What heart chambers are associated with pulmonary circulation?
What is..
-Right ventricle
-Left Atrium
-Left Ventricle
How many blood types are there?
What is 4
What is the three major types of blood vessels?
What is..
1. Arteries
2. Veins
3. Capillaries
Three types of Tachycardia
What is
-Supraventricular
-Ventricular
-Sinus Tachycardia

What is..
1. Tricuspid (right AV) valve
2. Aortic semilunar valve
3. Bicuspid (left AV) valve
4. Pulmonary semilunar valve
What are the different layers of the Heart wall
What is..
-Epicardium
-Myocardium
-Endocardium
Who can B+ give blood to?
What is..
B+ , AB+
Function of Purkinje fibers
What is carry the impulse to the heart apex and ventricular walls
Cardiac Output
What is the volume of blood being pumped by the heart (either by the left or right ventricle)
What type of receptor is the carotid sinus?
What is..
-Baroreceptors
What is an abnormally rapid heart rate?
What is tachycardia
Who can A+ give blood to?
What is..
A+ , AB+
Rank lymphocytes in order of most abundant to least abundant
What is..
-Neutrophils
-Lymphocytes
-monocytes
-Eosinophils
-Basophils
Blood Vessels
What is a closed system of vessels that carry blood
What type of capillary is found in the brain?
What is..
-Continous
With metabolic waste being removed, what source of blood is being nourished?
What is..
-Rich oxygenated blood
Who can AB+ give blood to?
What is..
AB+ only
What function is known for preventing its own loss by initiating clot formation thru plasma proteins & platelets
What is protection
The branches of the aorta and the aortic arch
What is..
Aorta
brachiocephalic artery (divides into the right common carotid artery and the right subclavian artery)
the left common carotid artery
the left subclavian artery
Aortic Arch
brachiocephalic trunk
left common carotid artery
left subclavian artery
Where does the exchange of gases and nutrients occur?
What is..
Gas exchange takes place in the millions of alveoli in the lungs and the capillaries.
Name the different parts of an ECG(EKG) and their interpretations
What is..
-P wave: corresponds to atrial depolarization
-QRS complex: corresponds to ventricular depolarization
-T wave: corresponds to ventricular repolarization
-Atrial repolarization record is masked by the larger QRS complex
(Answer is correct if you answered with majority question)
Who can O- NOT donate Blood to?
What is..
False, O- can donate to all blood types
(the answer is correct if group or individual identified that the statement is untrue entirely & can explain why)
What Leukocytes are classified as Granulocytes
What is..
-Eosinophils
-Neutrophils
-Basophils
Identify the two sounds of the heart & their functions
What is..
(lub-dup pause lub- dup) are associated with the closing of heart valves
First Sound: Occurs as AV valves close, signifies the beginning of ventricular blood pressure rising about atrial blood pressure
Second Sound: Occurs when SL valves snap shut, the beginning of ventricular diastole
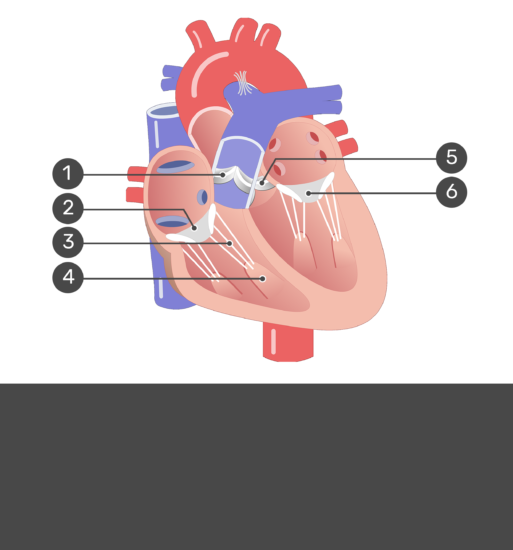
What is..
1. Pulmonary semilunar valve
2. Right AV valve
3. Chordae tendineae
4. Papillary muscle
5. Aortic semilunar valve
6. Left AV valve