The area between and around objects; can also refer to the feeling of depth.
What is Space.
This great river, which floods predictably once a year, was the main life source for the Ancient Egyptians.
What is the Nile.
An ancient Egyptian grid measurement system used for depicting the idealized human form.
What is the canon of proportions.
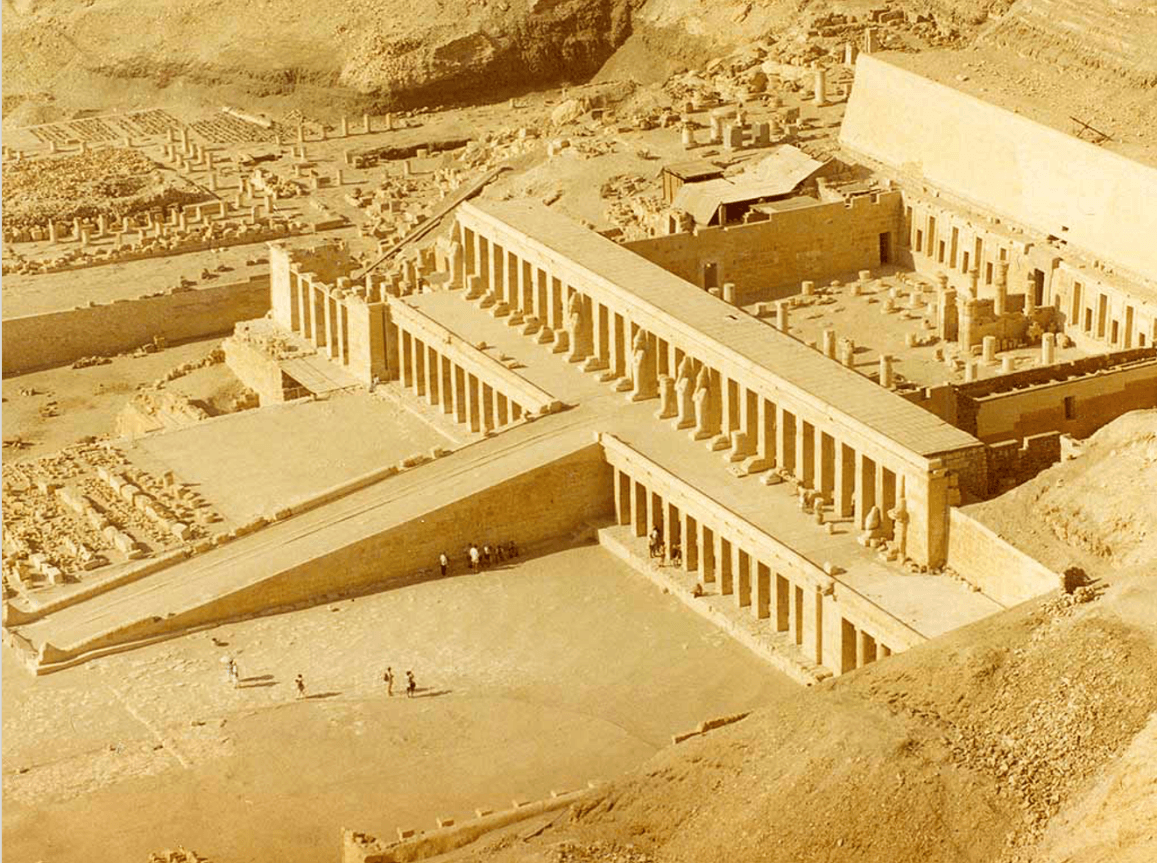


Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut. Near Luxor, Egypt. New Kingdom, 18th Dynasty. c. 1473–1458 B.C.E. Sandstone, partially carved into a rock cliff, and red granite.
This material was found in abundance around the Nile and was believed by the ancient Egyptians to be what made up the skin of the gods and was therefore used in the making of many burial artifacts found in tombs.
What is gold.
The repeating of an object or symbol all over the work of art.
What is Pattern.
These two rivers, which flood unpredictably, run through Mesopotamia.
What are the Tigres and Euphrates.
1. Material wealth/decoration
2. Ritual and Ceremony
3. Exclusivity
4. Location
What are characteristics of a sacred space.
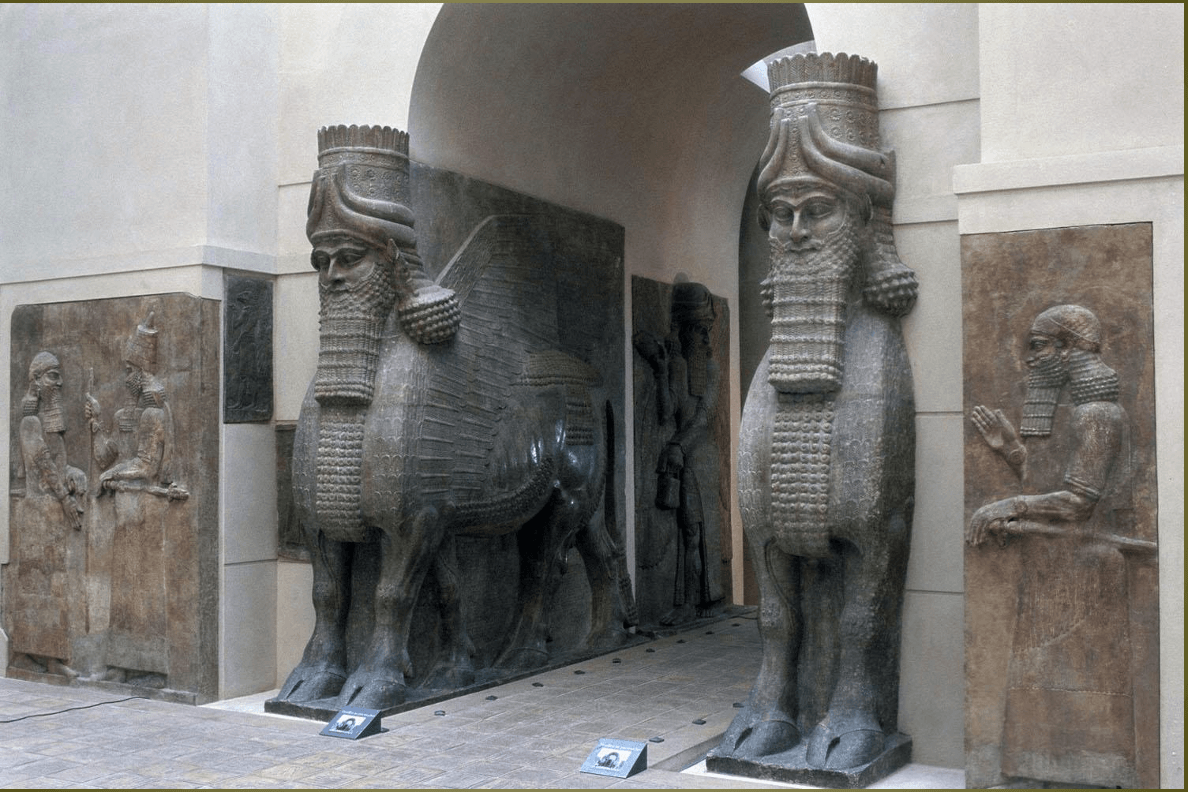

Lamassu from the citadel of Sargon II, Dur Sharrukin (modern Khorsabad, Iraq). Neo-Assyrian. c. 720–705 B.C.E. Alabaster.
This common material was used in the construction of Ancient Mesopotamian Ziggurats and did not stand the test of time.
What are mud bricks.
Surface quality that can be seen or felt.
What is Texture.
This region gave birth to three of the world's great modern religions; Christianity, Judaism and Islam.
What is Mesopotamia or Fertile Crescent
The Sumerian Votive Offering statues can be described as having this shape and were made using this type of carving technique.
What is Conical and Subtractive.

Palette of King Narmer. Predynastic Egypt. c. 3000–2920 B.C.E. Greywacke.
This earliest form of writing allowed history to be recorded for the first time and was invented by the ancient Sumerians.
What is Cuneiform.
The path the viewer's eye takes through the work of art, often to focal areas.
What is Movement.
This region offered very few resources and was prone to attack from outsiders, causing a general instability for the people there.
What is Ancient Mesopotamia or Sumeria.
Works of art such as the Palette of Narmar and the Standard of Ur use this narrative device to arrange imagery in horizontal bands for organizational and storytelling purposes.
What are registers.

. The Code of Hammurabi. Babylon (modern Iran). Susian. c. 1792–1750 B.C.E. Basalt.
This brief historical period in ancient Egypt was ruled by this Pharoah for about 17 years and is marked by a change from polytheism to monotheism.
Who is Akhenaton and what is the Amarna period.
The feeling of harmony between all parts of the work of art, which creates a sense of completeness.
What is Unity.
This region was well protected by desert from attack and offered numerous precious resources making for a very stable environment for the people there.
What is Ancient Egypt.
This type of architectural plan found in the temple of Amun-re at Karnak directs the visitor straight down a center axis.
What is an axial plan.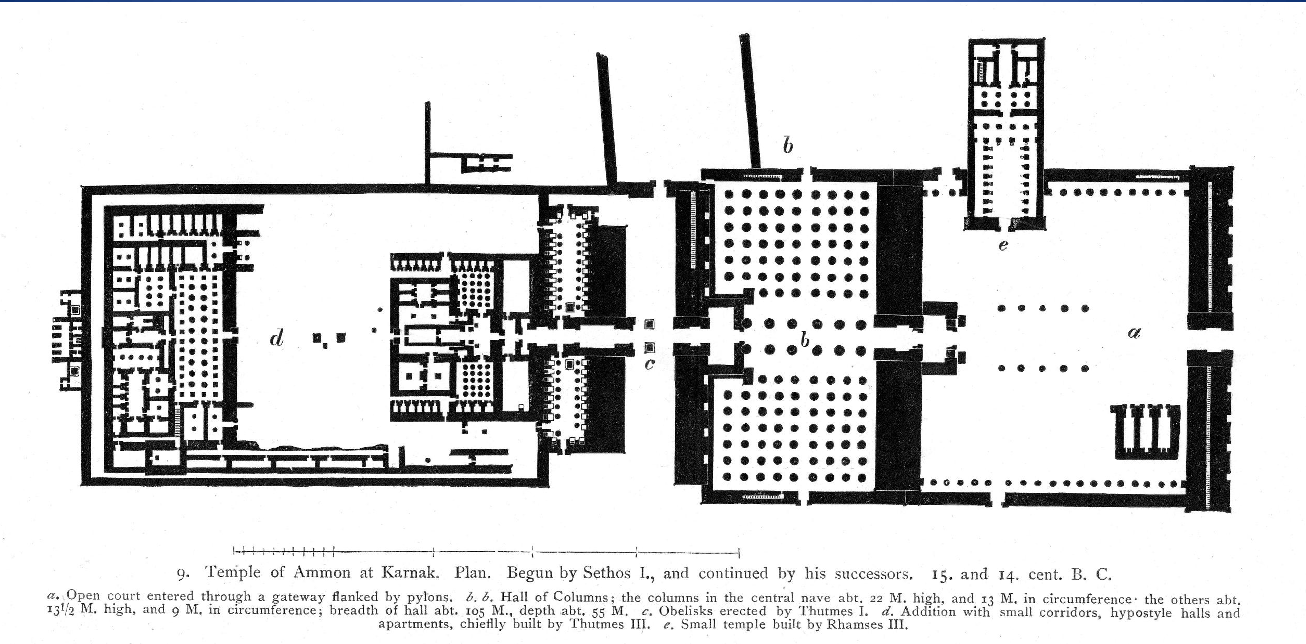
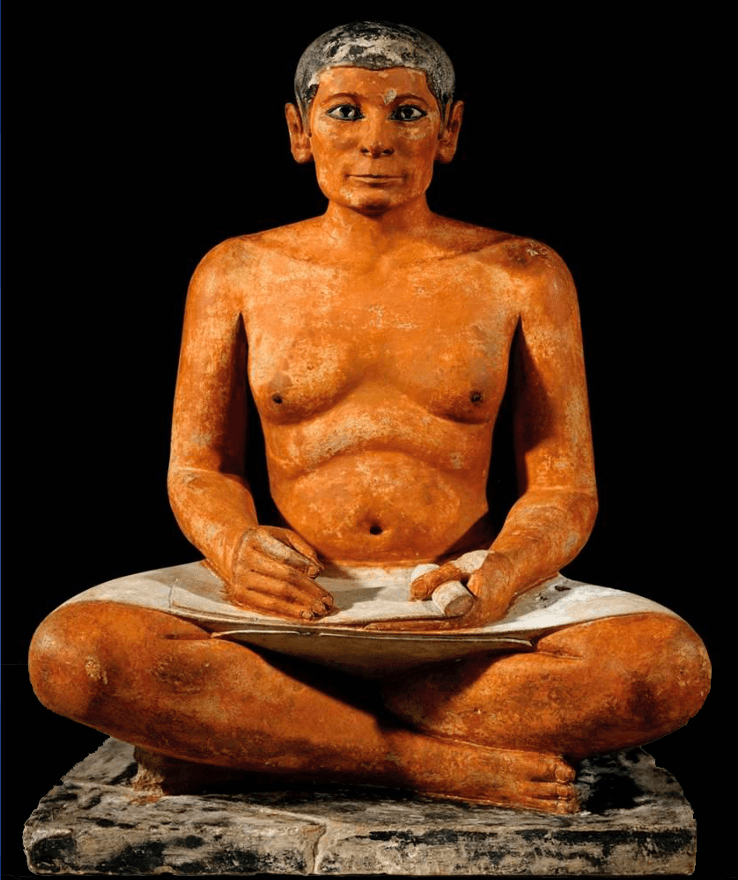

Seated scribe. Saqqara, Egypt. Old Kingdom, Fourth Dynasty. c. 2620–2500 B.C.E. Painted limestone
Ancient Egyptian statuary and 2-dimensional imagery of a person was believed to house the spirit of that person. This Egyptian word for the "spirit" of a person was believed to be destroyed if the statue or drawing was destroyed.
What is the ka