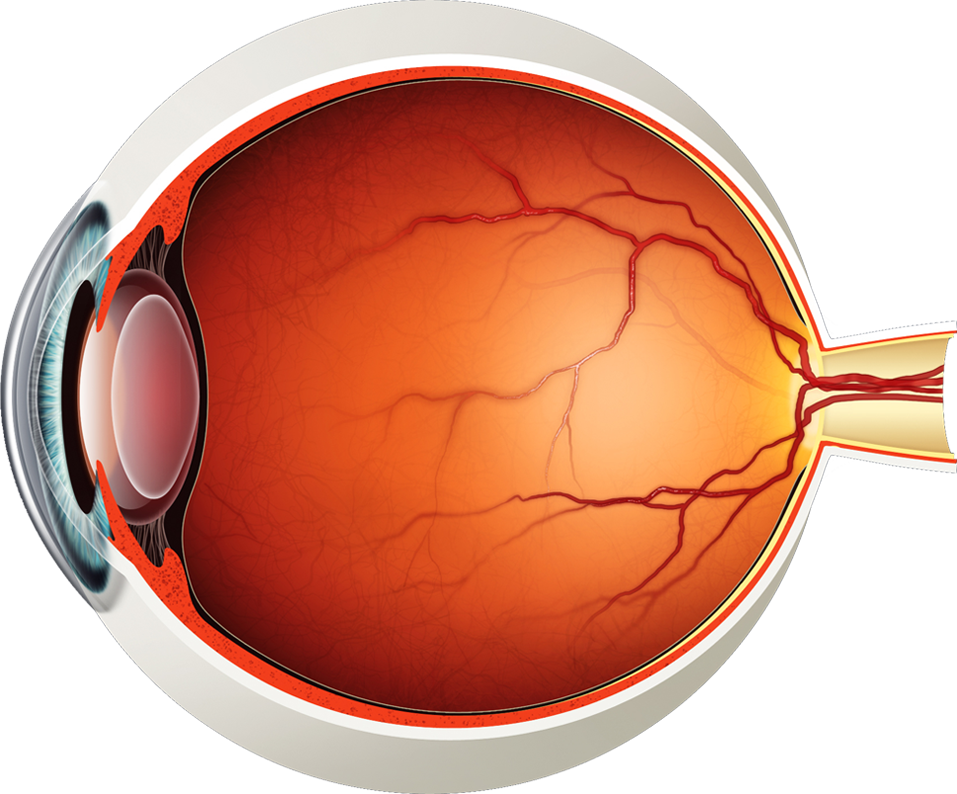
What is the white part of the eye?
What is the sclera.
What is gas exchange meaning oxygen goes into the blood from the lungs and carbon dioxide into the lungs from the blood.
How many parts of the brain are there?
What is 5
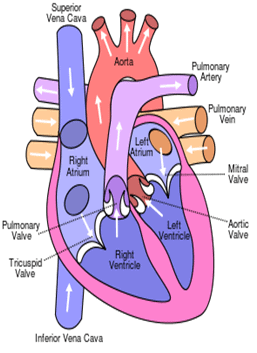
Muscular organ that contracts rhythmically, pumping blood through the blood vessels and around the body?
What is
The heart
Why does the pupil open and close?
What is to regulate the amount of light the retina receives.
The vacuum effect in the pleural space helps keep the lungs what?
What is expanded at all times.
The part of the brain that lies between the medulla oblongata superior to the cerebellum. One function is regulates sleep patterns.
What is the pons.
What is 4.
The immediate instrument of vision by receiving images formed by the lens and converting them into signals which reach the brain by way of the optic nerve.
What is the retina.
What lower respiratory tract structure contains cartilage and why?
What is bronchi and in order to stay open.
What does the medulla oblongata do?
What is collection of nerve cells that deal with respiration, circulation, and special senses.
The side of the heart that sends blood to the lungs?
What is the right side
What function does the lens have?
What is focuses light rays onto the retina.
What is the functional unit of the lung?
What is the alveoli.
What part of the brain is concerned with coordination?
What is cerebellum.
True or false.
Veins have a pulse.
What is false.
Identify the optic nerve and retina.

What are the special white blood cells called that fight infection in the alveoli?
What is alveolar macrophages.
What are examples of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems?
What is:
Sympathetic:
-Dilates pupils
-Increases heart rate
-Contracts blood vessels
of skin and viscera
-Relaxes gastrointestinal
tract
Parasympathetic:
-Contracts Pupils
-Decreases Heart Rate
-Dilates blood vessels
of the skin & viscera
-Increases contraction
of gastrointestinal tract
Identify the major artery and vein of the heart.
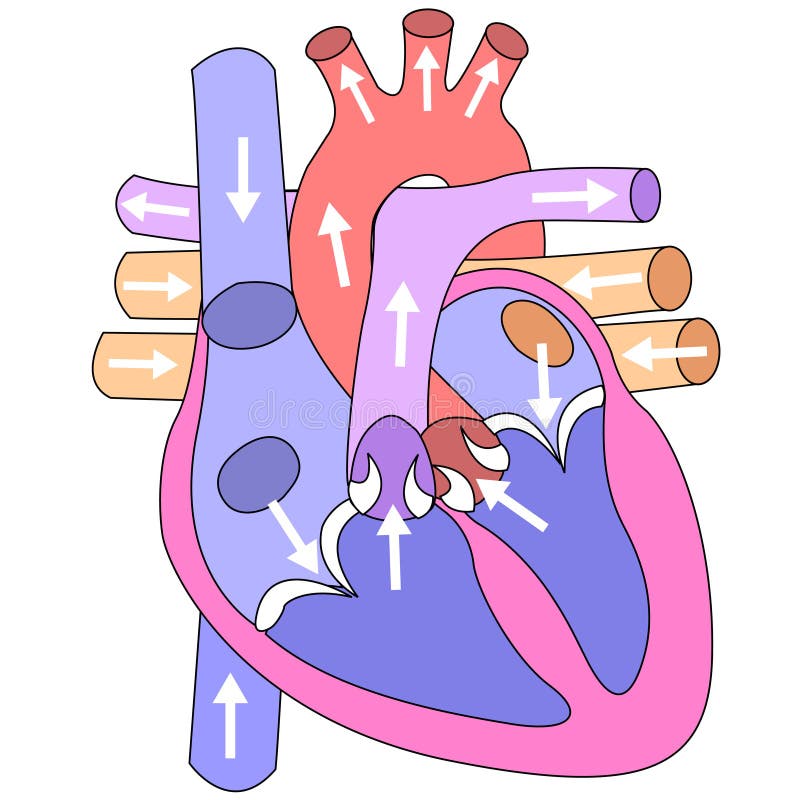
What is the aorta and vena cava.