when should you pause a heparin drip when preparing for surgery?
infusion should be stopped 4-6 hours prior to procedure.
Max dose of lido with epi is 7ml/kg
20 x 7 / 10=14 ml
note: 1% lidocaine=10mg/ml, 2%=0.02 20mg/ml
A 63-year-old man undergoes ventral hernia repair with component separation. On the third postoperative day, his serum potassium level is 6.7 mEq/L. Vital signs are stable. Electrocardiography discloses sinus rhythm with flattened P waves and peaked T waves. Initial therapy should include the administration of which of the following drugs?
A) Albuterol
B) Calcium gluconate
C) Dextrose and insulin
D) Furosemide
E) Sodium bicarbonat
The correct response is Option B.
Intravenous calcium gluconate should be given to this patient with severe hyperkalemia and associated electrocardiographic changes.
Hyperkalemia causes a decrease in the resting membrane potential, leading to increased myocardial excitability and cardiac arrhythmias, including ventricular fibrillation and asystole. Electrocardiographic changes associated with progressive hyperkalemia include peaked T waves, prolonged P-R segment, flattening/loss of P waves, widening of QRS complex, ectopic beats, ventricular fibrillation, conduction blocks, and asystole.
A 24-year-old man with a history of opioid use disorder is scheduled to undergo closed reduction and percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation of a right fifth metacarpal fracture. The patient is placed on an enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocol. Which of the following medications used to treat pain binds to voltage-gated calcium channels?
A) Acetaminophen
B) Gabapentin
C) Ketamine
D) Lidocaine
E) Oxycodone
B- Gabapentin binds to voltage-gated calcium channels at presynaptic terminals of hyper excited neurons. In conjunction with ERAS protocol, is associated with reduced postoperative opioid use
An otherwise healthy 60-year-old woman underwent breast reconstruction with right free transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous (TRAM) flap 1 day ago. Cardiac monitoring shows no P waves and an irregular QRS complex. The patient is asymptomatic. Blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg and heart rate is between 130 and 139 bpm. Which of the following is the most appropriate first-line therapy for this patient?
A) Amiodarone
B) Digoxin
C) Diltiazem
D) Metoprolol
E) Propafenone
d- afib. post-op fib after non-cardiac surgery has multiple etiologies, regardless the evidence shows rate control>rhythm control.
Diltiazem (non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker) is a second-line therapy, and is intended for use if first-line therapy is ineffective at rate control at maximum doses or the first-line therapy is contraindicated. Digoxin is considered when other options are ineffective or contraindicated because of its narrow therapeutic window. Amiodarone has both beta-blocking and calcium channel blocking properties in addition to its antiarrythmic effects.
if submental space measures less than ___cm, may be a more difficult intubation
6.5
A 35 yoF is interested in a tummy tuck and liposuction of the flanks and mid back. She does not smoke cigarettes, can climb two flights of stairs without shortness of breath or chest pain, and takes medication for hypothyroidism, which is well-controlled. BMI is 42 kg/m2. She is otherwise healthy. Which of the following is the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) physical status classification?
A) ASA I
B) ASA II
C) ASA III
D) ASA IV
E) ASA V
C- BMI>40, may not be a candidate for surgery center-based procedures
A 65-year-old man undergoes hemimandibulectomy and reconstruction with a fibular flap for oral squamous cell carcinoma. On postoperative day 4, the patient develops a cough and feels ill. Temperature is 39.4°C (102°F), blood pressure is 80/40 mmHg, heart rate is 120 bpm, and respiratory rate is 32/min. On physical examination, the surgical sites are unremarkable. Intravenous fluid resuscitation is promptly initiated. Blood cultures are collected and broad-spectrum antibiotics are administered. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
A) Administering additional fluid resuscitation with hydroxyethyl starch
B) Initiating low-dose dopamine for renal protection
C) Measuring lactate level
D) Narrowing antimicrobial therapy based on culture results
E) Placing a pulmonary artery catheter
C- measure lactate (surrogate of hypo perfusion). Surviving Sepsis guidelines promote the Hour 1 Bundle which includes:
1) measure lactate, remeasure in 2-4 hours if initial lactate is high
2) blood cultures BEFORE starting antibiotics
3) Rapid administration of 30ml/kg crystalloid for hypotension or lactate>4 (at Cooper this must occur within 3 hours of presentation)
4) vasopressors if still hypotensive after resuscitation
Tranexamic acid inhibits which of the following enzymatic conversions?
A) Factor VII to factor VIIa
B) Factor X to factor Xa
C) Fibrinogen to fibrin
D) Plasminogen to plasmin
E) Prothrombin to thrombin
D
A 165.3-lb (75-kg), 76-year-old woman is scheduled to undergo wide local excision of a large, invasive basal cell carcinoma of the cheek with flap reconstruction during general anesthesia. Medical history includes nonvalvular atrial fibrillation, hypertension, and an embolic stroke 3 months ago. Current medications include warfarin. Renal function is normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate preoperative anticoagulation management for this patient?
A) Discontinue warfarin 5 days prior to the procedure and initiate low-molecular-weight heparin bridging 3 days prior to the procedure
B) Discontinue warfarin 5 days prior to the procedure without bridging
C) Discontinue warfarin 7 days prior to the procedure and initiate low-molecular-weight-heparin bridging 3 days prior to the procedure
D) Immediately initiate low-molecular-weight heparin bridging and discontinue warfarin 5 days prior to the procedure
E) Do not discontinue warfarin
A- This patient has a very high thromboembolic risk and a high bleeding risk. Recommended heparin bridging is 3 days before a planned procedure (ie, two days after discontinuing warfarin), when the prothrombin time and international normalized ratio (PT/INR) has started to drop below the therapeutic range.
Suggested use of bridging in individuals taking warfarin includes:
Embolic stroke or systemic embolic event within the previous three months
Mechanical mitral valve
Mechanical aortic valve and additional stroke risk factors
Atrial fibrillation and very high risk of stroke (eg, systemic embolism within the previous 12 weeks, concomitant rheumatic valvular heart disease with mitral stenosis)
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) within the previous three months (preoperative and postoperative bridging)
Recent coronary stenting (e.g. within the previous 12 weeks)
Previous thromboembolism during interruption of chronic anticoagulation
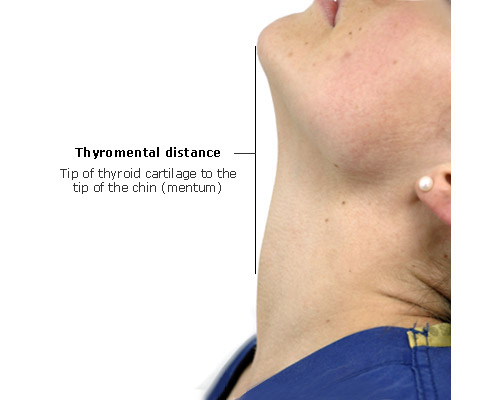
A 37 yo F
Which Malampati score would you assign her?

A 42-year-old man presents with partial degloving injury of the right leg and fracture of the pelvis sustained during a motorcycle collision 2 weeks ago. Medical history includes factor V Leiden. BMI is 31.1 kg/m2. Skin graft reconstruction of the degloving injury of the leg is planned. According to the Caprini Risk Assessment Model (2005), which of the following conditions in this patient represents the greatest risk for perioperative venous thromboembolism?
Bonus 100 pounds for calculating his carping
A) Age
B) BMI greater than 25 kg/m2
C) Major surgery (greater than 45 minutes in duration)
D) Pelvic fracture
E) Positive factor V Leiden
D- pelvic fracture = +5!
Age>40 is +1
BMI over 25 is +1
major surgery +1
factor V leiden +3

A 38-year-old woman is undergoing a routine abdominoplasty at an outpatient surgery center under general anesthesia. Thirty minutes into the operation, the anesthesiologist reports high end-tidal CO2 production and tachycardia. Which of the following is the most appropriate first step in management?
A) Administer dantrolene
B) Discontinue volatile anesthetic agents
C) Infusion of lipid emulsion
D) Switch to total intravenous anesthesia
E) Treatment of arrhythmia
B- this is the start of malignant hyperthermia. due to accelerated release of calcium from sarcoplasmic reticulum. tachycardia, high body temp, masseter muscle rigidity. treatment:
1) dantrolene
2) switch to total IV anesthesia (turn off the volatile gas)
3) treat the arrhythmia
A 37-year-old woman is scheduled to undergo skin-sparing mastectomy of the left breast with immediate deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP) flap reconstruction. Which of the following interventions is most likely to decrease this patient's postoperative narcotic needs?
A) Application of a preoperative compression garment
B) Hypnosis
C) Ondansetron therapy
D) Oxycodone therapy
E) Pregabalin therapy
The correct response is Option E.
Pregabalin (Lyrica) has been shown to decrease narcotic needs after breast surgery. It is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue and decreases GABA in the brain and acts primarily as an anticonvulsant. It is more potent than gabapentin as an analgesic.
A 30-year-old woman undergoes augmentation mammaplasty in an office-based operating room. Intravenous midazolam and fentanyl are used, and a lidocaine field block is administered. An hour later, while in the recovery room, the patient experiences disorientation, muscle twitching, and light-headedness. Administration of which of the following drugs is the most appropriate next step in management?
A) Dantrolene
B) Fat emulsion
C) Flumazenil
D) Naloxone
E) Propofol
B- this is lidocaine toxicity

How close to surgery should blood thinners like elliquis or xeralto be stopped?
3 days before surgery
A 42-year-old woman is scheduled for abdominoplasty, repair of diastasis recti abdominis, and incisional herniorrhaphy. At the start of the operation, 20 mL of 1% lidocaine with epinephrine 1:100,000 is injected into the lower abdominal incision. After incisional herniorrhaphy is completed, the general surgeon plans to inject liposomal bupivacaine into the lower abdominal hernia repair. Which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation regarding the injection of liposomal bupivacaine after lidocaine injection?
A) Do not use liposomal bupivacaine after lidocaine is used
B) Wait at least 20 minutes before injecting liposomal bupivacaine
C) Wait at least 60 minutes before injecting liposomal bupivacaine
D) Wait at least 90 minutes before injecting liposomal bupivacaine
E) There are no restrictions
Wait at least 20 minutes before injecting liposomal bupivacaine. Liposomal bupivacaine (Exparel), is a long-acting (approximately 72 hours) local anesthetic that is an extended-release multivesicular liposomal version of bupivacaine. (reduces post-op need for opioids)
WHEN MIXED WITH LIDOCAINE, can cause immediate release of bupivacaine, causes an overdose.
A 63 yoF with history of breast cancer presents for delayed reconstruction with bilateral latissimus dorsi muscle flaps. PMH includes CAD, HTN, and RA. Current meds include ASA, propranolol, and prednisone, which she has taken for 8 years. In preparation for surgery, prednisone is discontinued 6 weeks before and aspirin is discontinued 1 week before surgery. The surgical procedure is uneventful. In the PACU, her heart rate is 115 bpm and blood pressure is 80/40 mmHg. Physical examination shows no signs of hematoma. A total of 3 L of intravenous fluid boluses are administered, with no hemodynamic improvement. Chest x-ray, ECG, hematocrit and serum electrolytes, and troponins are normal. Despite increasing doses of vasopressors during the next 2 hours, the patient remains hypotensive. Administration of which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
A) Dantrolene
B) Desmopressin (DDAVP)
C) Hydrocortisone
D) Insulin and dextrose
E) Labetalol
C- hydrocortisone. This patient's refractory hypotension and use of long term steroids is consistent with an adrenal crisis
Signs: hypotension, hypoglycemia, dehydration, altered mental status, and hyponatremia, which can quickly progress to fatal hemodynamic collapse.
Other answers: Desmopressin causes release of von willebrand factor from platelets/endothelial cells, used if factor 8 deficiency.
A 55-year-old man undergoing excision of a soft-tissue mass of the left thigh develops malignant hyperthermia shortly after induction of general anesthesia. The surgical procedure is promptly aborted, and the patient is successfully treated. Six months later, he returns for another attempt at excising the mass. The use of which of the following anesthetic agents is most appropriate in this case?
A) Ether
B) Halothane
C) Propofol
D) Sevoflurane
E) Succinylcholine
C- lidocaine/local anesthetics are safe in those with history of malignant hyperthermia. volatile anesthetic agents and depolarizing muscle relaxants are potential triggers of malignant hyperthermia, should be avoided in patients who are susceptible.
A 42-year-old woman undergoes deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap breast reconstruction. An ultrasound-guided transversus abdominis plane regional block with liposomal bupivacaine is planned. The ultrasound probe is placed directly over the abdominal wall musculature in the anterior axillary line. What is the appropriate injection level for this block?
The sensory nerves in the abdominal wall are between the internal oblique and transverses abdomens muscles


Name three characteristics of propofol infusion syndrome
An otherwise healthy 45-year-old woman presents for abdominoplasty. Administration of liposomal bupivacaine for postoperative pain control is planned. Which of the following is the maximum dose of liposomal bupivacaine that can be administered in a single dose in this patient?
A) 50 mg
B) 133 mg
C) 200 mg
D) 266 mg
E) 399 mg
max dose of liposomal bupivacaine (exparil) =266 or 20ml. lasts 72-96 hours
CLJ is starting a bilateral SSM with sentinel lymph node biopsy. After uneventful induction of general anesthesia, she injects 1 mL of isosulfan blue dye intradermally. During removal of the sentinel node, blood pressure decreases to 60/40 mmHg. After discontinuing the procedure and administering a bolus of intravenous fluid, which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
A) Administer dexamethasone
B) Administer diphenhydramine
C) Administer lipid emulsion
D) Administer phenylephrine
D-This is an allergy to isosulfan blue, occurs in 1.5% of patients. should give a bolus and vasopressors.
Once this is done, both a corticosteroid (dexamethasone) and an antihistamine (diphenhydramine) should be given to counteract the allergic reaction.
A 65-year-old man presents to the office for panniculectomy evaluation. Medical history includes anxiety, controlled hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and borderline diabetes that is controlled by diet only. Current medications include lisinopril, carvedilol, atorvastatin, zolpidem, and sertraline. After consultation, the surgeon determines the patient is a good candidate for panniculectomy. It is most appropriate for the patient to stop taking which of the following medications the night before surgery?
A) Atorvastatin
B) Carvedilol
C) Lisinopril
D) Sertraline
E) Zolpidem
All the medications listed are safe for use the night before surgery with the exception of an ACE inhibitor.
While there have been some questions in the past regarding the safety of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like sertraline due to bleeding concern, the current consensus is that it is safe to take.1 Beta blockers can have a beneficial effect for the cardiovascular system before surgery and thus, patients may take them even the morning of surgery.2 Lisinopril, however, can lead to hypotension during surgery and anesthetic management, and should be stopped the night before surgery. As an ACE inhibitor, it may counter the medications the anesthesiologist uses for blood pressure control.
According to the Malignant Hyperthermia Association of the United States guidelines, which of the following intravenous agents should be avoided during the acute resuscitation phase of malignant hyperthermia, following dantrolene administration, when treating subsequent cardiac dysrhythmias?
A) Dextrose 50% solution
B) Epinephrine
C) Lidocaine
D) Metoprolol
E) Verapamil
E- malignant hyperthermia is caused by disturbance of calcium channel homeostasis, causing unregulated release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Dantrolene inhibits the release of calcium from the sarc relic by inhibiting the ryanodine receptor on the skeletal muscles. Verapamil is a calcium channel blocker that has been associated with life-threatening hyperkalemia when combined with dantroline
