
-inhale deeply and forcefully(fast must be at least 40-60Lpm)
-hold your breath and repeat if needed for dosage
-monitor adverse reactions
-assess beneficial effects overtime
what is a:
DPI(dry powder inhaler)

the phase that describes the mechanisms of drug action by which a drug molecule causes its effects in the body
"what the drug does to the body"
what is:
-the Pharmacodynamic phase (purpose)
the aerosol medicine that matches the following:
brand name: Foradil
drug class: Beta-Adrenergic, LABA, Noncatecholamines
Effects: more rapid & similar to albuterol but long-acting
Uses: maintenance therapy only
-not a rescue inhaler
Dosage: DPI 12 ug per puff Duration: 12 hours (BID)
what is:
Formoterol
the aerosol treatment that matches the following:
brand name: Mucomyst
Drug Class: Mucolytic(prophylactic)
usage: used to reduce excess viscous section in airway & Tylenol OD must retreat with adrenergic bronchodilator(to reduce the irritation of mucolytic)
side effects: bronchospasm, airway obstruction due to rapid liquefaction of secretions, stinky due to hydrogen sulfide, incompatibility with certain antibiotics
what is:
Acetylcysteine
the aerosol medication that matches the following:
combines Fluticasone and Salmeterol
Brand names: FLovent & Serevent (purple)
Drug class: glucocorticoids (inhaled steroid) & LABA
Effects: steroid reduces inflammation & LABA for bronchodilator
Dosage: flovent DPI 100, 250, 500 mcg
Serevents DPI 50 mcg
Frequency: BID(twice a day)
what is :
Advair Diskus(DPI)
the most common devices used for aerosol delivery

what is:
MDI, SVN, DPI
the neurotransmitter and receptor for parasympathetic system
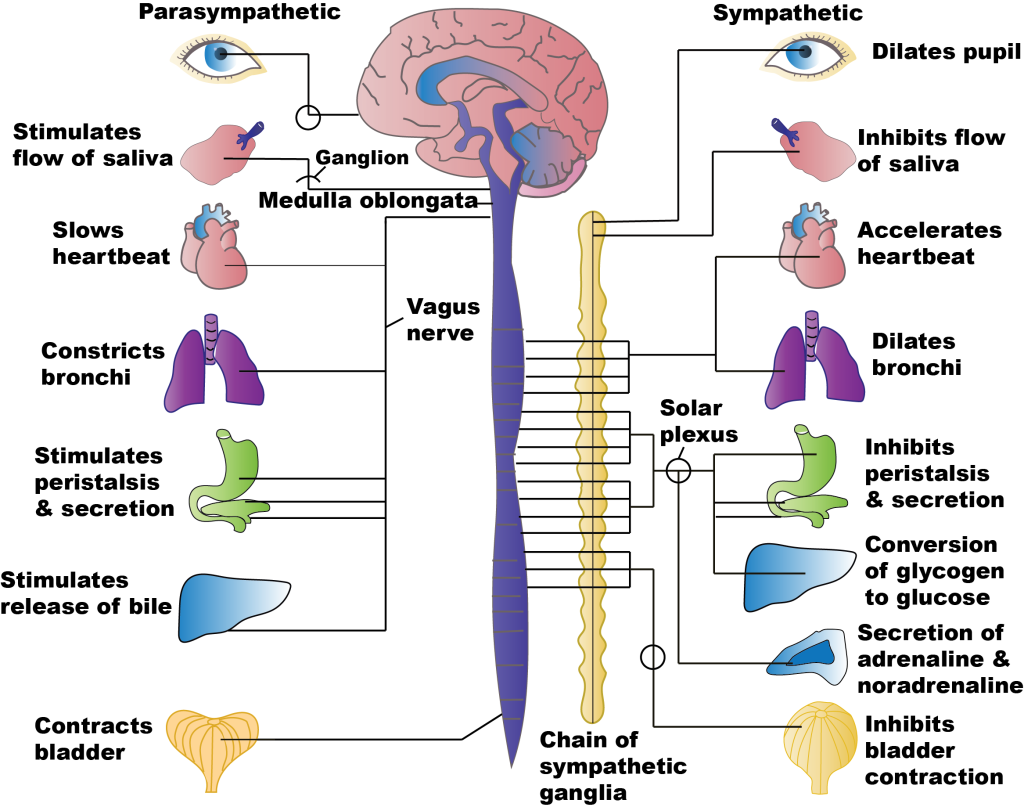

what is:
PSNS – Acetylcholine (cholinergic)
the quick-acting “rescue” treatment (Albuterol)


what is:
Short acting beta agonist (SABA)

the following are the side effects of what:
Tachycardia, nervousness, palpitations, V/Q mismatch (in pneumonia), and hypokalemia

what is:
adrenergic bronchodilators
the following are the advantages of what drug
-smaller dose than for systemic administration
-onset of drug action is rapid
-delivery targeted to organs requiring treatment
-systemic side effects minimal
what is:
advantages of inhalation aerosols
the actions to prevent yeast or infection associated with MDI steroids


what is:
Rinse your mouth and/or use a spacer
the following is the proper procedure for giving what treatment
-assess the patient for needs (clinical signs, breath sounds, peak flow)
-select a mask or mouthpiece for delivery
-use a conserving system (thumb port, breath actuator, or reservoir) if indicated
-place the drug in the nebulizer(if using multidose vial, add saline to the approved dose volume per label
-set gas flow to nebulizer at 6-10L/min
-patient is upright or mask added to keep the nebulizer upright
-coach the patient to breathe slowly through the mouth at normal VT
-continue until the nebulizer begins to sputter
-rinse with sterile water or discard
-monitor patients for adverse response
-assess outcome (change in peak flow)
what is a:
SVN

the phase that is the method by which the drug is made available to the body
what is:
Drug administration phase(elements: MDI,SVN,DPI)
the aerosol medicine that matches the following:
Brand name: Atrovent(type of atropine)
Drug class: Anticholinergic
enhances: sympathetic effects
Effects: blocks cholinergic induced bronchospasm(fully ionized)
-often used with Albuterol(enhances bronchodilation)
Dosage: 0.5 mg SVN, MDI 17mcg/puff
frequency: Q4-6 hours or 2 puffs QID
Side effects: cough and dry mouth, pupil dilation
Ipratropium Bromide
the aerosol medication that matches the following:
brand name: Pulmozyme
drug class: Mucolytic
indication: for management of cystic fibrosis
action: proteolytic enzyme breaks down DNA material from neutrophils found in purulent secretion (cells)
what is:
Dornase Alfa
the following are actions of what type of aerosol drug:
Mast cell stabilizers(stop breaking down)
Antileukotrienes(modifiers)
Monoclonal antibodies/ anti-IgE agents
includes: anti-viral, anti-protozoal, & antibiotics
Instructions: pre-treat with beta-adrenergic, risk to healthcare workers so proper PPE
Side effects: bronchospasms
what is: Nonsteroidal antiasthma drugs
the largest group of drugs RTs aerosolized(beta#,brand names are Albuterol or Xopenex)

what is:
Adrenergic bronchodilators ( most common beta 2 agonists)
the neurotransmitter and receptor for the sympathetic system
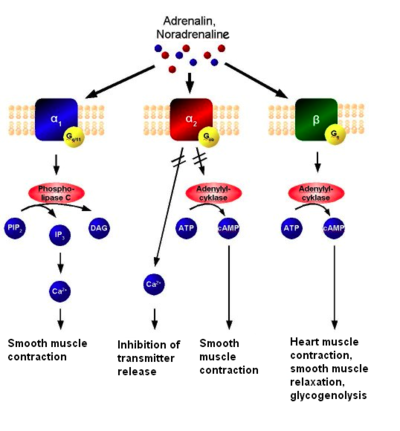

what is:
SNS – Norepinephrine (Adrenergic)
the treatment that takes time and aids with“controlling” (Serevent)

what is:
-Long-acting beta agonist (LABA)
the treatment of acetylcysteine for RTs is breaking up thick secretions, what is another indication when acetylcysteine should be used

what is:
Tylenol (acetaminophen) overdose
the following are the disadvantages of what drug
-unable to ascertain the exact dosage
-lack of adequate knowledge of device performance
what is:
inhalation of aerosols
the following are actions that should take place before, during, and after what treatment
Vital signs, peak flow, breath sounds, and patient’s response

what is an:
aerosol treatment
the common side effect of Atrovent
what is:
Dry mouth and cough
the key that opens the door to neurotransmitters
"stimulates agents"

what is:
an agonists
-would want this for the sympathetic system to cause relaxation of the bronchi which is dilation making it easier to breathe
the subgroups of adrenergic bronchodilators
what is:
Ultra-short acting catecholamine agents(race epinephrine)
short-acting non-catecholamine agents (albuterol, levalbuterol) duration 4-6hrs, rescue inhaler
long-acting adrenergic bronchodilators (salmeterol- serevent, formoterol- Foradil, arformoterol- Brovana) duration of action is about 12 hours, controller inhaler- maintenance
the aerosol medication that matches the following:
is orally inhaled preparation used for anti-inflammatory maintenance therapy of persistent asthma and severe COPD(chronic inflammation), control allergic and nonallergic rhinitis
mode of action: takes 3 weeks since it modifies cell transcription
instructions: use with spacer & brush your teeth to prevent thrush
what is:
inhaled corticosteroids
the aerosol medicine that matches the following:
Brand name: NebuPent
Drug class: Anti-protozoal
usage: treatment of opportunistic pneumonia caused by Pneumocystis jiroveci(often seen in AIDS patients)
delivery: via RespirGard nebulizer
what is: Pentamidine
the most common drug-aerosol delivery systems for pulmonary patient(3 part)


what is a:
-DPI,
-inhaler MDI,
-& Nebulizer (SVN)
the problems that may occur after administering MDI and who would struggle to use this device(adding a spacer would help)



what is:
thrush
if the patient is in distress, infants and young children, the elderly finger pain
the decrease in heart rate & strength of contraction
what is:
Chronotropic & inotropic
the hazards of aerosol therapy and the primary one:
what is:
- a primary adverse reaction to medication
Others: infection, airway reactivity, pulmonary and systemic effects of bland aerosols, drug concentration changes during nebulizer, eye irritations.
the following are what types of drugs and what do they treat
Mast cell stabilizers – cromolyn sodium (Intal)
Antileukotrines – zileuton, montelukast (singular)
Anti-IgE - Xolair

what is:
nonsteroidal anti-asthma drugs
what do we do if the heart rate increases by more than 20BPM during treatment was 80BPM at the start and is now 110BPM (4 parts)



what is:
- stopping treatment
-remain with patient till heart rate comes down
- inform the doctor of the reaction
-MAKE SURE YOU CHART ADVERSE EFFECTS
the patient is not improving with SVN what should you ask the doctor to consider doing

what is:
to up the dosage and recommend continuous nebulizer
the term associated with blocking the door to neurotransmitters that acts on receptors

what is:
Anatogonist
the aerosol medicine that matches the following:
Brand name: Vaponephrin, MicroNefrin
Drug class: Adrenergic Catecholamine
Receptors: Alpha, Beta 1, Beta 2 (catecholamine)
concentration: 2.25%
volume: 0.25-0.50 mL (given with NS)
routes: aerosol or ETT
frequency: 2-4 hours
Indications: to reduce airway swelling after extubation or with acute upper airway inflammation from croup, epiglottis, or bronchiolitis
what is:
Racemic Epinephrine
the following are generic/brand names associated with which aerosol medicine
-beclomethasone dipropionate (QVAR)
-Fluticasone propionate (flovent HFA)
-Budesonide (Pulmicort Flexhaler, Pulmicort Repules)
what is:
inhaled steroids
the aerosol medication that matches the following:
Brand name: Virazole
usage: severe lower respiratory tract infections caused by RSV(disrupts DNA/RNA of the virus)
administration: requires the use of a small particle aerosol generator (SPAG)
Warning: teratogenic(birth defects), carcinogenic, healthcare worker must use protection, cannot be pregnant while receiving or administrating
adverse effects: skin rash, eyelid erythema, conjunctivitis
what is:
Ribavirin
the 2 things that should be asked before administrating the medicine to the patient
what is:
name & DOB
the following are what type of aerosol treatment
Pentamidine(NebuPent), Ribavirin(Virazole), Tobramycin(TOBI)
what is:
an aerosol anti-infective Agents
the following are needed for what:
patient name, drug name, dose, frequency, route of administration, doctor signature

what is: a prescription

the aerosol medicine that matches the following:
Brand name: Spiriva (long-acting)
Drug class: Anticholinergic
Usage: maintenance management of COPD
Dosage: 18ug/ inhalation
Frequency: once daily
what is:
Tiotropium bromide
the aerosol medication that matches the following:
Brand name: Flovent (red)
Drug class: Glucocorticoids(inhaled steroids)
primary use: orally inhaled corticosteroid for anti-inflammatory maintenance therapy of persistent asthma and serve COPD
Dosage: MDI- 44,110, 220mcg per puff, DPI- 50, 100, 250 mcg per puff
what is:
Fluticasone
the aerosol medication that matches the following:
Drug class: antibiotic
Usage: manage chronic infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis
Prevents: lung deterioration due to recurrent infections
benefits: reduces systemic side effects, eliminates organisms colonized in the respiratory tract
what is: inhaled tobramycin (TOBI)