Draw out & identify the planes of the body.
1. Transverse
2. Frontal
3. Sagittal

List the steps of a muscle contraction
A lecture by TA Courtney
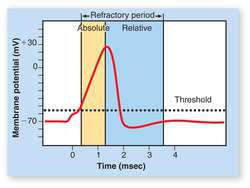
What are the stages of an action potential? Draw out the 'curve' and identify the different points at which channels open and close. Also, identify refractory period(s).
Graded potentials are summed on the dendrites and soma (EPSPs and IPSPs)
Sum of graded potentials exceeds threshold
Na+ channels open and Na+ rushes in
Na+ channels close, K+ channels open
K+ rushes out
K+ rushes out so much so that the cell hyperpolarizes
Repolarization back to equilibrium/resting potential
Draw out anatomy of the ear; what sense are these cells involved in (explain)
Vestibular system of the inner ear → responsible for sensation of balance/motion
Use of hair cells
Mechanoreceptors
Respond to touch, pressure, gravity, stretching
Draw out a:
- positive feedback loop
- negative feedback loop
What is the main characteristic difference between these feedback loops?
What can pass through a lipid membrane?
Small, nonpolar
Non-charged molecule
Let's talk about polarity ...
List and describe the different types of tissue
Simple Squamous
- All sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
- Allows materials to pass through via diffusion and filtration, and secretes lubricating substance
Stratified Squamous
- Lines the esophagus, mouth, and vagina
- Protect against abrasion
Simple Columnar
- Bronchi, uterine tubes, digestive tract, bladder
- Absorbs; also secretes mucous & enzymes
Stratified Columnar
- Male urethra and gland ducts
- Secrete and protect
Stratified Cuboidal
- Sweat, salivary glands, and mammary glands
- Protective tissue
Make a table of the glial cells and list their functions.
Astrocytes: Maintain the blood-brain barrier*
Microglial cells: Phagocytic and serve as the rubbish removal cells of the CNS
Ependymal cells: Make CSF (which cushions the brain and neural tissue)
Oligodendrocytes: Myelinate nerve axons in CNS
Schwann cells: Myelinate axons in the PNS
*What can cross the blood brain barrier? Water, oxygen, and lipid soluble molecules
Explain how the lateral corticospinal tract works if you are contracting a muscle on the right side of the body.
Contract muscle on the right side
2. Signal starts in primary motor cortex on left side of the body- left precentral gyrus (cell body of upper motor neuron)
3. Axon travels through brain and crosses medulla
4. Enters the right lateral corticospinal tract
A neurotoxin that destroys all troponin in a cell is circulating in the air- how will your muscles be affected? What would happen if this neurotoxin destroyed both troponin and tropomyosin?
Just troponin: you would die from your muscles being relaxed
Both troponin and tropomyosin: you would die from your muscles being contracted
What are the different kinds of transport across a cell membrane?
Passive transport:
Simple diffusion
High to low concentration
Osmosis
Movement of water molecules dependent on solute concentrations
Facilitated diffusion:
Movement of large/charged molecules via membrane proteins
Active transport:
Requires energy in the form of ATP produced by mitochondria
Ex: sodium-potassium pump, exocytosis (pushing material outside cell membrane with help of secretory vesicles), endocytosis(swallowing particles through cell membrane)
_____ is to bone degradation as _____ is to bone creation
osteoclasts; osteoblasts
Draw out a diagram separating the different parts of the nervous system. Include what they control, and go into depth for the sympathetic/parasympathetic nervous system in regard to the physiological response to when they are active.
List the different parts of the brain and identify their function.
Diencephalon: thalamus (relay center; directs signals from one part of CNS to another), hypothalamus (main visceral control center of the body:maintains homeostasis, controls autonomic nervous system, regulates body temperature, initiates physical responses to emotions, controls endocrine function), epithalamus (contains pineal gland, involved in regulating sleep/waking cycles)
Midbrain:contains multiple nerve tracts and processing nuclei
Pons: connects the spinal cord with more superior brain structures
Medulla: in the brainstem; important relay center for sensory and motor information
Cerebrum:contains centers for conscious thought and processing
Cerebellum: communicates with motor centers in the cerebrum through pontine fibers
Brainstem: involved in basic life functions
Spinothalamic and corticospinal tracts...
Rewatch Jay's previous 2 review sessions (located in 'external resources' on Moodle)
What are the three kinds of bonds? Describe them.
1. Hydrogen bonds: hydrogen bound to an electronegative atom such as nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine (weak)
2. Ionic bonds: unequal sharing of electrons
3. Covalent bonds: equal sharing of electrons (strong)
Identify the different types of cartilage and their functions
Hyaline:
Resists compressive force
Location: Ends of long bones in joint cavities, costal cartilages of ribs
Fibrocartilage:
Absorbs compressive shock
Location: Intervertebral disks, pubic symphysis
Elastic:
Maintains shape of structure while allowing great flexibility
Location: External ear
Differentiate graded potential VS action potential
Graded potential:
- Dendrites or cell body
- Travel short distances
- Vary in size and polarity
- Due to opening of ligand (chemically) gated ion channels
- Sum to determine effect
- Last as long as stimulus is present
Action Potentials:
- Axon
- Travel long distances (the distance of an axon)
- Always the same size and depolarizing
- Due to opening of voltage gated ion channels
- Do not sum: all or none
- Last the same amount of time
Please describe the anatomy of the eye and the pathway of light as it hits the eye.
Cornea = surface layer of the eye → focuses light, allows for penetration of the eye
lens= changes shape to focus light reflecting from near or distant objects
Retina = contains the photoreceptors (lights final destination)
Rods = vision at low light levels
cones= vision at high light levels
Take light, convert into graded membrane potentials
Muscarinic VS Nicotinic
AGAIN: *rewatch the 'new material' lectures*
Answer the following using anatomical terminology:
The nose is _______ to the pelvis
The spine is ______ to the skin
The fifth digit in your hand (little/pinky finger) is _______ to the thumb
1. Superior
2. Deep
3. Medial
What is melanin?
Pigment produced by melanocytes- found in the skin
Natural protective against UV rays
Afferent VS Efferent
What comes before the other, talk to the people around you about how they incorporate into a nervous system response to stimuli
Afferent = in
Efferent = out
White Matter VS Gray Matter- what are they composed of?
ALSO: Draw the anatomy of a spinal nerve
White Matter: axons
Gray Matter: cell bodies and dendrites
What should I do if I came into individual exam reviews?
What should I do if I did not come into individual exam reviews?
I will go over my notes!
I will also/ I will watch Jay's recap videos going over exam statistics from when grades were released.