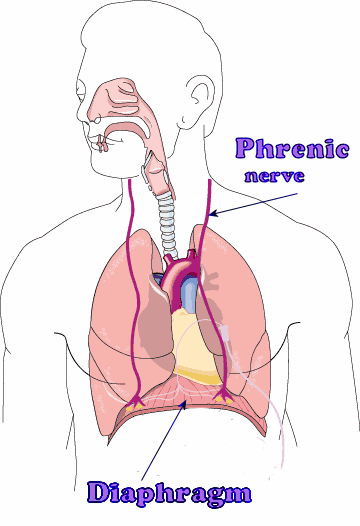
This nerve provides sensory innervation to the mediastinal pleura, pericardium, and its namesake organ
The phrenic nerve
The colon receives blood from two major arteries. Name them!
Superior and inferior mesenteric arteries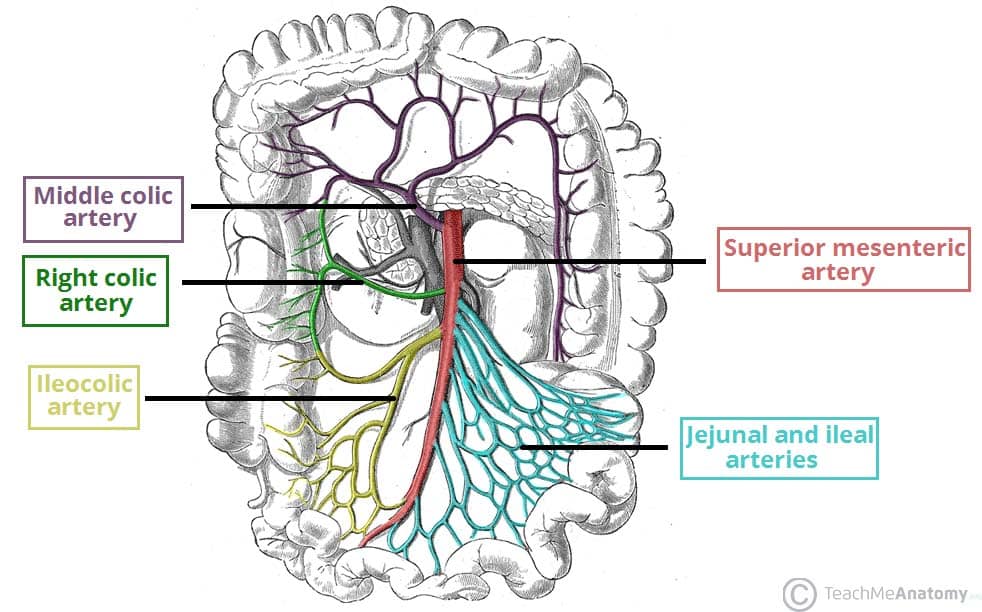
Generally, the right coronary artery will provide a branch to this conductor of the heart system.
SA Node (SA Branch of the RCA)
The visceral pleura is derived from which layer of the developmental tissue?
Splanchnic lateral plate mesoderm
Describe this general term for the branching connections of veins in the intestines. The ileum has more that are closer to the organ, while the jejunum has some with straight arteries.
Arcade arteries
This nerve branches off of the left vagus nerve after it loops by the ligamentum arteriosum - turns out it forgot to innervate something!
(Left) Recurrent laryngeal nerve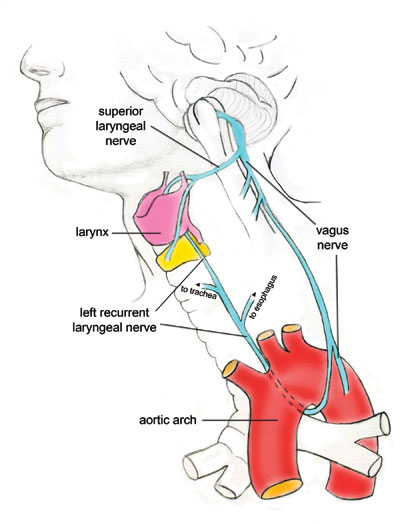 ]
]
The fundus of the gallbladder and the falciform ligament sandwich this lobe of the liver
The quadrate lobe
This muscular structure provides a connection between the inter-ventricular septum and the papillary muscles of the tricuspid valve
The moderator band 
Failure of proper partitioning of primordial pharynx and larynx by the tracheoesophageal septum leads to this condition.
Tracheoesophageal Fistula (TEF)
The internal thoracic artery splits into two arteries - the superior epigastric and the musculophrenic. What does the superior epigastric anastomose with and where?
Anastomoses with the deep circumflex iliac and the inferior epigastric at the abdominal wall. 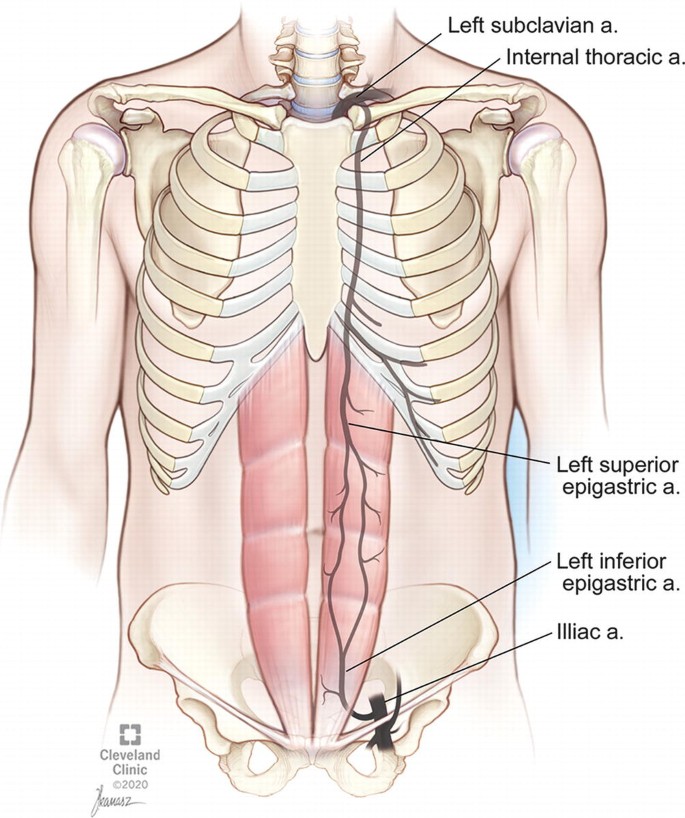
The acronym DATES indicates this structure that sits in the posterior mediastinum
The sympathetic trunk
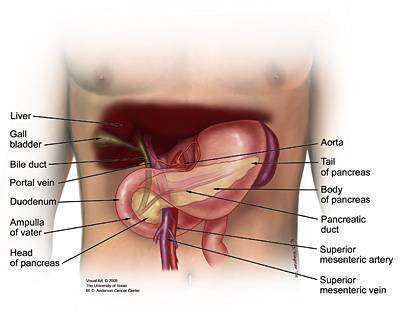
The head of this organ is cradled in the C-shape of the duodenum, and the rest sits inferior to it.
The pancreas :D
List the four valves of the heart, in the order of proper blood flow starting from the Right Atrium
Tricuspid --> Pulmonary (to lungs) ---> Bicuspid --> Aortic valve
Ventral mesentery tissue later forms the falciform ligament and this larger connective tissue in the gut region?
The greater omentum
These two arteries meet at the apex to spread love around their organ!
The anterior and posterior IV arteries of the heart
These nerves bring pain sensation to the abdominal organs - that explains why they hurt after crunches
Greater and lesser splanchnic nerves
Anterior and superior structures to this part of the duodenum include the SMA, SMV, and the head of the pancreas
The transverse (third part) of the duodenum
Let's stop going around the subject - what are the branches of the left and right coronary arteries?
RCA: Remember RPM!
- Right coronary, Posterior IV, Marginal Artery
LCA: Remember LAC!
- Left coronary, Circumflex, Anterior IV
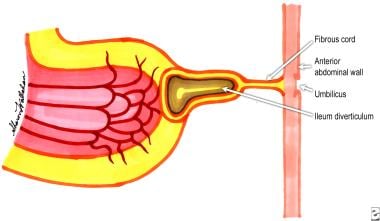
This condition is an outgrowth of the ilium in fetal development. If it forms a fistula with the umbilicus, provide a route of transportation for fecal matter to the umbilicus in rare cases.
Meckel's Diverticulum
This wandering artery provides an important connection in the colon. Name that artery and the two things it connects!
Marginal artery of Drummond - joins the SMA and IMA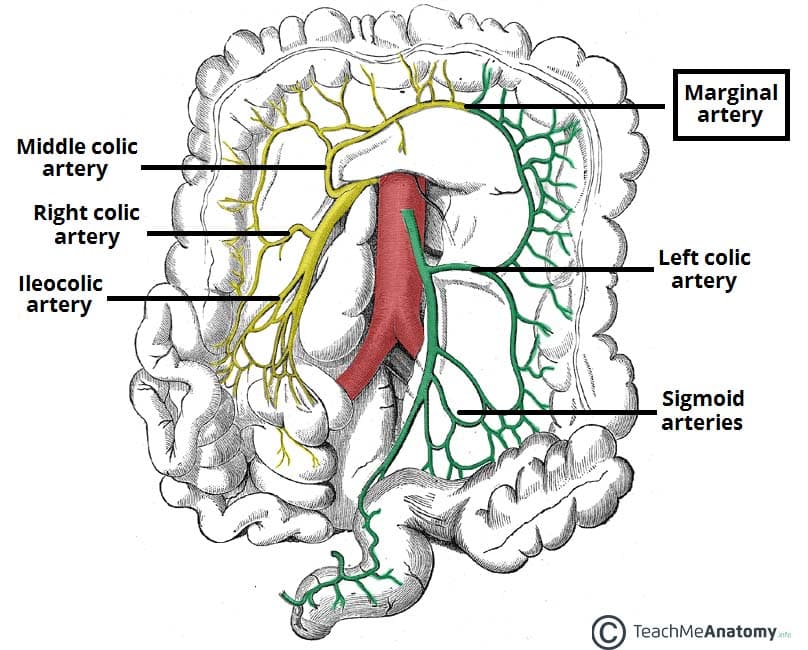
Diaphragmatic paralysis
Indirect hernias present laterally to the inferior epigastric vessels, while the direct hernias appear medially to them and through this structure.
The triangle of Hesselbech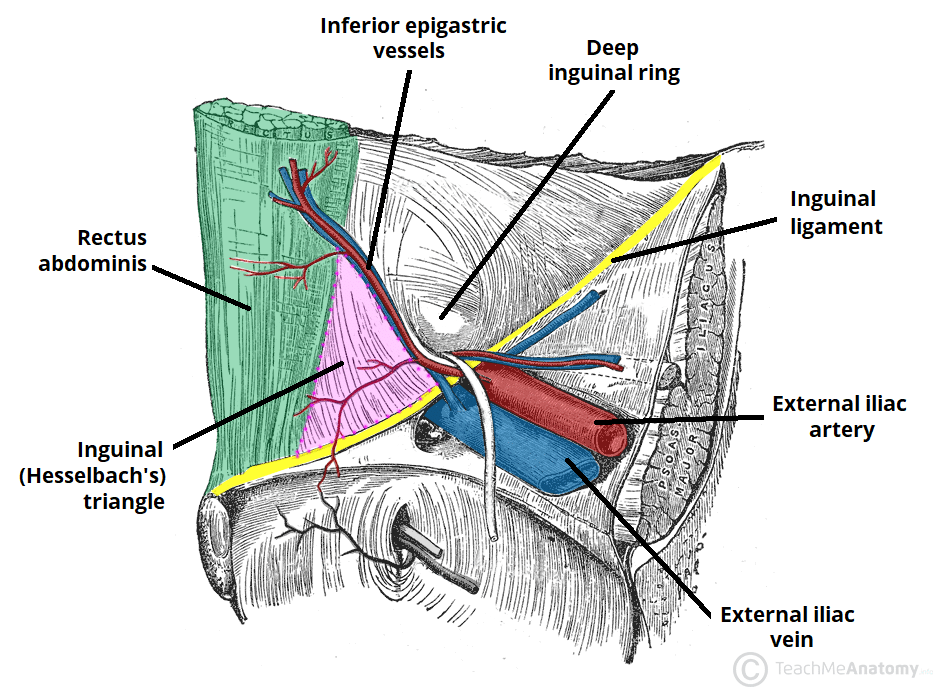
This passageway located posterior to the aorta and pulmonary trunk & anterior to the SVC allows for clamping of the aorta & pulmonary trunk
The transverse pericardial sinus
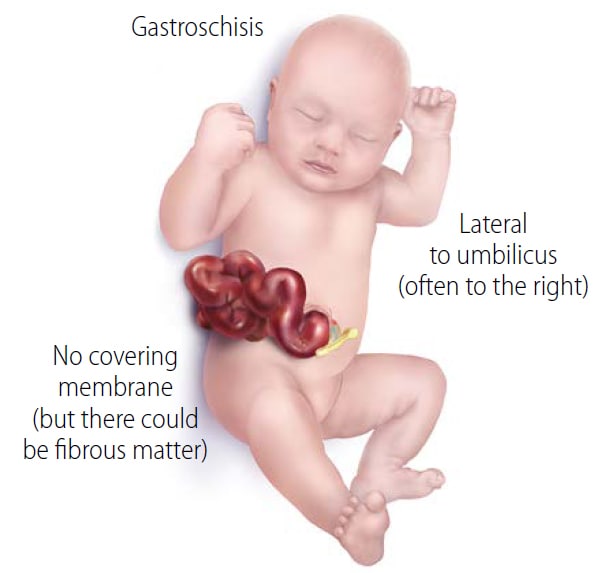
This condition comes from an improper closure of the anterior abdominal wall which allows for viscera to herniate outwards!
During dvlop, it comes from a failure of the bilateral somatic lateral plate mesoderm to properly fuse during formation of the body cavity.
Gastroschisis
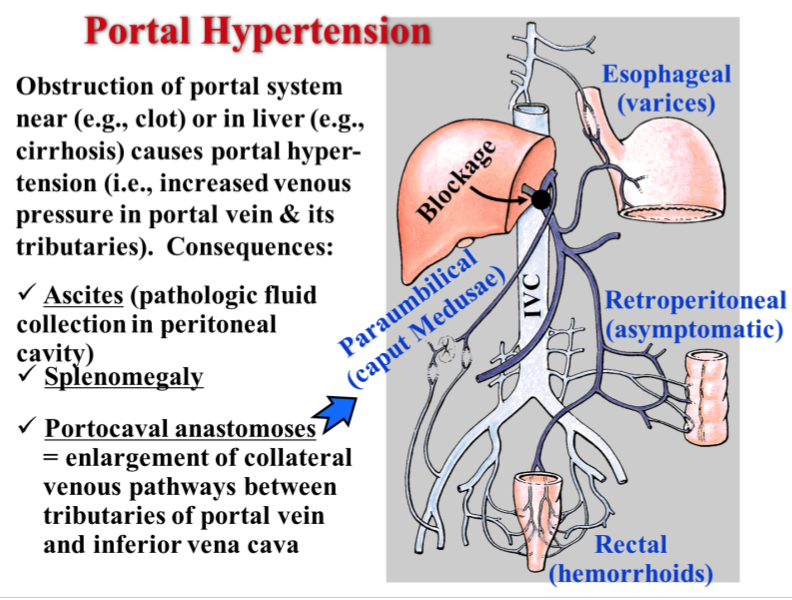
This Gorgonic condition occurs when an anastomosis forms between these two veins - name the condition, the portal, and the caval veins.
Paraumbilical veins (drains into the portal vein) @ Epigastric vein (common iliac) → caput medusae