Increased heart rate and dilated pupils in response to a stressful situation. Which part of the nervous system is responsible for these changes?
Sympathetic
Sudden onset of severe HA, worst of their life, the nurse will
Perform focused Neuro exam
CT Stat
1st line drug for prolonged seizure
2mg IV Lorazepam
Signs of TIA that require immediate medical attention include
Temp numbness in face or limbs
Severe HA
Confusion
Dizziness / loss of balance
ischemic stroke. What is the most appropriate immediate intervention
Antithrombotic Therapy
CE caused by DKA is what type of CE
Osmotic
Most common diuretic used to decrease ICP
Mannitol
head injury is presenting with worsening headache, confusion, and slurred speech. What is the most appropriate immediate action for the nurse to take
Notify MD STAT
Which diagnostic test is most appropriate to confirm the presence of a ruptured cerebral aneurysm
Cerebral angiography
Parkinson's Med that causes hallucinations
Levodopa
How does Amitriptyline work?
Blocks pain signals to CNS and improves nerve function.
Cerebellum
headaches 20 days each month for the past three months. What is the most appropriate intervention?
Preventive meds
Seizure patient begins to show signs of respiratory distress. What should be the nurse's priority action
Reposition to open airway
Left sided weakness that resolved within 12 hours. What might be the culprit
TIA caused by blocked carotid artery
Name the 2 types of CVA's (Strokes)
Ischemic, Hemorrhagic
Name the most common type of Cerebral Edema
Vasogenic involving an interruption of the blood brain barrier
signs of increased ICP. Which intervention should the nurse prioritize
Administering diuretics to reduce fluid volume.
Explain the Monro-Kellie Doctrine
the cranial vault is a fixed space comprised of the brain, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid.
If one of these three components increases, at least one of the other two must decrease or an increase in ICP will occur
The initial formation of an aneurysm develops within the Tunica _______
Tunica Media
Pt teaching included for Parkinson's pt with increased difficulty with mobility
Encourage daily physical activity
The most common cause of PN is
Diabetes mellites
assessment to determine the function of the autonomic nervous system
Pupillary light reflex
Primary and Secondary
diagnostic tests to assess the cause of seizures
CBC, LP, MRI, CT, EEG
In the context of TIAs, which of the following interventions is most crucial in preventing subsequent strokes?
Antithrombotic Meds
Imaging reveals a hemorrhagic stroke. What is the priority intervention?
emergency surgery to relieve pressure
Type of CE caused by CVA
Cellular/cytotoxic
25-30mmHg
damage to the neurons from stretching or tearing is called.
diffuse axonal injury (DAI)
Name 2 modifiable risk factors for aneurysm formation
HTN and Smoking
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a degenerative, progressive condition primarily caused by the gradual loss of cells in the ______ of the brain
substantia nigra
DKA with numbness / tingling in feet. What mechanism is most likely responsible.
Axonal degeneration
artery responsible for supplying blood to the frontal areas of the brain?
Internal carotid artery
A primary headache that is recurrent and last for up to 72hrs is called
Migraine
Describe the tonic phase of a "tonic-clonic" seizure
Muscle rigidity
The acronym FAST stands for
Name the 2 main causes of Ischemic Strokes
Stenosis and Atherosclerosis
patient with hyponatremia. What is the most appropriate nursing intervention to prevent cerebral edema
Hypertonic Saline
What is the normal ICP pressure
7-15 mmHg
9-20 cmH20
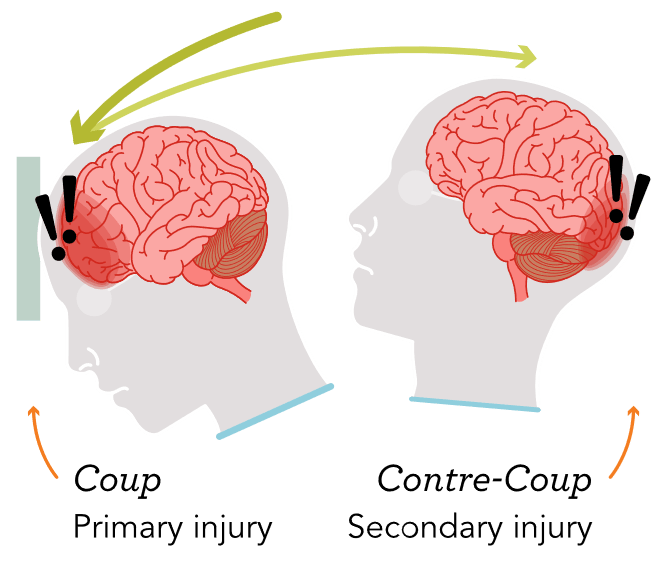
Explain Coup/Contre-Coup
Unruptured, Ruptured, Leaking
the substantia nigra of the brain produce the neurotransmitter _____
dopamine
Name an anti-seizure med that helps alleviate PN pain
Gabapentin, Neurontin, Pregabalin
Which nervous system controls voluntary movements
Somatic Nervous System
Headache with unilateral pain that has lasted longer than 72 hours and has not responded to usual treatment is called
Status Migrainosus
Interventions for managing Status Epilepticus
Maintain airway (lay on side)
O2 if needed
Lorazepam STAT
Monitor for injury during seizure
True or false. A TIA resolves completely without direct intervention.
True
hemorrhagic stroke, what is the nurse's primary concern
Controlling intracranial pressure
intervention for a patient with cerebral edema following high-altitude exposure?
Provide supplemental oxygen
What causes CE in a TBI or CVA patient
Influx of sodium and water into parenchyma
What is the Glasgow Coma Scale range for severe injury
8 or less
When caring for a client who has a CA, maintain the head of the client’s bed between ______ to decrease ICP
30 to 45 degrees
Outward symptoms of PD include.
tremors, slow movement, stiffness, and problems with balance
patient with peripheral neuropathy reports a new onset of difficulty swallowing. Which type of nerve is most likely affected
Motor nerves