A body of land that is surrounded by water on 3 sides.
What is a peninsula?
The belief or worship of more than one god or goddess.
What is "polytheism?"
This ancient Greek thinker taught his students by asking questions. His curiosity made the people of Athens think he was corrupting the minds of the youth.
Who is "Socrates?"
Government where the power lay in the hands of the citizens.
What is "democracy?"
An agricultural crop grown to sell for profit.
What is a "cash crop?"
These were the "qualifications" for citizenship in many Greek city-states.
What are:
- Be a free male.
- Be born in the city-state.
- Own land.
These 3 bodies of water surround the Greek peninsula.
What are the Ionian, Aegean, and Mediterranean Seas?
The Greeks believed some of their gods and goddesses lived here, the highest mountain on the Greek mainland.
What is "Mt. Olympus?"
This student of Socrates believed that a perfect "Republic" should be run by an elite class of learned philosophers.
Who is "Plato?"
A government in which a few wealthy individuals hold power.
This ancient Greek form of currency, or money, was a silver coin whose name, when translated, means "a handful"
What is a "drachma?"
What are "political and legal rights?"
These two adjectives describe the geography and soil of mainland Greece.
What are "mountainous" and "rocky?"
The god of war.
Who is "Ares?"
This ancient Greek thinker contributed significantly to the field of Geometry.
Who is "Pythagoras?"
A government in which absolute power is vested in a single, obsessive ruler.
What is "tyranny?"
These two cash crops, eventually processed into wine and oil, were used by ancient Greeks as food, fuel, and for trading both locally and abroad.
What are "grapes and olives?"
Women born in this Greek city-state, while unable to participate in government, could own property, become wealthy, and express their opinions.
What is "Sparta?"
How did the geography of Greece influence trade, farming, and how people lived?
What is:
- Trade: lots of coastline & access to the Mediterranean like a trade super highway
- Farming: rocky, mountainous soil made growing most food difficult, but olives and grapes grow really well.
- Way of life: city-states instead of unified government due to mountainous terrain; no farmland, but access to the Mediterranean meant more sailors, fishermen, and merchants than farmers.
The god of the sea.
Who is "Poseidon?"
Graduates of medical school take an oath to "do no harm," a pledge that alludes to the medical work of this ancient Greek thinker.
Who is "Hippocrates?"
A government that has a hereditary chief of state with life tenure and powers varying from nominal to absolute.
What is a "monarchy?"
Ancient Greek governments controlled the buying and selling of this cash crop in order to ensure fair prices.
What is "grain?"
This ancient Greek city-state used Homer's "Iliad" and "Odyssey" to teach boys the art of public speaking and how to explain their beliefs with reasoning.
What is "Athens?"
How did the geography of Greece lead to the formation of city-states instead of a unified country?
What is:
- Mountains = natural barriers = no communication
- No communication = difficult to unify under one set of ideas
This series of athletic events was originally held to honor the god, Zeus.
What are "The Olympics?"
Identify each type of column from left to right.
A B C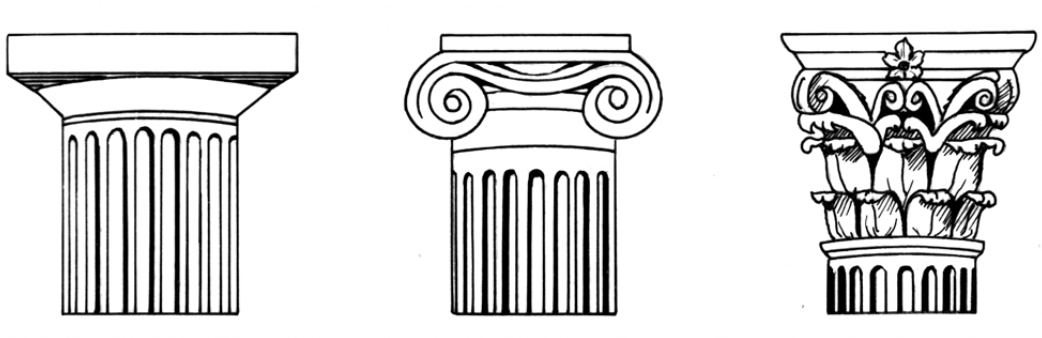
What is:
- A. Doric
- B. Ionic
- C. Corinthian
What were the main differences between the governments of Athens and Sparta?
What is:
- Democracy vs. oligarchy
- Political philosophy comes education & the arts in Athens; Political philosophy comes from militaristic way of life.
How did the sea shape the Greek economy?
What is:
- Goods could be made in one part of the Mediterranean and bought, sold, and exchanged in another part
- New food, materials, and goods became available to Greeks for trade or purchase.
- Exporting Greek goods like wine, olive oil, and pottery helped to spread Greek culture.
How did the social structure differ between Athens and Sparta?
What is:
- Athens focused on art & education, Sparta focused on the military.
- Spartan women had more rights and responsibilities, while Athenian women were not citizens, did not receive any formal education, and had few political rights.
- Sparta was known for a strong army, Athens was known for a strong navy.