Outflow problem, in which pressure overload develops when ventricle has to pump harder against resistance.
What are causes of ventricular hypertrophy?
–Hyperkalemia
–Ventricular tachycardia
–Idioventricular rhythms (including heart block)
–Drug effects and overdoses (especially tricyclics)
–Wolff-Parkinson-White
–Bundle branch blocks and intraventricular conduction delay
–Premature ventricular contractions
–Aberrantly conducted complexes
What are causes of wide QRS complexes?
1.QRS prolongation
≥ 0.12 seconds
2.Slurred S wave in leads I and V6
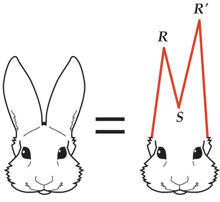
3.RSR′ pattern in lead V1, with R′ taller than R
What are the main criteria for RBBB?
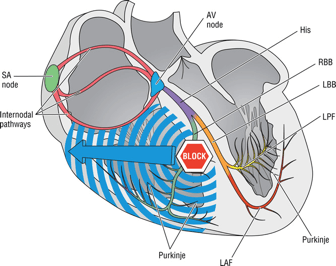
1.Duration ≥ 0.12 seconds wide.
2.Broad, monomorphic R waves in I and V6; no Q wave.
3.Broad, monomorphic S waves in V1; may have small r wave.
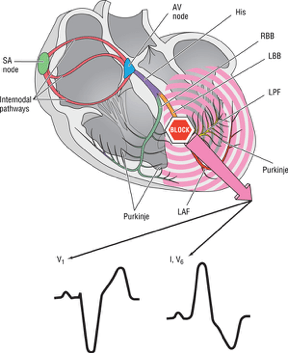
What are the criteria for LBBB?
When an impulse from the atria cannot proceed through the normal conduction system. Instead, it travels by direct cell-to-cell transmission in a slow and chaotic way to innervate the myocardium. It causes wide and bizarre complexes.
What is a BBB?
The number of cells and the size of the ventricles
–Effusion
–Body fat: obese patients
–Amyloid deposits: hypothyroid patients
–Localized pleural effusion
What are factors that effect amplitude of the QRS complex?
This dog.

Who is the best dog?
This wave is a graphical manifestation of the additional vector seen in RBBB (slow conduction through interventricular septum and RV).
What is the R' wave?
Hypertension
Coronary artery disease (CAD)
Dilated cardiomyopathy
Rheumatic heart disease
Infiltrative diseases of the heart
Benign or idiopathic causes
The vast majority are due to hypertension, CAD, or both.
What are the common causes of LBBB?
QRS complexes are 0.12 seconds wide or greater without all characteristics of LBBB or RBBB.
What is IVCD?
–Voltage in all limb leads < 5 mm
–Waves < 10 mm high in precordial leads
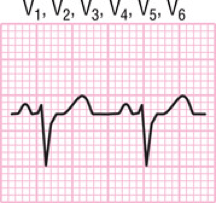
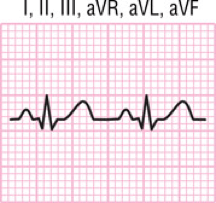
What are criteria for abnormally small QRS complex?
More than one-third the total height of the QRS complex and wider than 0.03 seconds.
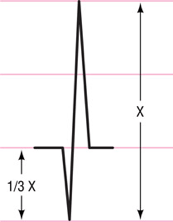
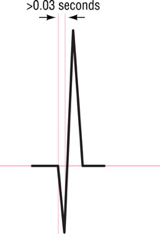
What is the criteria for a pathologically Q wave?
When assessing RBBB you look for this wave in leads I and V6.

What is a Slurred S wave?

What is Colchuk Lake?
IVCD may represent this life threatening condition.
What is hyperkalemia?
(S in V1 or V2 ) + (R in V5 or V6) ≥ 35 mm
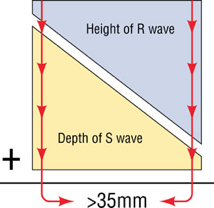
What is the criteria for LVH?
The area of precordial leads where there is a change from a mostly negative QRS complex to a mostly positive complex, occurs at point where QRS complex is isoelectric.
What is the transition zone?
This wave is an alternative RBBB pattern to the classic rSR′ pattern in V1 (rabbit ears).
What is the QR' pattern?
When “half” of LBBB is blocked after it splits into left anterior and left posterior fascicles.
What is a Hemiblock?
1.LBBB
2.RBBB
3.IVCD
4.Ventricular or aberrantly conducted beats
What are 4 differential diagnoses for wide QRS complexes?
R:S ratio is greater than or equal to 1 in leads V1 and/or V2.
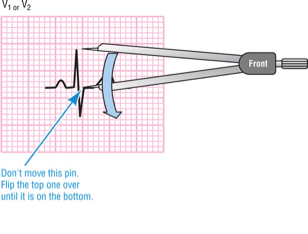
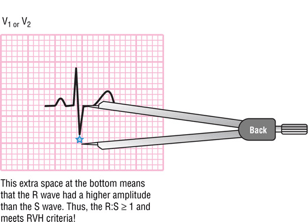
What is the criteria for RVH?
This event.

What is the most recent solar eclipse?
Determine if the terminal portion (last 0.04 second) of the QRS complex is positive.
What is the steering wheel method of finding RBBB?
Determine if the terminal portion (last 0.04 second) of the QRS complex is negative.
What is the steering wheel method of finding LBBB?

What is the national beer of Haiti?