Which division of the ANS increases the actions of nerves they innervate?
Sympathetic division
Skeletal muscles and tendons have what type of receptors?
Proprioceptors
What are the largest but least numerous of all papillae on the tongue?
Circumvallate papillae
What is a reflex arc that doesn't need the brain in order to work?
Autonomic reflex
What are the two neurotransmitters used by the ANS?
Acetylcholine and sometimes norepinephrine
What is a mechanoreceptor located within the skeletal muscles that responds to stretching?
Muscle spindle
What are the bones that protect the olfactory bulbs?
Cribriform plates
What is the term for determining where a stimulus occurs?
Modality
How many neurons does the SMNS use? What about the ANS?
SMNS uses one
ANS uses two
What can the Ruffini's end organs sense?
Pressure and stretching
Where are simple receptors found?
All over your body
What is the difference between somatic receptors and visceral receptors?
Visceral receptors - sensory receptors in the internal organs
Somatic receptors - sensory receptors in the skin, muscles, and tendons
Explain where the nerves exit the spinal cord for the sympathetic vs. parasympathetic division of the ANS?
Sympathetic division - the bottom 1/3 of the spinal cord
Parasympathetic division - from the brain or the lower regions of the spinal cord
What is the difference between lacrimal canaliculi and puncta?
Lacrimal canaliculi - ducts in which tears get drained into the nasal ducts
Puncta - openings of the lacrimal canaliculi
What makes a substances smellable?
The substance must be airborne, and must be able to reach the nose hairs
How does the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the ANS affect the digestive system?
Sympathetic - slows the activity in the digestive system
Parasympathetic - increases the secretion and movements of the digestive system
Explain the differences in neuron structure between the SMNS and the ANS.
In the SMNS, the neuron axons are always myelinated.
In the ANS, the neurons may be myelinated or unmyelinated.
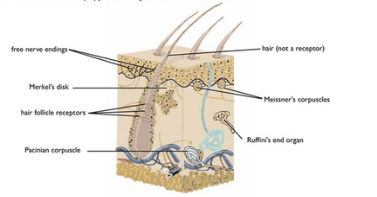
On the diagram of cutaneous receptors, label: free nerve endings, Merkel's disk, hair follicle receptors, Pacinian corpuscle, Messner's corpuscles, and Ruffini's end organ
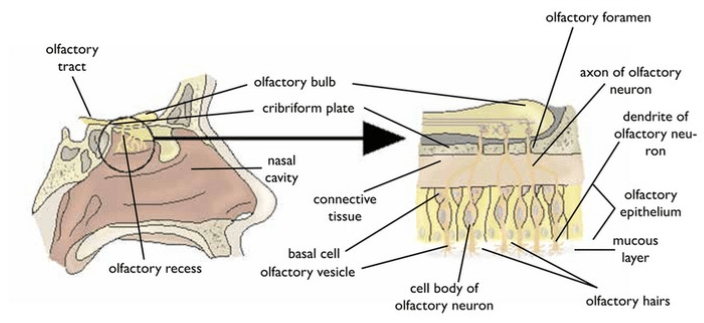
On the nose diagram, label: olfactory bulb, cribriform plate, olfactory vesicle, olfactory foramen, olfactory epithelium, mucous layer, olfactory hairs
How does the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the ANS affect the bladder?
Sympathetic - contracts the bladder
Parasympathetic - relaxes it