What organelle contains enzymes to break down substances?
Lysosomes 
What are the 4 major types of tissue
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, and Nervous
Bone tissue is called ____ tissue
Osseous
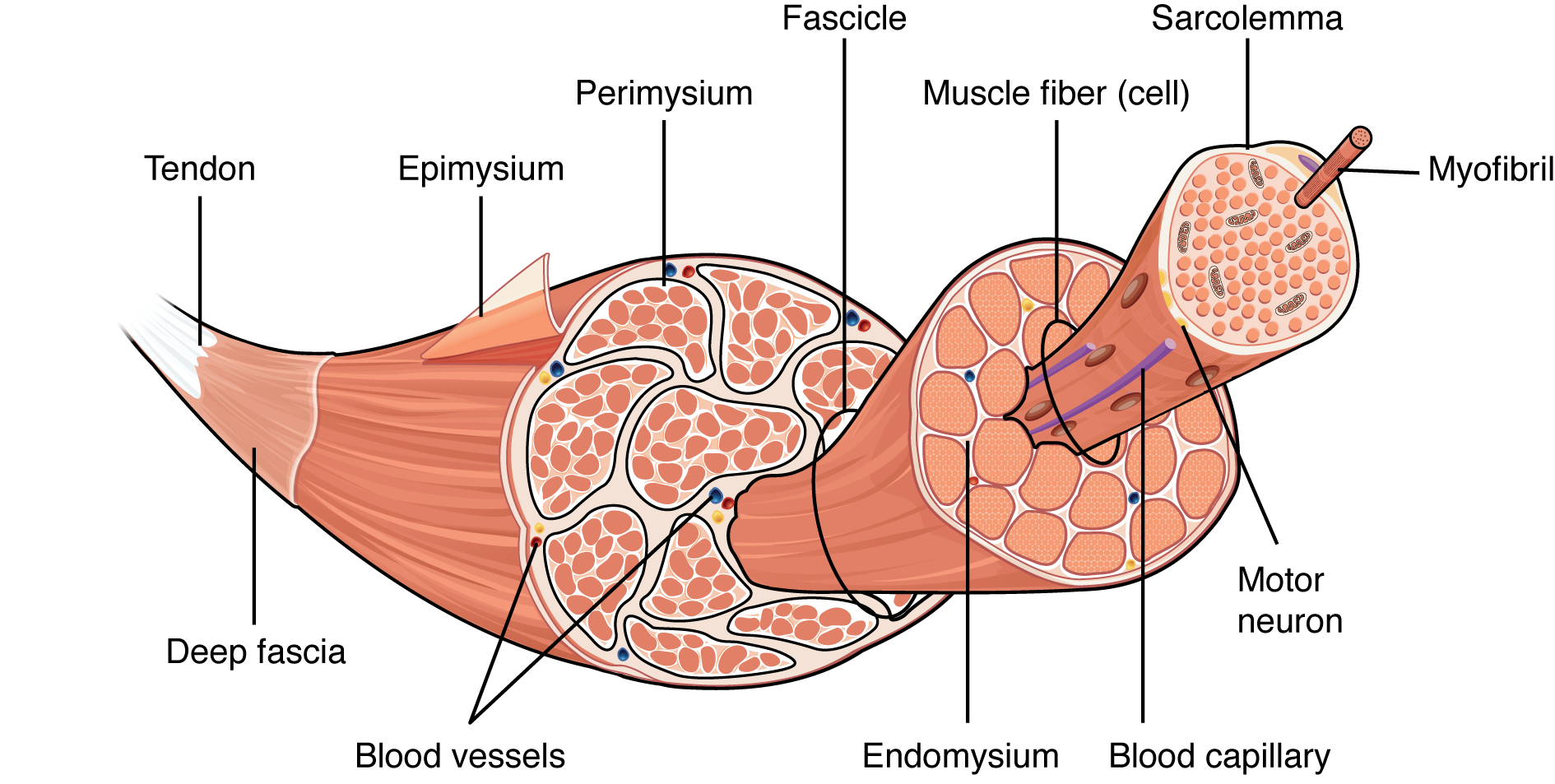
A muscle is composed of many fibers arranged in bundles called
Fascicles
What is the difference between Dendrites and Axons?
Dendrites: receive messages
Axons: send information away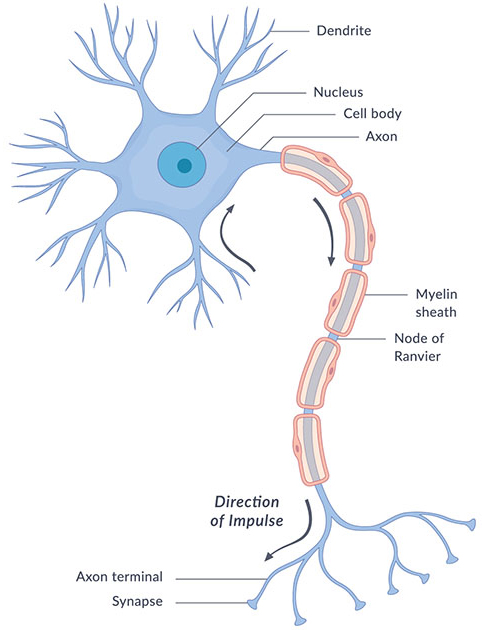
In which step of Mitosis do the chromatids separate and move to the opposite sides?
*Think IPMAT*
Anaphase

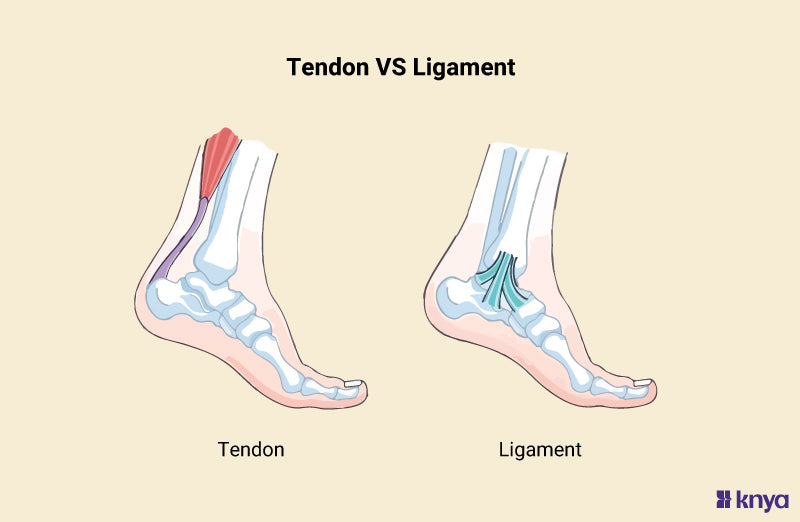
Name two examples of fibrous connective tissue and their differences?
Tendons = muscles to bones
Ligaments = bones to bones
*Few cells, poor blood supply, thus slow healing*
Red marrow vs. Yellow marrow
red: produces blood (spongy bone)
yellow: fat storage (Medullary cavity)
Myosin Vs. Actin
Myosin - Think filaments (A bands)
Actin - Thin filaments (I Bands)
Parasympathetic vs. Sympathetic
Parasympathetic - relaxes your body " Rest and digest
Sympathetic -Activates your body "Fight or flight"
Molecules tend to spread out, moving from ___ concentrations to ___ concentrations.
High, low
Note -*It is natural to molecules to move from high to low like a waterfall. This doesn't require any energy and is called Passive Transport.*
Name 3 types of cartilage
Hyaline cartilage, Elastic cartilage, and Fibrocartilage
Describe the Epiphysis, Diaphysis, Articular Cartilage, Periosteum, and Medulla cavity.
Epiphysis - ends of bone
Diaphysis - shaft of bone
Articular cartilage - cartilage covering the ends of bone (cushions)
Periosteum - membrane covering entire bone
Medulla - within the diaphysis, contains the yellow bone marrow.
During the Sliding Filament Theory, what allows the myosin heads to separate from the Actin Filaments?
ATP
*Serves as a cross bridge breaker*
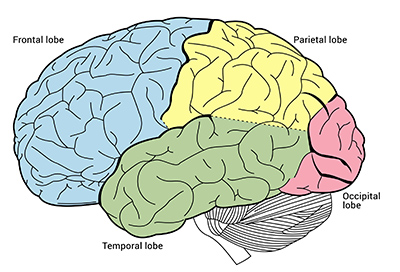
Name the different lobes of the brain?
Frontal lobe(personality) , Temporal lobe (auditory information and memory) , Parietal lobe (sensory perception), and Occipital lobe(sight).
What is the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis?
Exocytosis: secretion, things exit the cell
Endocytosis: things enter the cell
What are is the function of mast cells, macrophage, and fibroblasts in the connective tissue matrix?
Mast Cells - Prevent blood clots
Macrophage - consumers: consume debris and foreign objects
Fibroblasts - produce fibers.

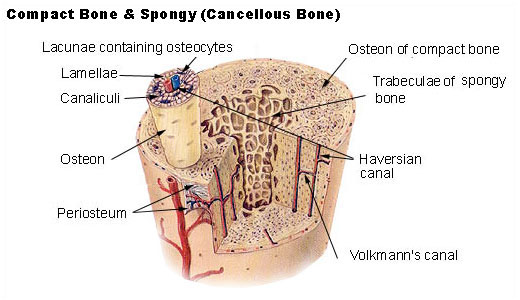
Describe the structure of the lamella, lacuna, and canaliculi
Lacuna are tiny enclosed chambers that house osteocytes.
Osteocytes then form rings called Lamella around the Haversian Canal.
Canaliculi connect the osteocytes.
What is the Neuromuscular junction?
A complex where a nerve and a muscle fiber come together together to communicate.
What are the functions of the Oligodendrocytes, Astrocytes, microglial, ependymal, and Schwann cells?
Oligodendrocytes- Make myelin sheath that provide insulation around the axons in the Central Nervous System (CNS)
Astrocytes- connects blood to neurons
Microglial- digests debris and kills bacteria (immune function)
Ependymal - forms membrane around the tissue and filters blood to make cerebrospinal fluid (protective cushion for structures)
Schwann cells - supply myelin for peripheral neurons (PNS)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/glialcellsillustration-5a94d585642dca00362568c4.jpg)
Cells are limited in size by ______ and _____.
the surface area (membrane), volume (insides) ratio
Note - *Increasing surface area can increase the cells efficiency moving substances.
What is the function of simple squamous cells?
Form: Flat and thin, single layer
Function: diffusion and filtration
*Found in air sacs of lungs, capillaries*
What are the types of joint articulations
Synanthropic - Immovable joints called sutures, skull
Amphiarthrotic- slightly movable, vertebrae
Diarthrotic- movable joint, (synovial joints) ex. knees, elbow, wrist, shoulder
During the sliding Filament theory, The sarcomere must shorten to contract a muscle. In order to to this, the Myosin heads bind to Actin and uses energy from ATP to create a "power stroke" and slide. As a regulation, what blocks actin when a muscle fiber is at rest?
Troponin and Tropomyosin
*However, the release of Calcium can override them*

Multiple Sclerosis damages myelin sheaths what affect does this have on neurons?
a neurons lose their myelin sheaths, the nerves are unable to send or receive signals. (signals travel slower)