This island is just south of Greece, and was the home of the ancient Minoan civilzation.
Crete
This type of gathering place is a fortified area on top of a hill, the most famous being the Parthenon in Athens.
Acropolis
This Persian monarch took over the Ionian Greek city-states and squashed an unsuccessful revolt by the Ionian cities.
Darius
The 12 chief gods and goddesses in Greek religion reside here.
Mount Olympus
This ruler was only 20 when he became the king of Macedonia.
Alexander the Great
This group is remembered as the first Greek State and were led by Agamemnon in the sacking of the city of Troy.
The Mycenaeans
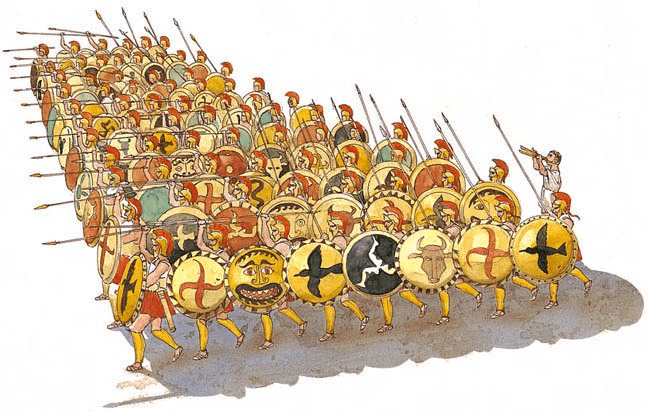
This military formation was the most-common in ancient Greece.
Phalanx
The Greeks, led by the Athenians, created this defensive alliance in 478 B.C.E.
The Delian League
These support structures are seen in ancient Greek architecture.
Columns
Alexander the Great built this city to be capital of Egypt.
Alexandria
This type of written work tells the deeds of a great hero.
Epic Poem
This form of government means 'rule by few.'
Oligarchy
This is the Athenian practice of banning a person considered harmful to the city-state.
Ostracism
These were the first Greek dramas.
Tragedies
This era spread throughout Southwest Asia as a result of Alexander the Great's conquests, and means 'to imitate Greeks.'
Hellenistic Era
The Iliad and The Odyssey are two of the most well-known works by this famous ancient author.
Homer
This city-state would eventually return to 'rule of the many,' also known as Democracy.
Athens
Over 7,000 Greeks, including 300 brave Spartans, delayed the invading Persian army at this location.
The Pass of Thermopylae
This person is considered the first person to analyze past events and wrote History of the Persian Wars.
Herodotus
One of the most famous scientists of the Hellenistic Era, from Syracuse.
Archimedes
This sea is to the west of the Greek mainland.
Ionian Sea
This city was the most-notable of the Greek colonies established on the Bosporus and Hellespont Straits.
Byzantium
As a result of the Great Peloponnesian War, the Greeks were left susceptible to this invading group from the North.
Macedonians
This philosopher is seen as the most influential thinker in the western world and his works are still studied today.
Aristotle
This mathematician wrote the Elements, a textbook on plane geometry.
Euclid