Name four organelles that exist in a cell
Ribosomes ; Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough/Smooth) ; Mitochondria ; Chloroplasts ; Golgi apparatus ; lysosomes ; peroxisomes ; vacuoles ;
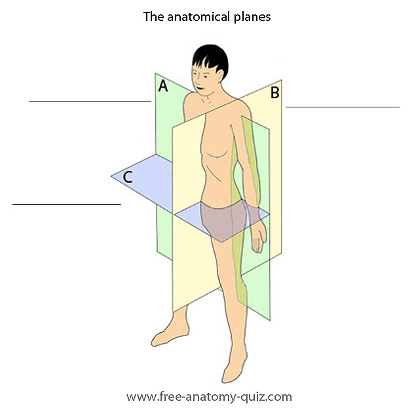 What are the names for each anatomical plane shown in the image (A, B, and C)?
What are the names for each anatomical plane shown in the image (A, B, and C)?
- Sagittal plane (divides body into right and left portions) (specifically midsagittal here)
- Frontal/coronal plane (divides body into anterior and posterior portions)
- Transverse (divides body into superior and inferior portions)
The existence of blood vessels and plasma membranes are examples of which of the functions of life?
Maintaining boundaries
What plasma membranes composed of? Explain the components of their formation in terms of their polarity.
Plasma membranes are composed of a phospholipid bilayer. They contain a hydrophilic (polar) head and a hydrophobic (non polar) tail.
What are the appropriate ranges for systolic and diastolic pressures?
Systolic - 120-139 mmHg
Diastolic - 80-89 mmHg
What are the functions of a ribosome?
Protein synthesis
What sub-cavities does the dorsal cavity contain? What sub-cavities does the ventral cavity contain?
Dorsal Cavity: cranial cavity and spinal cavity
Ventral Cavity: Thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
Define metabolism as a function of life. What is metabolism and how does it help the body to maintain homeostasis?
- All chemical reactions taking place in our cells. Anabolism (synthesis)/Catabolism (breaking down). Anabolism – the body makes larger molecule from smaller one (releases energy). Ex: Glucose to glycogen or amino acids to polypeptides (anabolic reaction). Catabolism – the breaking down of larger molecules to a smaller one. Ex: glycogen to glucose or protein to amino acid (catabolic reaction).
What is the difference between active transport and passive transport across a membrane. Give examples of both.
Active transport: requires energy (ATP). Examples include endocytosis and exocytosis
Passive transport: does not require energy. Examples include Diffusion, Osmosis, Facilitated diffusion.
Give an example of a positive feedback loop.
Tons of different answers. 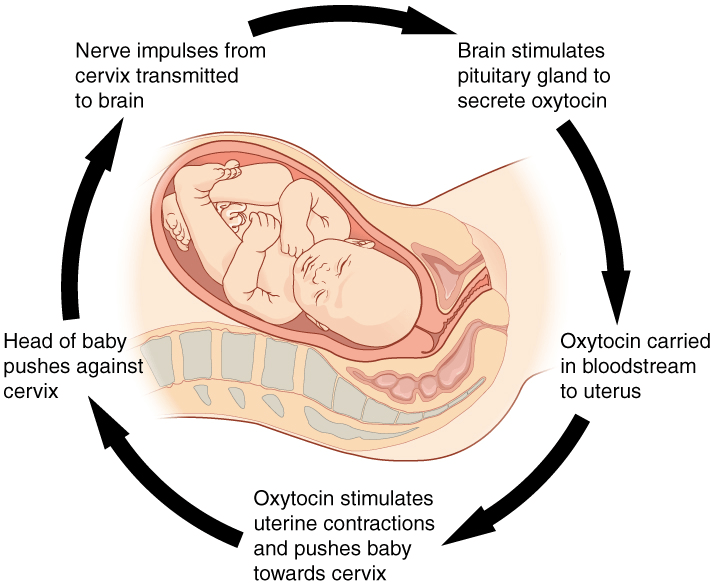
What organelle is used to process and package proteins and lipids?
Golgi apparatus
In the anatomically "correct" position, the eyes are _____ to the ears.
Medial
The kidney's getting rid of nitrogenous waste/nutrients is an example of what function of life?
Excretion
Isotonic - the same concentration inside/outside the cell
Hypertonic - higher solute concentration outside of the cell
Hypotonic - higher solute concentration inside of the cell
Give two examples of a serous membrane.
Pericardium, pleura, peritoneum, vaginal tunics
Smooth ER: (phospholipid synthesis; cholesterol/steroid hormones; detoxify chemicals [drugs, alcohol, etc]; contains enzyme that can convert glycogen to glucose; can store/release calcium)
Rough ER: (modification of proteins to activate into tertiary structure)
In the anatomically "correct" position, the hand is ______ to the shoulder
Distal
What are the 5 requirements for Human Life? Briefly describe each one in a few words.
Nutrients
- Nutrients assist in the production of ATP. This is done by the cellular respiration process (this occurs in mitochondria).
Oxygen
- In cellular respiration process, oxygen is the ultimate electron accelerator.
Water
- To stay hydrated. 60% of body is water.
Normal body temperature
- Organs need a certain temperature to function. Certain temperature is required to catalyze chemical reactions. Needed for maintenance of homeostasis.
Appropriate atmospheric pressure
760 mmHg is atmospheric pressure. Very key for maintaining respiration.
It is a pump that exists in eukaryotic cells. This pump allows 3 sodium ions to leave the cell and 2 potassium ions to enter the cell. These ions move against their concentration gradients and keep a high concentration of sodium ions outside the cell and a low concentration of potassium ions inside the cell. This helps with a variety of cellular functions.
What organ system maintains fluid levels within the body?
Lymphatic system
The inner membrane of the mitochondria contains folds that are called what?
Bonus: What are the functions of these folds
Crista (cristae) are the folds in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. They increase the surface area of the within the mitochondria for chemical reactions to take place
The popliteus region refers to what part of the body?
Back of the knee (popliteal)
When referencing homeostasis, there are 4 separate components. What are these 4 components? Give an example of the body maintaining homeostasis using these 4 components.
Stimulus
Receptor/sensor
Control center
Effector
There are tons and tons of examples, I like to remember the homeostatic response of exercise.
What are the three types of endocytosis? List and define each.
Phagocytosis - the cell engulfs a large molecule
Pinocytosis - the cell takes in a small molecule in fluid
Receptor-mediated endocytosis - a very selective method of endocytosis a ligand that has external receptors binding to it. Coated vesicle carries the external ligand.
Chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism.
What body region refers to the forearm area in the anatomically "correct" position?
The antebrachium region
What is standard atmospheric pressure (numerical value)? Why is it essential to have an appropriate atmospheric pressure?
Standard atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg. It is essential to maintaining gases in solution and continuing respiration in the body.
Explain facilitated diffusion. What is the difference between carrier and channel proteins.
Facilitated diffusion of
substances crossing the cell
(plasma) membrane takes
place with the help of
proteins such as channel
proteins and carrier
proteins. Channel proteins
are less selective than
carrier proteins, and usually
mildly discriminate between
their cargo based on size and
charge.
(b)Carrier proteins are more
selective, often only allowing
one particular type of
molecule to cross.