This is the map projection we see most commonly.
Mercator
a population pyramid with a large base and a very thin top shows us what about the area?
low economic development
energy resources, minerals or agricultural products, and transportation routs are the main factors of____
deciding where to put a factory
A grocery store is an example of a
on this map projection, the sizes of land masses are the most accurate
Peters
what can we assume about the region based on the population pyramid
high guest worker population
closer to the resource
large shopping districts are an example of
agglomeration and the gravity model
This map projection has longitude lines converge at only 1 pole
Conic
the region shown has had what major event happen within their population?
Where a car factory should be located
closer to the market
Actions that generate new money are considered
Basic economic activities
This map projection doesn't extend to the polar regions of the earth
Robinson
what can be inferred about the region shown?
economically developed
small, home-based businesses are called
cottage industries
When the location decision for one factory is dependent upon the location of other related factories
Locational Interdependence
Which map projection was made in 1963
Robinson
what can be inferred about the region in the population pyramid shown?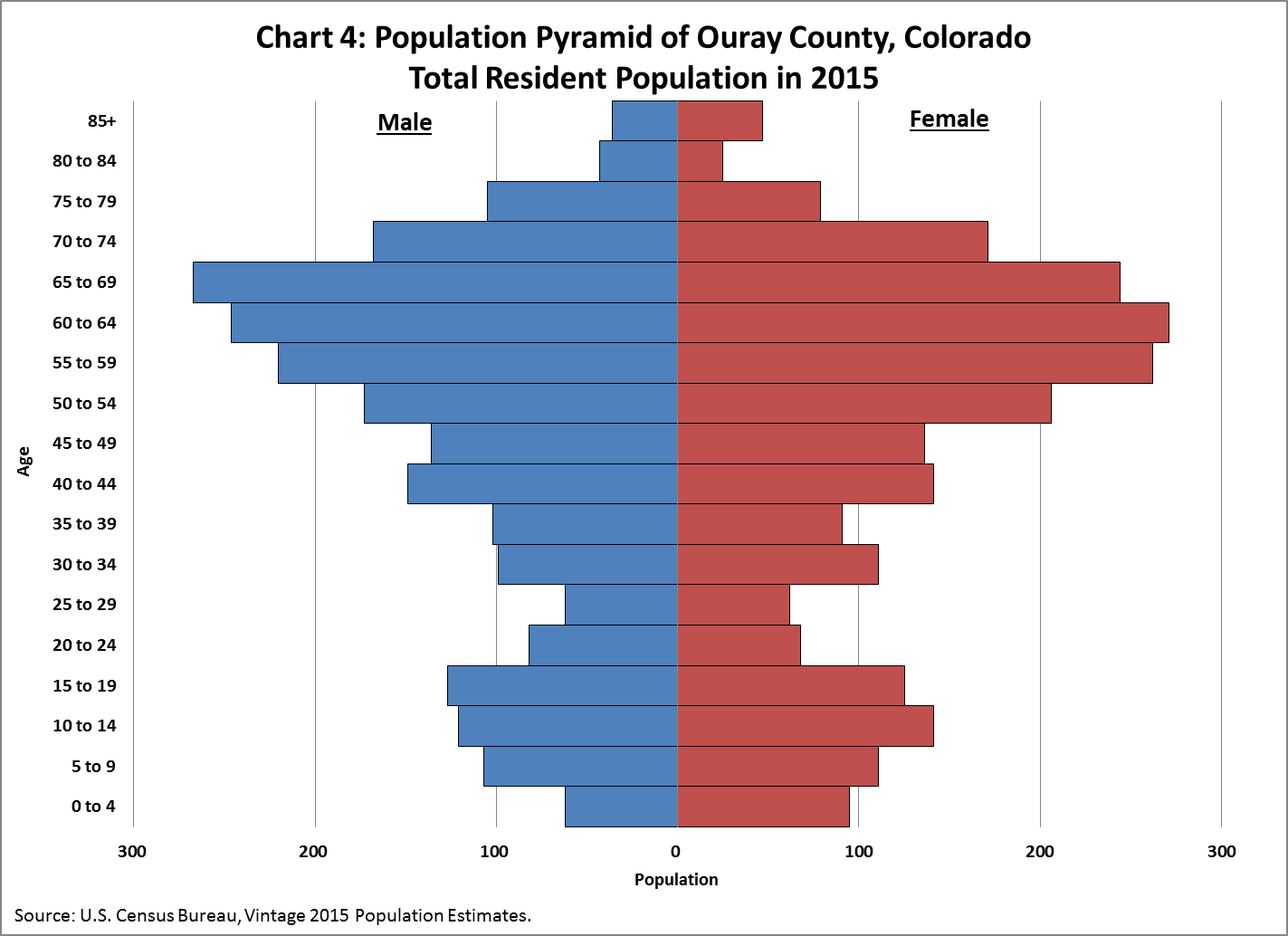
lack of job causes young people to move away; attracts retirees
Who developed the least cost theory?
Alfred Weber
technopoles