This muscle is the primary muscle that opens and closes the eye and the primary target for crows feet treatment
photo credit: Anatomy of Facial Expression; Zarins 2019
What is the obicularis oculi?
This very important artery arises from the external carotid artery, loops around the mandible and ascends up the nose towards the eye; when injecting filler into the NLF it is critical to avoid occluding it
Photo credit: AMI Anatomy App, 2020
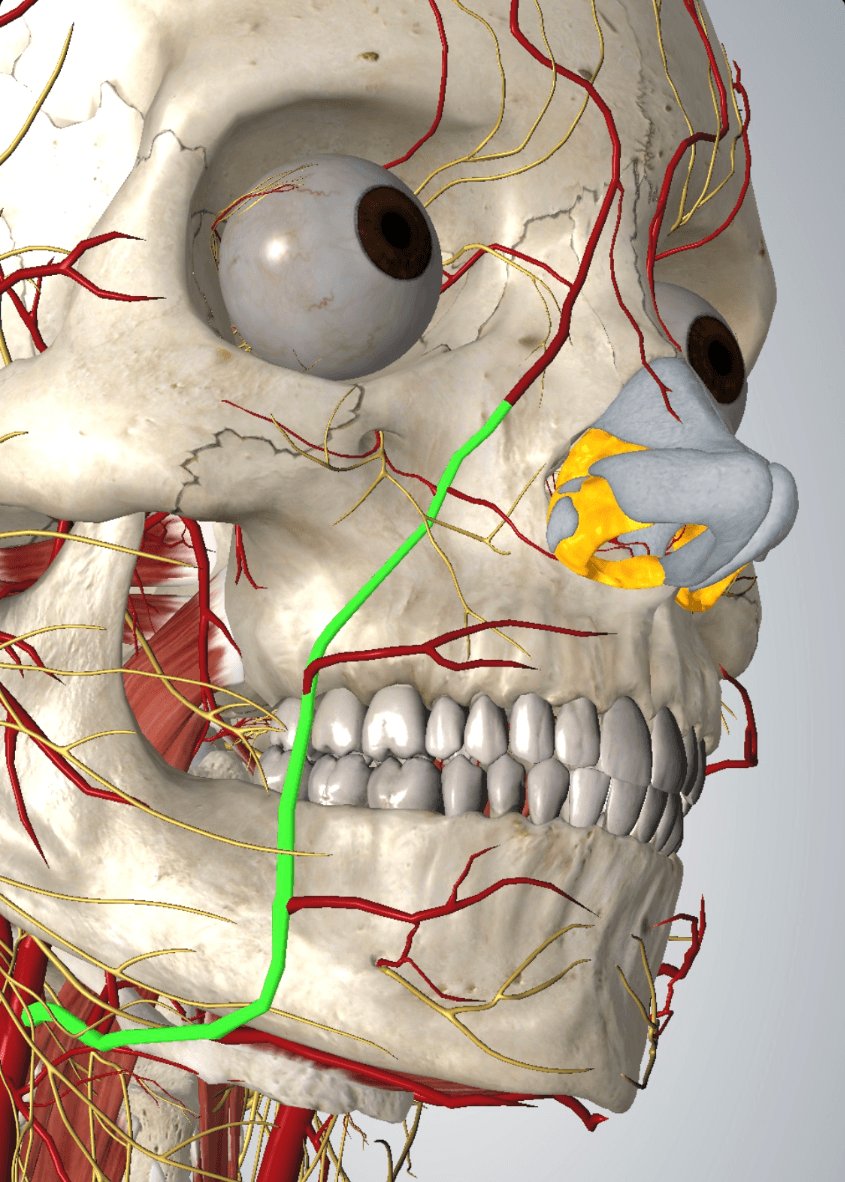
What is the facial artery?
This bone is often referred to as the forehead; it is the bone behind the frontalis muscle (Label 1)
photo credit: Anatomy of Facial Experession; Zarins 2019
What is the frontal bone?
game created by Loretta Nguyen Zanetti, APRN
Erasable Inc. Medical Spa
When using a straight needle for cheek injections at a 90 degree angle, this anatomical landmark will let you know you are in the right plane for placing product
What is the periosteum?
HA fillers are typically placed in one of these 3 planes (A, B, & D)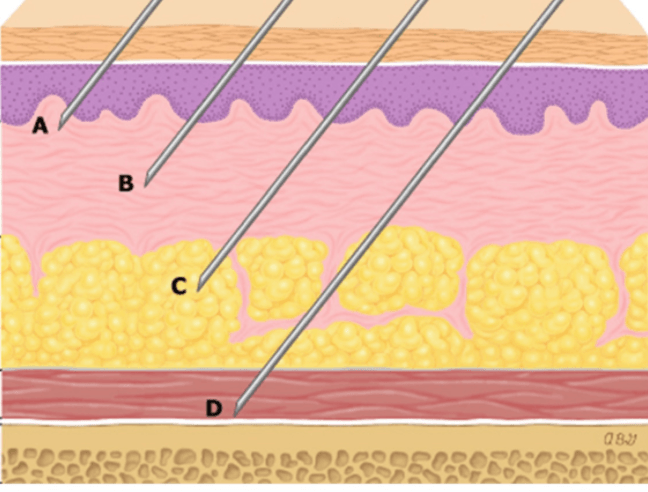
What is the papillary dermis, reticular dermis and supra periosteum?
These two muscles make up what is considered the glabella complex
What are the procerus and corrugator muscles?
This artery is a continuation of the facial artery; although this is a terminal branch, anastomosis with other vessels can lead to retrograde occlusion affecting the ophthalmic artery and leading to blindness
Photo credit: AMI Allergan App, 2020
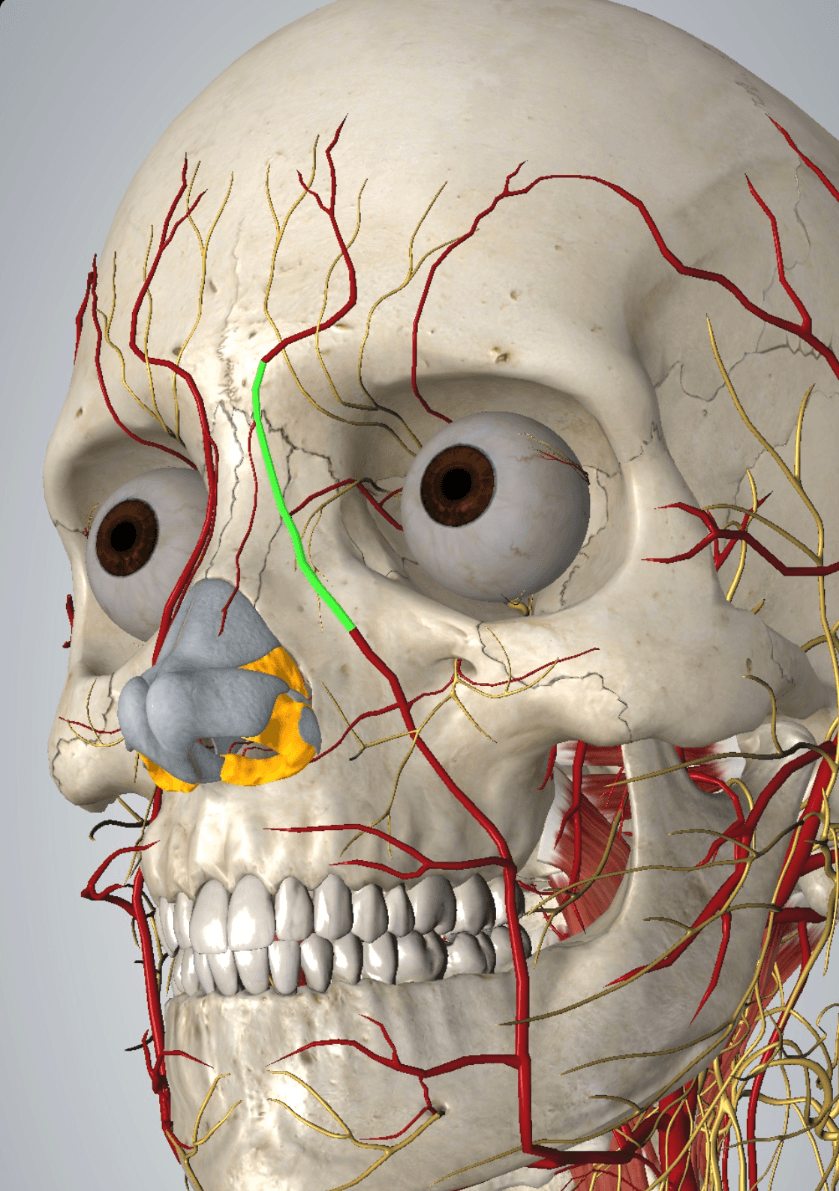
What is the angular artery?
This bone is the skeletal support for the cheeks and the site for injection to create contour and lift in the midface (Label 3)
photo credit: Anatomy of Facial Expression; Zarins 2019
What is the zygomatic bone?
The most lateral superior point of the obicularis oculi and the temporal fusion line is good landmark for this neurotoxin injection
What is the eyebrow lift?
It is important to understand the differences in facial structures for men and women when contouring jawlines with filler. The following photo is used to illustrate that females have a ______ gonial angle than men.
A. Sharper
B. Softer
C. More acute
Photo credit: Anatomy of Facial Expression, Zarins 2019
What is softer?
A look of p'eau d'orange in the chin can be softened by injecting 2-6 units of neurotoxin into this muscle
What is the mentalis muscle?
An injector who is filling lips needs to be very mindful of this artery that arises from the facial artery and ascends into the nose; it lies between the mucous membrane and obicularis oris
What is the superior labial artery?
This bone is called the "upper jaw" and supports the nose, upper palate and teeth (Label 4)
photo credit: Anatomy of Facial Expression; Zarins 2019
What is the maxilla?
This bony landmark is best palpated on the lateral forehead and is used as a landmark for eyebrow lift and for filling temporal hollows
photo credit: Anatomy of Facial Expression; Zarins 2019
What is the temporal fusion line?
As the face ages, these skeletal changes occur making the face look older.
The 3 photos below provide hints to these changes.
Describe at least one of these changes.
Bonus points for describing two of these changes.
Extra bonus points for naming all 3 changes depicted in these photos.
Photo credit: Anatomy of Facial Expressions, Zarins 2020
What is:
1. Elongation of the jaw and mandible and maxilla increasing the length of the face?
2. Enlargement of the eye sockets?
3. Widening and elongation of the nasal cavities
These two sets of muscles of the lower face can cause a look of Bell's palsy if injected incorrectly or unevenly, injection points can be targeted in one of these muscles to soften marionette lines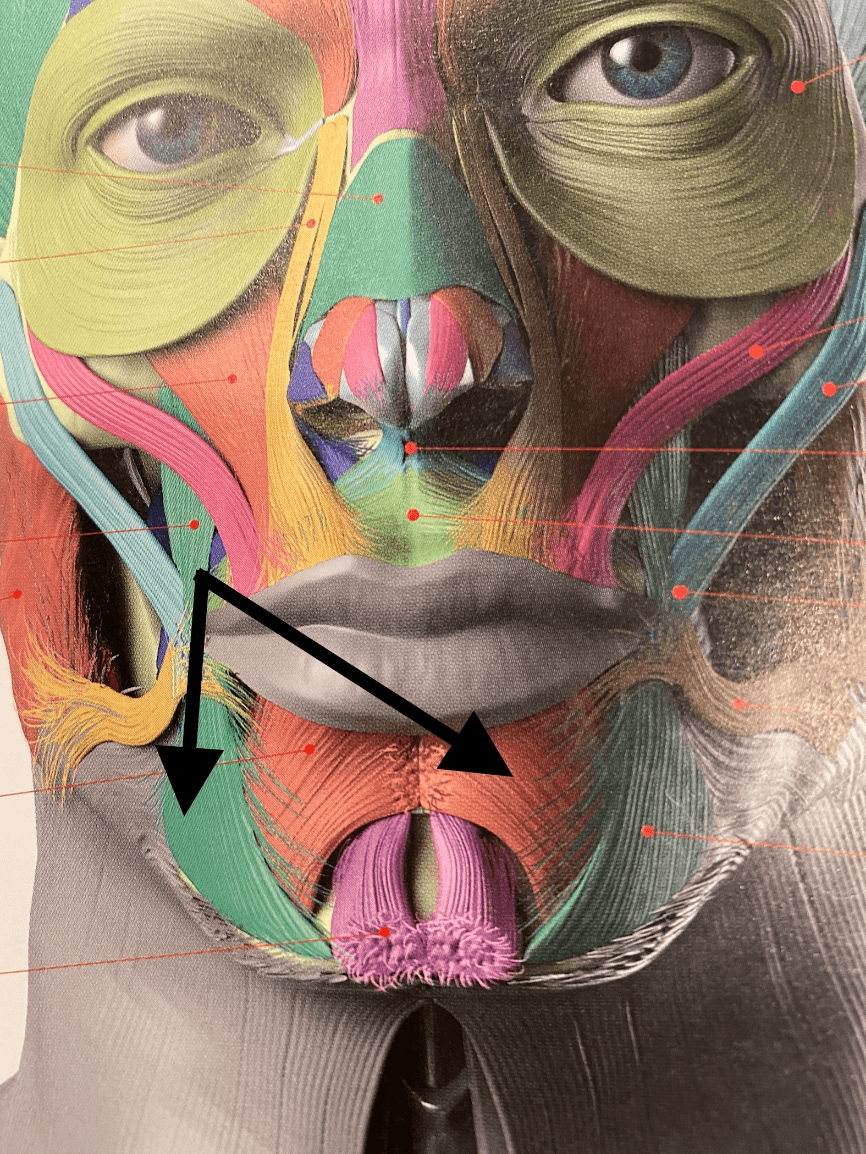
What is the depressor anguli oris and the depressor labii inferioris (DAO and DLI)
This artery arises from the carotid and is a major artery of the head, it can be palpated at a superficial point near the tragus of the ear just above the zygomatic arch; it should be palpated and avoided prior to injecting hollows of the same name
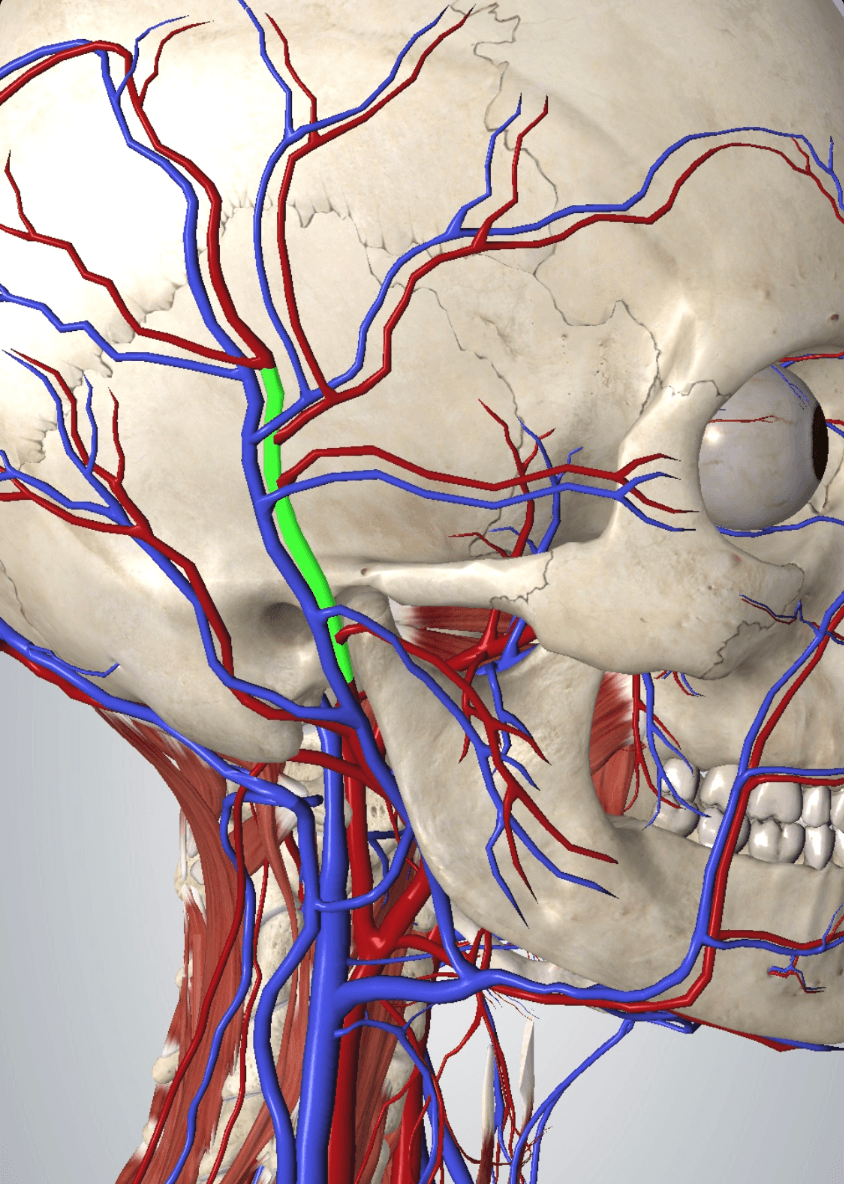 Photo credit: AMI Allergan App, 2020
Photo credit: AMI Allergan App, 2020
What is the superficial temporal artery?
This bone is on the lateral side of the head, filler in this area may cause pain while chewing, a common side effect when filling this "hollow"
photo credit: Anatomy of Facial Expression; Zarins 2019
What is the temporal bone?
The antigonial notch found in the mandible is an important landmark to palpate prior to many aesthetic treatments including filler and neck treatments. What important vessels are anterior to this anatomical landmark?
What nerve is found close to this area?
What is the facial artery and vein?
What is the marginal mandibular nerve?
These are the only FDA approved neurotoxins in the US as of July 2020
What is Botox®, Dysport®, Jeuveau®, and Xeomin®
This muscle aids in the control of the upper lip and is a common injection point with neurotoxin to treat gummy smiles (Label L)
photo credit: Anatomy of Facial Expression; Zarins 2019
What is the LLSAN or levator labii superiorus alequai nasi?
One of the two arteries that could be punctured during neurotoxin placement in the corrugators that could cause bruising
Bonus points if you can name both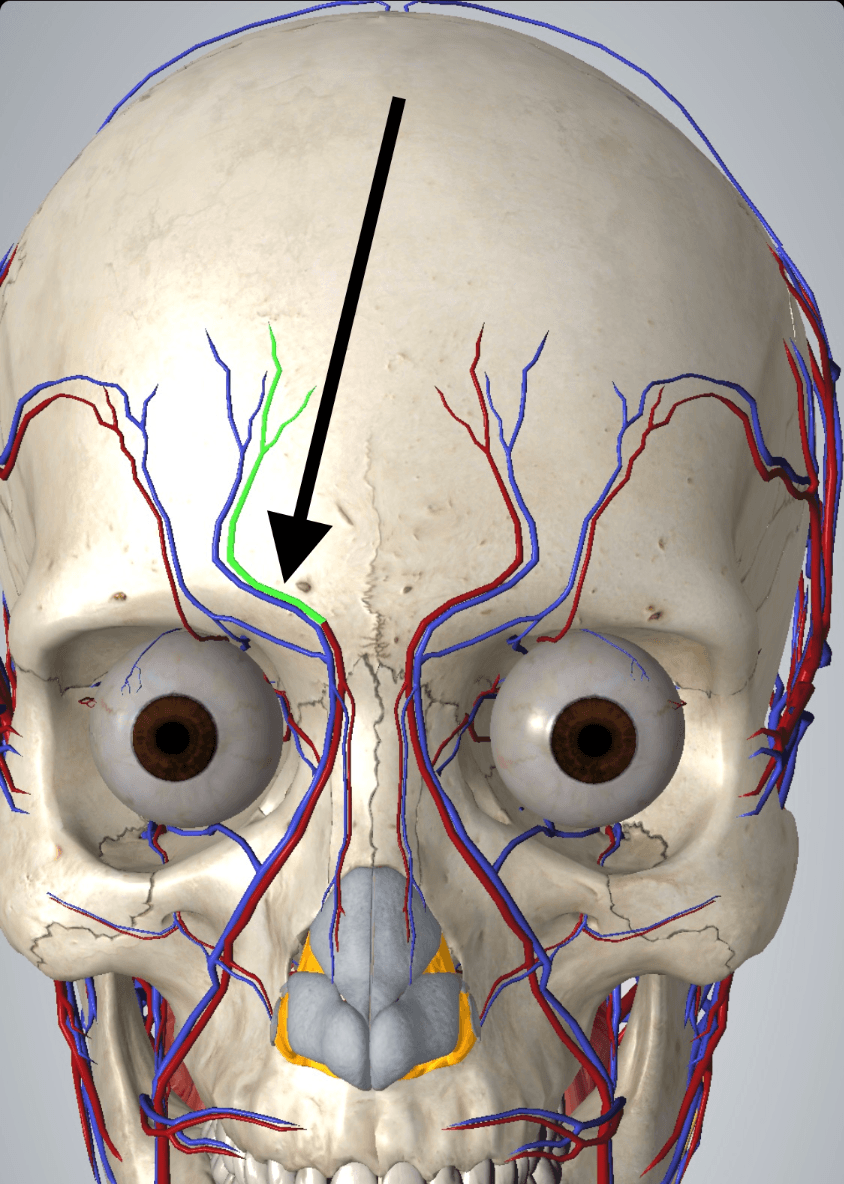
What is the supratrochlear artery and the supraorbital artery?
This bone is located in the back of the head and is a common site for injections for chronic migraines
What is the occipital bone?
This dangerous intersection of critical nerves and vessels should be palpated, marked and avoided while filling tear troughs
Photo credit: AMI Allergan App, 2020
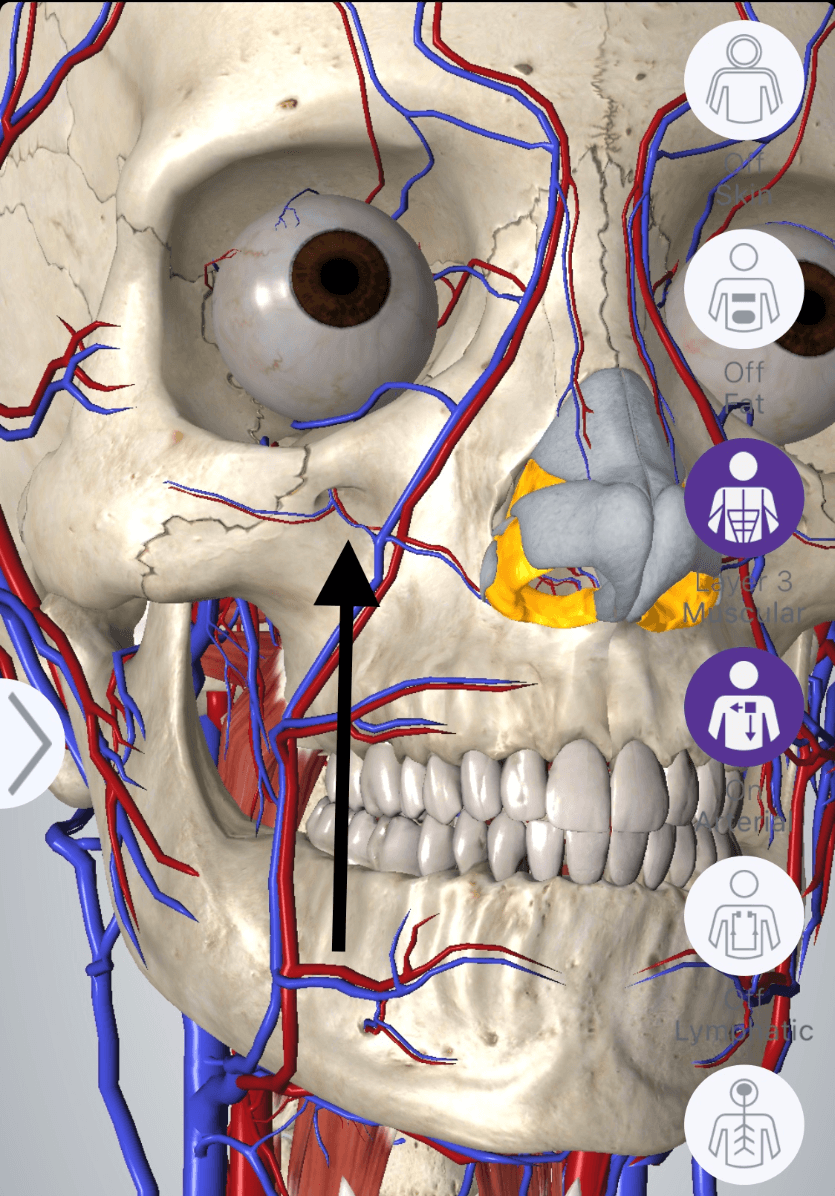
What is the infraorbital foramen?
Levido reticularis is the medical term; in lay terms, the skin can be described this way when there is an occlusion
What is grey, mottled, with lace-like appearance; this tissue will likely have slow capillary refill
game created by Loretta Nguyen Zanetti, APRN
Erasable Inc. Medical Spa