There are three types of interactions, they are... (3 answers)
Competition, Predator-Prey, and Symbiosis
There are _________ who make their own food and __________ who have to eat to survive.
Autotrophs/Producers and Heterotrophs/Consumers
A simple representation of who eats whom in an ecosystem, showing the flow of energy and nutrients from one organism to another.
What's wrong with this food chain? What's the importance? 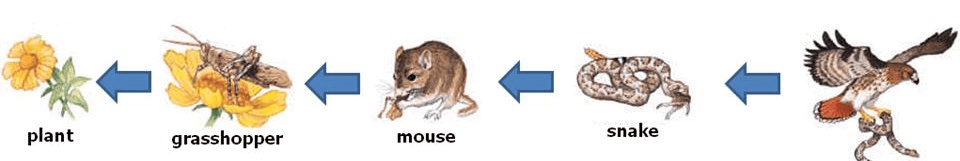
The arrows are pointing in the wrong direction which shows the opposite flow of energy.
There are 3 types of symbiotic relationships, they are....
Commensalism, Mutualism, and Parasitism
What are the levels of feeding in a food chain? (3 answers)
Producers, Consumers, Decomposers
What is the definition of a food web?
A visual representation, or "who eats whom" diagram, showing the complex feeding relationships (or food chains) within a specific ecosystem.
What animal solely relies on grasses for energy?
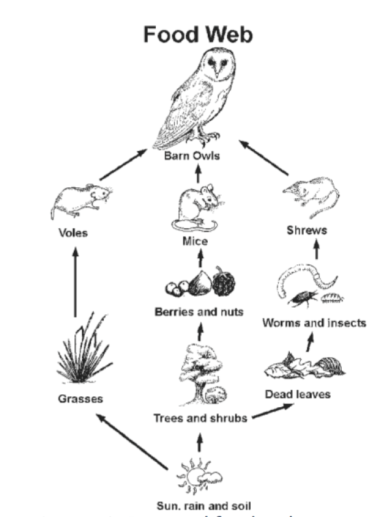
The Vole!
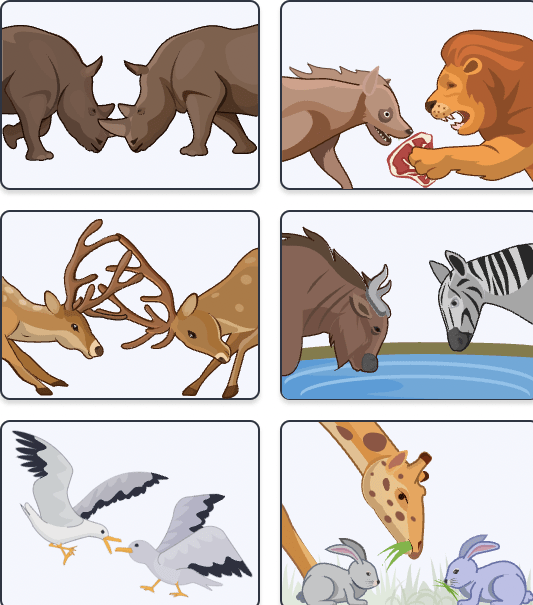 This is an example of... (give name and definition)
This is an example of... (give name and definition)
Competition, where organisms fight over limited resources.
These are nature's clean-up crew members in an ecosystem... give the name of the kingdom that helps the most in this area. (2 answers)
Decomposers / Fungi
Who is missing in this food chain? 
A tertiary consumer / an omnivore / a penguin / a seagull / a carnivore
What is this model explaining? 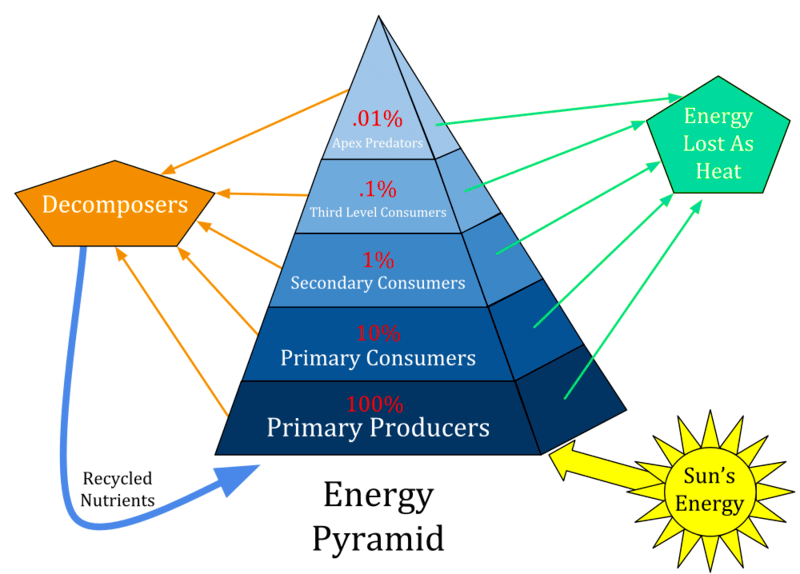
This model shows how energy is lost as you go up the pyramid. Producers receive all the energy from the sun while apex predators receive the least amount of energy from the sun.
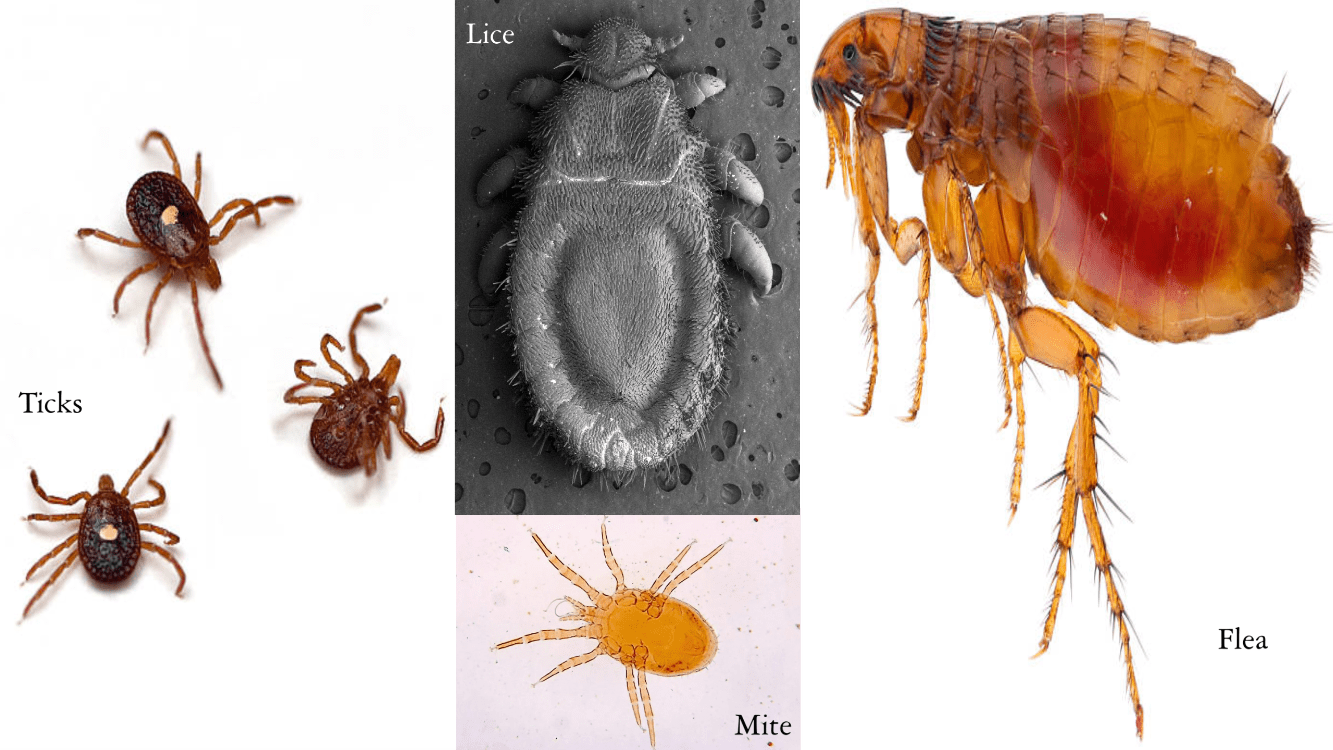 Tapeworms, Fleas, and Lice provide what kind of relationship? Give the definition
Tapeworms, Fleas, and Lice provide what kind of relationship? Give the definition
Parasitism, when one organisms benefits (the parasite) while the other is harmed (the host).
What are the names of the different levels of consumers (not the types of consumers but the hierarchy/order)? (3 answers)
Primary Consumers, Secondary Consumers, Tertiary Consumers
What would happen if there was a surplus of grasshoppers in this food web? Explain! 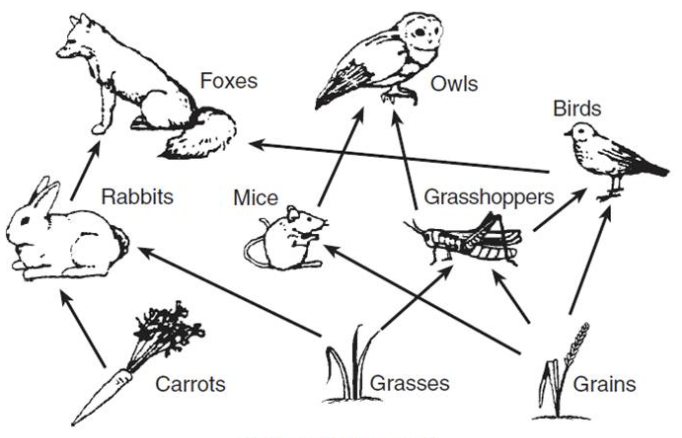
The grasshoppers population would increase, but the grass and grains' population would decline because they are getting consumed quickly. Bird and owl population then increase because they have more food to eat.
What are the levels of organization starting after organ system?
Organism (Individual), Population, Community, Ecosystem, Biomes (Biospheres)
What could happen if you remove true predators from an ecosystem? Explain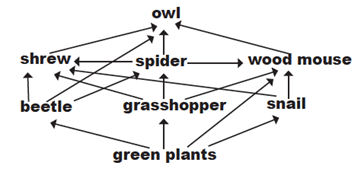
True predators control the populations of herbivores. Without them, herbivore populations can explode. This leads to overgrazing, where herbivores consume vegetation at an unsustainable rate.
_________ have developed adaptations to help them hunt, while __________ have developed adaptations to help them evade. This is called ________.
Predators / Prey / Predator-Prey Relationships or Coevolution
There are 4 types of consumers, they are... (4 answers) and they consume... (4 answers). 8 answers total.
Herbivores - consume only plants
Omnivores - consumes plants and meat
Carnivores - consumes only meat
Scavengers - consumes dead animals
What would happen if there was a disease that impacted the carrots? Who would that harm the most? Explain in at least 2 sentences. 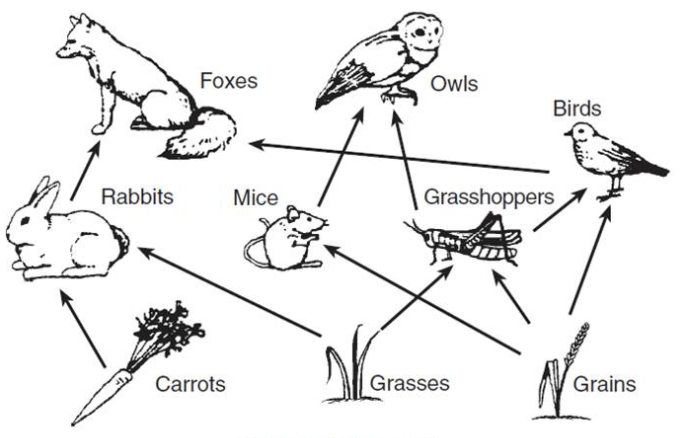
The rabbits' would be directly affected, which would lower their population, which would then lower the foxes' population.
What is this model explaining? Explain what the lines mean and what they're saying. 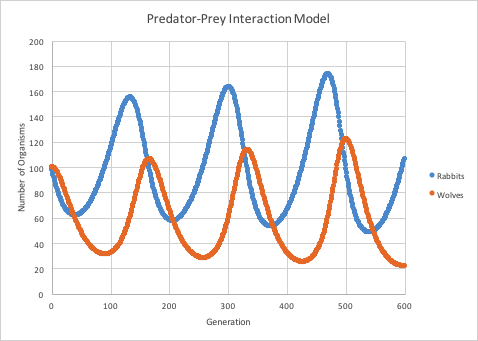
Predators and prey rely on each other for balance within the ecosystem. When there is an increase in the prey population, the predator population will increase soon after. When the predator population increases, then the prey population decreases.
How does the Water Cycle impact ecosystems? (5 potential answers, just give 2 answers). 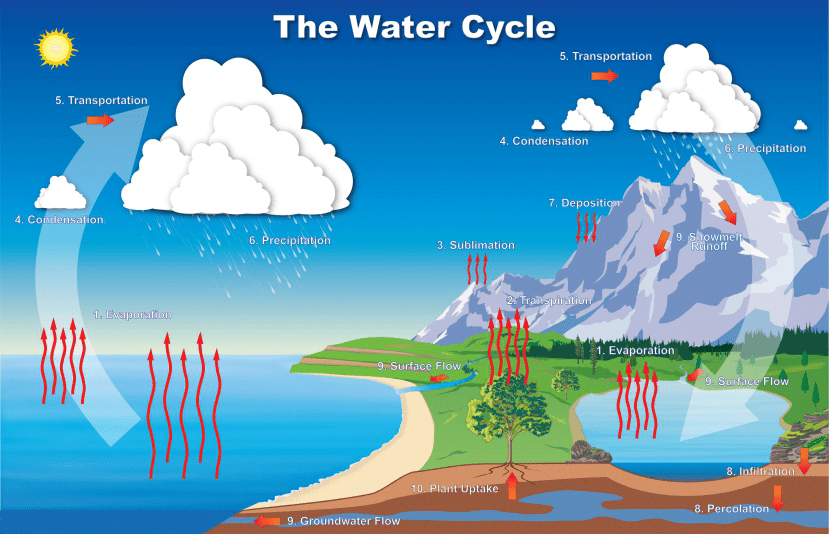
Without the water cycle, (1) water wouldn't be able to return to lakes/streams so animals lose out on water access, (2) water transports nutrients (minerals) throughout the ecosystem, (3) Water regulates climate/weather, (4) Animals live in water so it's a habitat source, and (5) Plants need water for photosynthesis.