1 definition of anaphylaxis
What is 2 systems involved, skin symptoms plus respiratory symptoms, or hypotension after exposure to a known allergen
Dose and route of epinephrine
What is 0.01 mg/kg IM (max 0.5 mg) q5-15 min, mid outer thigh preferred, may need longer needle in obese patients
Treatment of wheezing not relieved by epinephrine
What is nebulized albuterol
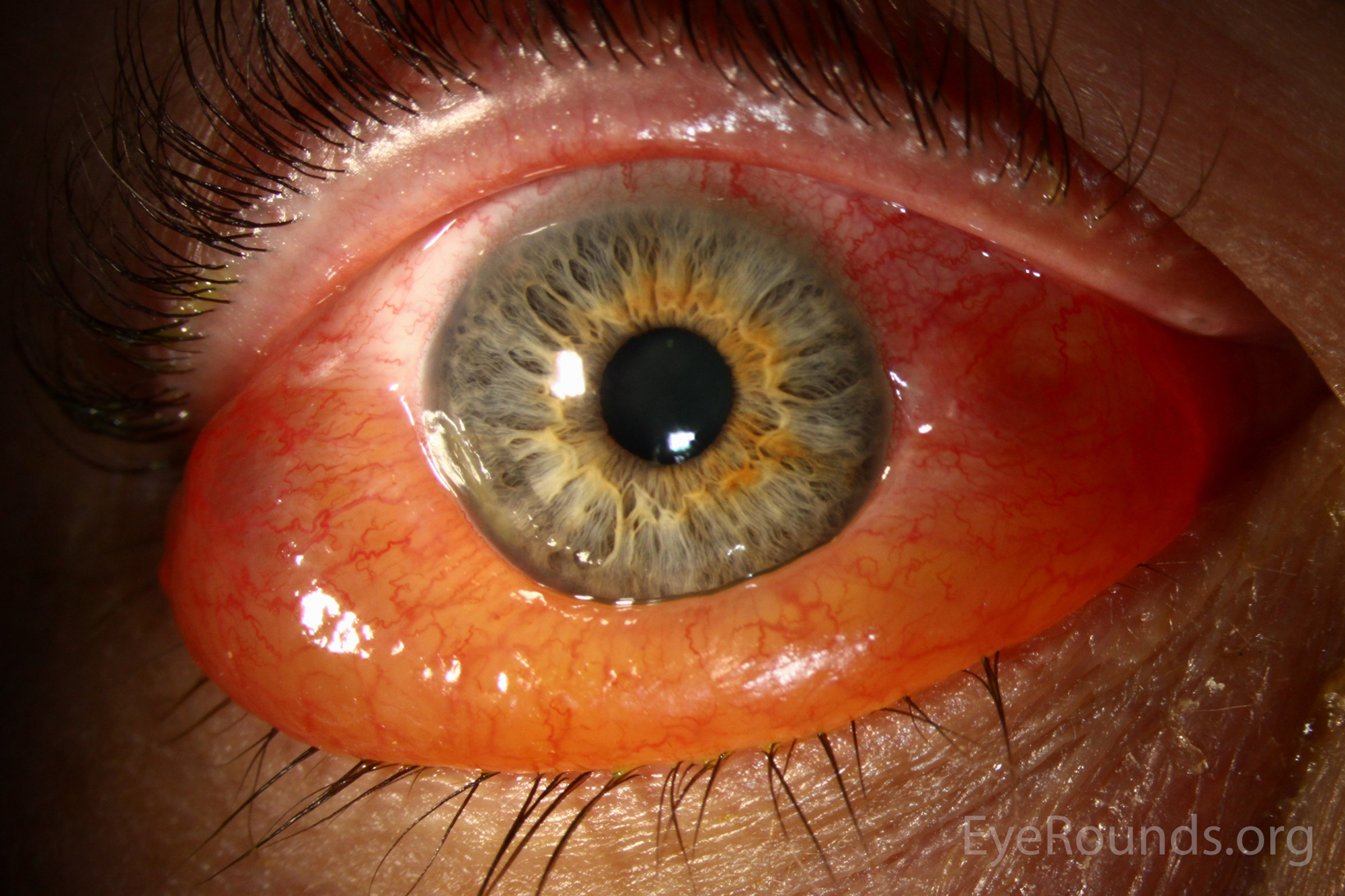
What is chemosis
Medication treatment of vasoplegia (profound vasodilation) in refractory anaphylaxis
What is methylene blue
- inhibitor of NO synthase and guanylate cyclase
- bolus of 1-2 mg/kg over 20-60 minutes
- contraindicated in pulm HTN, G6PD def, acute lung injury
Also ECMO
Anaphylaxis is this type of hypersensitivity reaction
What is I (immediate hypersensitivity)
4 medications commonly given in anaphylaxis with no proven effect in studies
What is
H1 antihistamines (help with itching)
H2 antihistamines (famotidine) (some help with itching)
glucocorticoids (take hours to work, little evidence of benefit, ?prevent biphasic reactions - no evidence)
inhaled beta-agonists
NONE OF THESE RELIEVE AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION, HYPOTENSION OR SHOCK
Position of patient with anaphylaxis
What is recumbent with legs elevated (increase venous return to heart), unless vomiting or pregnant (LL decub) or airway edema (tripoding)
Overdose of this medication used to treat allergic reactions:
What is benadryl or diphenhydramine
Common food sources that cause anaphylaxis - must name 4 of 8
What are eggs, peanuts, milk, shellfish, tree nuts, soy, wheat, or fish
Treatment of hypotension (name at least 2)
What is: 2 large bore IVs, NS boluses 20 ml/kg, repeat as needed (may need up to 100 ml/kg), pressors (epi, infusion of epi, NE, vasopressin, dopamine)
Median time to cardiac arrest in fatalities due to anaphylaxis caused by insect stings
What is 15 minutes (5 min for iatrogenic, 30 min in food-induced anaphylaxis
Dose in children
What is 1-1.25 mg/kg/dose every 6-8 hours
no. of fatal cases of anaphylaxis/year in US
What is 500-1000
Rate of epinephrine infusion
What is 0.1-1 mcg/kg/min
When and how to control airway
What is as soon as airway involvement suspected, intubate, back up adjuncts (cricothyroidotomy as last resort)
This rash and treatment

What is contact dermatitis, stop offending agent and topical corticosteroids
A plant when burned could cause anaphylaxis, especially when inhaled
What is poison ivy
Treatment of hypotension if patient is on beta-blockers
What is glucagon (20-30 mcg/kg over 5 minutes), as rapid infusion can cause vomiting so LL decubitus position or protect airway
Who to admit with anaphylaxis (name 2)
What is patients with severe anaphylaxis (sig cardio or resp symptoms), requiring multiple doses of epi, hypotension at any time, delayed epi (>60 minutes) due to high risk of biphasic reaction

What is urticaria multiforme: peak 4 mo-4 yrs, caused by viruses/bacteria, target lesions with ecchymotic center resembles erythema multiforme, large annular pruritic lesions, fever, angioedema, recent abx or imms, self-limited in 8-10 days, Rx antihistamines
