A piece of equipment used in all basic nursing assessments, made up of a bell, diaphragm, and ear buds.
What is a stethoscope?
Regular rhythm that is associated an atrial and ventricular rate of 150-250. 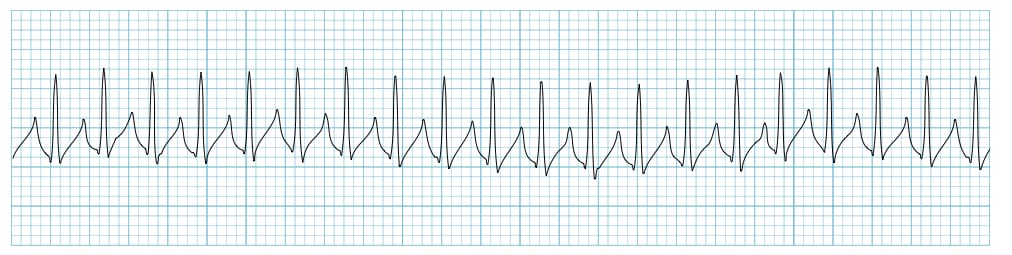
What is SVT?
The dominant pacemaker of the heart, located in the right atrium/superior vena cava, rate dependent on sympathetic and parasympathetic stimulation.
What is the SA node?
The normal heart sound that occurs with the closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves, best heard at the apex of the heart, described as a "lub" sound.
What is S1?
Drug recommended for treatment of asystole, 0.5-1mg, may be given every 3-5 minutes during CPR.
What is epinephrin?
Color, temperature, moisture, and integrity are all important components of this nursing assessment that should be completed and documented on every patient in admitting and recovery.
What is a skin assessment?
Characterized by no rate, no rhythm, and no pulse, treated with CPR, epinephrin, looking for probable causes.

What is asystole?
The backup pacemaker taking over as when SA node fails.
What is the AV node?
The normal heart sound that occurs with the closure of the aortic and pulmonic valves, best heard next to the sternum at the second intercostal space, described as a "dub" sound.
What is S2?
A parasympatholytic used to treat symptomatic bradycardia, given in 0.5mg IV doses to a max of 3 mg, potential side effects include tachyarrhythmia, increased myocardia O2 demand and reduced vagal tone.
What is atropine?
A ___ ___ of HR, BP, RR and O2 sats that can provide diagnostic clues and serve as a reference point, alerting the nurse to potential complications with changes.
What is a baseline assessment?
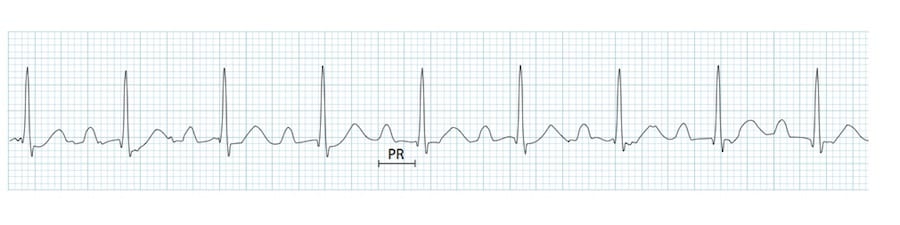 Regular rhythm, potentially slow rate, PR >0.20, QRS <0.12, may be symptomatic or asymptomatic, possible causes are drug induced or vasovagal reactions.
Regular rhythm, potentially slow rate, PR >0.20, QRS <0.12, may be symptomatic or asymptomatic, possible causes are drug induced or vasovagal reactions.
What is 1st degree heart block?
Caused by blunt force trauma to the chest, cardiac surgery or infection, characterized by muffled heart tones, may require pericardiocentesis.
What is cardiac tamponade?
The part of the stethoscope that is used to best hear S2 and S3.
What is the bell of the stethoscope?
Given to treat acidosis and hyperkalemia, usual dosing 1mEq/kg IV bolus, not recommended for routine use in cardiac arrest patients.
What is sodium bicarbonate?
A late finding that presents as a color change in the mucus membranes, earlobes, cheeks, and lips, reflective of reduced oxygen concentration.
What is central cyanosis.
Regular rate and rhythm, 60-100 BPM, PR interval 0.12-0.20, QRS is 0.06-0.10, asymptomatic, no treatment required.
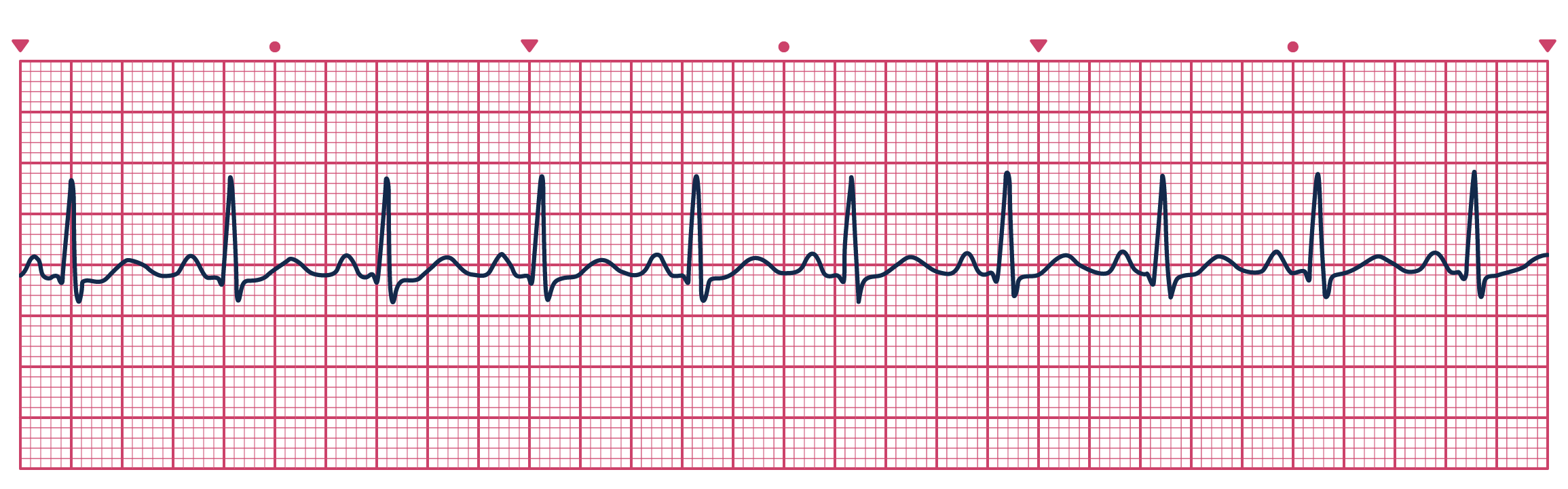
What is sinus rhythm?
Electrical representation of ventricular repolarization, the isoelectric line between the end of the S wave and the start of the T wave, elevation of greater than 0.5mm can indicate ischemia or infarction.
What is the ST segment?
Abnormal heart sounds described as whooshing or swishing, associated with turbulent blood flow through an incompetent valve, often benign in young children.
What is a murmur?
May be given as a sedative prior to synchronized cardioversion, starting at 1mg and titrating to effect, potential to cause respiratory depression.
What is Midazolam or Versed?
Invasive monitoring device recommended for patients receiving vasoactive medications, used in critical care areas by specially trained staff.
What is an arterial line.
Irregular rhythm >100 BPM, requiring expert consultation, often described as a sawtooth pattern.

What is atrial flutter?
Anatomical position that approximates the location of the right atrium, used when calibrating the arterial line for proper monitoring.
What is phlebostatic axis?
A condition in the thoracic cavity with the potential to impede cardiac function, requiring immediate intervention with needle decompression, noted in part by absent lung sounds.
What is tension pneumothorax?
Antiarrhythmic used to treat VF, pulseless VT, 300mg IV push, repeating in 3-5 minutes at 150mg dose, potential side effects of hypotension and bradycardia.
What is amiodarone?