Stand in the correct anatomical position.
What is flat-footed, facing forward, arms with palms forward.
Name the four types of tissues.
What are epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous.
Name the three layers of the integumentary system in order from superficial to deep.
What is the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layer.
What are the main components of compact bone tissue?
What are osteons.
Name 2 of the 4 functions of muscle tissue
Movement, Posture, Body heat, as smooth muscle in other systems
Simple Epithelial tissue has how many layers?
what is one?
Explain what causes skin color.
What is: melanin is made by melanocytes, and there are different types of melanin that have different pigments to show different skin colors.
Name two of the 3 types of bone tissue cells and describe their function.
What are: osteoblasts build bone tissue, osteoclasts break down bone tissue, and osteocytes are mature bone cells.
Give an example of a striated voluntary muscle
any skeletal muscle
What is another name for the backside?
What is dorsal.
Connective tissue is comprised of these 3 parts
What are protein fibers, specialized cells, and ground substance.
Describe three functions of the integumentary system.
What is: thermoregulation, blood reservoir, protection, cutaneous sensations, excretion and absorption, and synthesis of vitamin D.
Describe three functions of the skeletal system.
What is: support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell production, and triglyceride storage.
Place the following muscle structures in order from smallest to largest:
myofilament, Fascicle, myofiber, muscle belly
myofilament, myofiber, fascicle, muscle belly
The plane shown in the diagram
What is sagittal? (midsagittal)
Two structural features that would allow me to identify cardiac tissue from smooth muscle tissue
branching, intercalated discs, striations
Name the types of tissues that make up each layer of the integumentary system.
What is: the epidermis is epithelial tissue, the dermis is connective tissue, and the subcutaneous layer is adipose tissue (connective tissue.)
The structure pictured and its purpose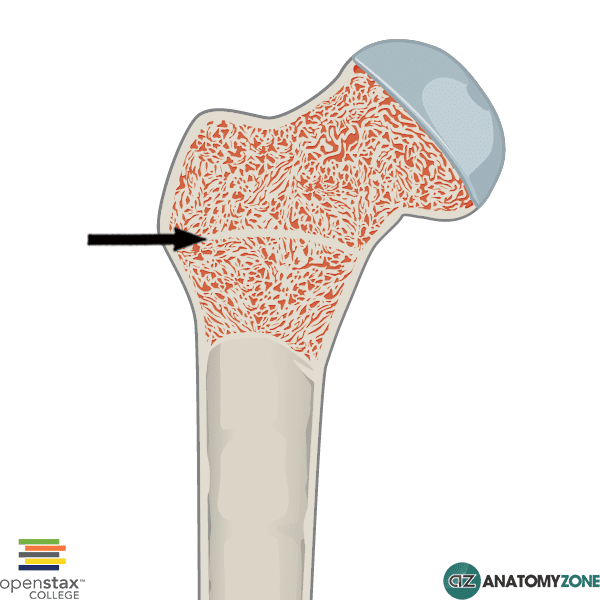
Epiphyseal Plate--for growth
Explain the difference between the origin and insertion of a muscle.
What is the origin is the attachment site for the stationary bone and the insertion is the attachment site on the movable bone.
Name the 2 body systems that are responsible for initiating response to the environment.
What are endocrine and nervous system?
Name 4 of the connective tissues that we discussed.
What is loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, cartilage, bone tissue, and liquid connective tissue. (others acceptable)
What is keratinization and what is its importance?
What is: keratinization is the process where the protein keratin is laid down in epidermal cells. It is important because it is used for protection for skin cells.
Describe the process of intramembranous ossification
What is osteoblasts form from mesenchymal cells. They cluster in ossification centers laying collagen. Collagen gains minerals and hardens. Spongy bone forms along the center and compact forms along the sides of the bone near the osteoblasts.
Describe in detail how muscle contraction occurs.
What is actin and myosin connect and form crossbridges when calcium is released from a muscle fiber. The actin and myosin slide past each other, which decreases the length of the sarcomere and of the entire muscle.