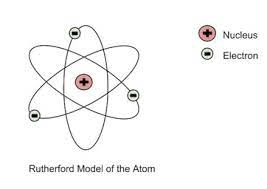
 In 1911, Ernest Rutherford proposed that atoms had a dense, positively charged nucleus that was orbited by _____________.
In 1911, Ernest Rutherford proposed that atoms had a dense, positively charged nucleus that was orbited by _____________.
What are electrons?
 The number that represents atomic weight
The number that represents atomic weight
What is 4.003?
Negatively charged particles found outside the nucleus of an atom
What are electrons?
These are constantly in motion, more or less based on their state
What are atoms?
The "stuff" all objects and substances in the universe are made of
What is matter?
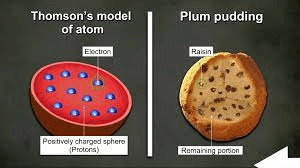 The 1898 model of the atom proposed by J.J. Thomason was called the plum pudding model because he thought the electrons were spread out ____________ throughout the positively charged material of the atom.
The 1898 model of the atom proposed by J.J. Thomason was called the plum pudding model because he thought the electrons were spread out ____________ throughout the positively charged material of the atom.
What is evenly?
The atomic number
What is 14?
The electrically neutral part of an atom
What are neutrons?
This determines the speed of which atoms move
What is heat?
The amount of matter in an object, similar to weight
What is mass?
This Greek philosopher proposed the existence of atoms in 440 B.C.
Who is Democritus?
Russian chemist who organized the periodic table of elements
Who is Dimitri Mendeleev?
What are protons?
The different levels at which electrons move around a nucleus
What are shells or energy levels?
The amount of space a thing fills
What is volume?
John Dalton's early 1880s model of the atom proposed that atoms were small, dense, ________ spheres that could not be created, altered, or destroyed.
What is hard?
The method in which the elements are organized on the periodic table
What is their properties?
What are protons and neutrons?
The name of two or more atoms joined together
What are molecules or compounds?
How much matter is packed into the space an object fills
What is density?
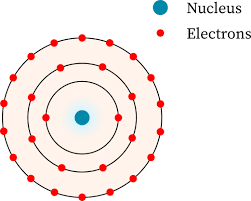 In 1913, Niels Bohr changed the model proposed by Rutherford to note that electrons traveled in circular orbits around the nucleus at certain ________ _________.
In 1913, Niels Bohr changed the model proposed by Rutherford to note that electrons traveled in circular orbits around the nucleus at certain ________ _________.
What are energy levels?
The chemical symbol
What is B?
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
What are isotopes?
Two types of changes matter can go through
What is chemical and physical?
The absence of matter
What is a vacuum?