What is the effect of intensity on the way the human ear perceives sound?
loudness
Which two notes will have the highest consonance and frequency?
1:2
What is a substance through which a wave transfers its energy?
medium
What can sound not travel through?
vacuum
Why can an echo not be heard if the source of the sound is less than 17m from the reflecting source?
the sounds are too close in time to be distinguished
What is the bending of the path of a wave as a result of a change in wave speed?
refraction
What is a set of frequencies at which an object vibrates?
natural frequency
When a driving frequency on objects is the same or nearly the same as one of the objects natural frequencies it is called _________.
resonance
What is two notes interfering harmoniously called?
consonance
What uses reflection of sound to calculate distance?
echo ranging
What is the relationship between sound intensity and distance?
intensity is inversely proportional to the square of distance
What is a sound heard distinctly after being reflected from an object?
echo
What is a wave that has particles of the transmitting medium oscillating at right angles to the direction of wave travel?
transverse wave
The speed of a wave is _________ proportional to the _____________.
inversely/frequency
What is a sound that has too low a frequency to be heard?
infrasonic
What is the sound quality of a musical intrument?
timbre
What is directly proportional to wave speed?
wavelength
What is random sound with no intended pattern?
noise
What is the number of waves that pass a point per unit of time?
frequency
What is the process of dissipating the energy of sound waves in matter?
absorption
If the train conductor hears his train whistle at 1200Hz and a pedestrian hears it at 1350Hz, what can be inferred?
the train is moving toward the pedestrian
What is the lowest frequency of the different sounds produced when an instrument plays a note, usually the same as the pitch being played?
fundamental
What is the most dominant sound of a musical note?
fundamental
What is mutual reinforcement or cancellation that occurs when two or more waves meet?
interference
What is maximum distance particles?
amplitude
supersonic
What is the high point of a wave train?
crest
How do you calculate the speed of sound in air?
speed of sound = 331m/s + 0.61m/s x Celsius temp.
What is the strength of sound waves?
intensity
What is the frequency relationship between a fundamental and its overtones?
harmonic series
What happens to a wave when it passes between two media?
it bends toward the medium that causes slower speed
What is the perpendicular line from which reflection is measured?
normal
How does an ocean vessel use sonar to map the ocean floor?
distance between the sound and returning wave = closer object
What is change in frequency caused by an object's motion?
How do you calculate the frequency of waves?
t= N/T
What is the length of a wave?
wavelength
What is a series of organized sound waves with specific pitches that have been deliberately arranged?
music
What is the low point in a wave?
trough
What is vibrations travelling through a medium as longitudinal pressure waves?
sound
What are waves that strike an object?
incident waves
What is the spreading out of a wave after it passes through a narrow opening?
diffraction
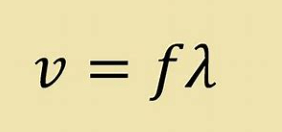
What is the effect of frequency on the way our ear perceives sound?
pitch
What is the musical distance between two notes?
interval
What is the portion of a wave in which the particles are spread out?
rarefaction
What is the study of sound?
acoustics
How do original and reflected wave trains interfere destructively and will a sound be heard when the wave returns to the start of the wave?
nothing will be heard, the original and reflected wave trains will interfere destructively
What is the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection?
law of reflection
What is the kinetic theory of matter?
theory stating that all molecules of a substance are in constant motion and move more rapidly as the object is heated
Rank 4 substances in order of slowest to fastest speed of sound?
steel, 25 degree Celsius air, 50 degree Celsius air, water
What is the difference in pitch between a note and a second note that has twice the frequency of the first note?
octave
What is the periodic oscillation that transmits energy?
wave