The three types of muscle cells in the human body are …?
What is cardiac, skeletal & smooth?
The _______ system consists of cartilage, bone, ligaments, tendons, joints, and skeletal muscle.
What is musculoskeletal?
A young boy is recovering from the flu. His temperature five hours ago was 99.7℉. For the past two hours, it has been 98.5℉. This is an example of the body returning to what?
What is set point?
______________ are chemical messengers released into the synaptic cleft by neurons.
What are neurotransmitters?
Juan’s immediate response to a hazard in the roadway is to remove his foot from the gas pedal and firmly press the brake pedal. This is an example of a/an ______ reflex.
What is Learned/Acquired?
True or False
Epithelial tissue covers the surfaces of the body, inside and out (includes skin, inside of blood vessels, abdominal cavity, etc).
What is True?
True or False
Tissues are the simplest structural units of complex multicellular organisms.
What is False?
________ is to developments to improve generational survival as ________ is to developments to improve the functions of an existing organism.
What is adaptation; acclimatization?
The endocrine glands secrete ____ that travel throughout the body using ____.
What is hormones; blood vessels?
“The study of bodily structures of organisms.”
What is Anatomy?
Name this Tissue:
What is Simple Squamous Epithelium?
What are the levels of organization from smallest to largest structure?
What is cell, tissue, organs, organ systems, organism?
True or false: Despite the characteristics of your external environment, your body will always return to homeostasis.
What is False?
By what mechanism are channels formed between cells that connect their cytosol and allow for molecular transport without entering the ECM?
What are Gap Junctions?
“The study of how organisms function.”
What is Physiology?
This tissue consists of a single layer of cube-shaped cells with round nuclei, covers ovaries, lines many kidney tubules and glandular ducts, and functions in secretion and absorption. Which tissue is it?
What is Simple Cuboidal Epithelium?
“Transforming an unspecialized cell into a specialized, functional cell” refers to which term.
What is Cell Differentiation?
When homeostasis is maintained, we refer to _________; when it is now, we refer to ____________.
What is physiology, pathophysiology?
Local responses are often mediated by these two types of substances.
What is Paracrine and autocrine?
These types of cells conduct electrical signaling to neighboring cells and originate within the brain and spinal cord.
What is neurons?
A single layer of epithelial cells with different heights and uneven nuclei; some do not reach the surface.
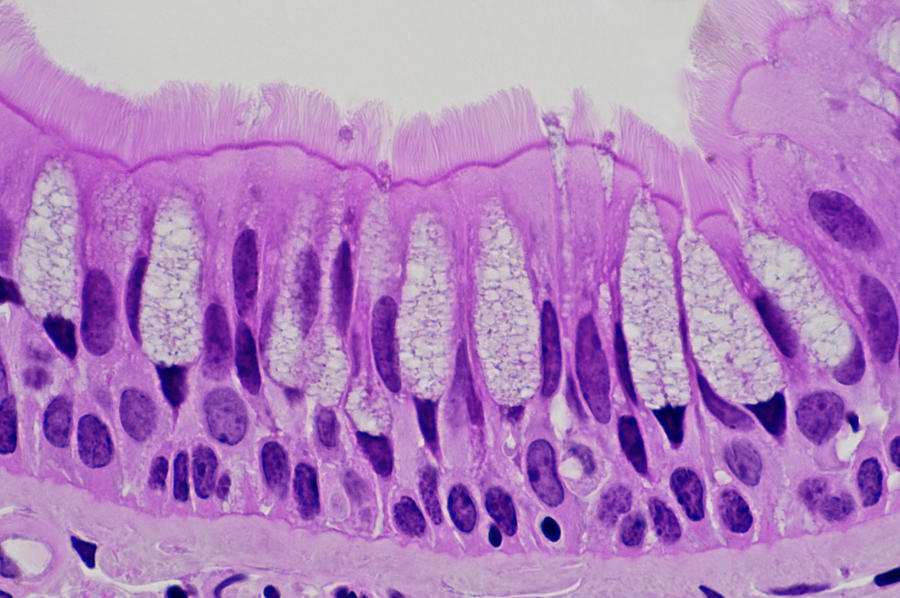
What is Pseudostratified Columnar?
Which organ system protects against injury and dehydration, protects against pathogens, and regulates body temperature?
What is Integumentary?
The presence and detection of antibodies leads to b-cell differentiation (separation of cells into various functionalities), creating more plasma and memory B-cells. This is an example of what type of feedback loop?
What is Positive Feedback Loop?
This type of cellular communication occurs when a signal is sent out by the plasma membrane and interacts with another cell via membrane-bound messengers.
What is juxtacrine signaling?
When touching a hot stove, your receptors send information to your spinal cord which reacts by telling your muscles to pull away. In the proper order, which two pathways are involved?
What is Afferent and efferent pathways?