aminocaproic acid (Amikar) & aprotinin
Antifibrinolytic agents
slide 22
Name 5 risk factors for CAD
Male, age, smoking hx, family Hx, DM, Obesity, Personality, HLD
Slide 5
Name 5 basic components of the CPB machine
Venous Reservoir, main pump, oxygenator, heat exchanger, arterial filter
Slide 32
What Blood Pressure is recorded while the patient is "on-pump"?
MAP
Slide 29
Distant heart sounds
Distended jugular veins
Decreased arterial pressure
Beck's Triad - associated with cardiac tamponade
Slide 48
A minimally invasive procedure for the correction of severe AS
TAVR (transaortic valve replacement) or
TAVI (transcatheter aortic valve implantation)
Which anesthetic agents produce a preconditioning effect on the mycardium?
Volatile agents: Especially Sevoflurane and Isoflurane
Identify 4 determinants of myocardial oxygen supply
Coronary artery anatomy/patency, diastolic blood pressure, diastolic time (HR), Hb, Oxygen tension/saturation
Slide 4
Name the suction used to drain blood collecting in the mediastinum
The Cardiotomy suction
Slide 33
Wide Receiver Most Valuable Player
Off pump checks!
Warm. Rhythm. Monitors. Ventilation. Perfusion
Slide 43
How do you calculate SVR?
SVR = [(MAP - CVP)/CO]*80
Slide 44
Name 2 approaches for the TAVR procedure
Retrograde :trans-femoral
Antegrade: left ventricle apex (via minithoracotomy)
Associated with increased incidence of arterial spasm, but generally remain patent for a longer period of time
LIMA/ITA grafts
Slide 13
EF <25%
Severe LV dysfunction
Slide 9
Describe the cardioplegia solution
Cold, hypertonic crystalloid solution that contains potassium and many other additives including lidocaine, aspartate, glutamate, dextrose, mannitol, bicarb and or adenosine
Slide 30
Strictures, varices, diverticula or recent suture lines.
Contraindications to TEE
Slide 19
What is the reversal dose for Protamine?
1mg protamine per 100 units heparin administered
Slide 44
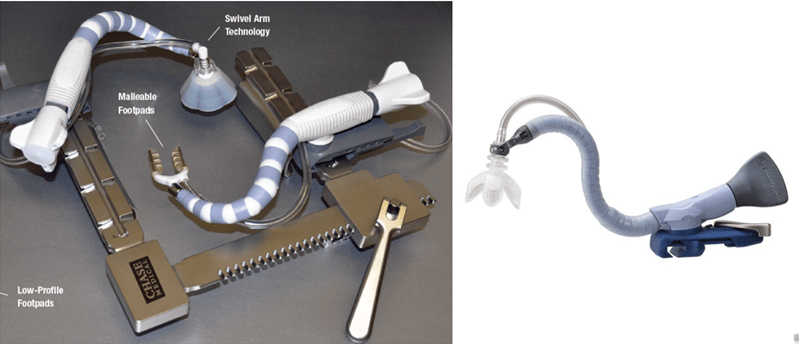
The Octopus, Urchin and Starfish: stabilizing devices used during off-pump CABG procedures
Slide 51
Percentage of cardiac cases that return to the OR for bleeding
4 - 5%!!
Slide 48
Independent risk factor for perioperative M&M
Renal disease/Chronic renal insufficiency
(Up to 40% for ARF and 60%+ if needing replacement therapy!)
Slide 8
Instantaneous hemodilution and reduction of blood viscosity
Causes of initial Hypotension following initiation of CPB
slide 29
Ensure adequate muscle relaxation, hold ventilation, allow exhalation and be prepared for resuscitation
Anesthetist actions prior to sternotomy
Slide 24
Identify and Treat:
Persistently low blood pressure (SVR) despite normal to high cardiac output
Vasoplegic syndrome!!
Treat with norepinephrine and vasopressin
Slide 45
Medications generally not needed for "Off-Pump" CABG
Heparin, antifibrinolytics and protamine
An S3 Heart sound is often a sign of.... ?
Systolic heart failure
Overly compliant ventricle= dilated LV
AKA- "ventricular gallop)
LBBB on ECG
Can become 3rd degree block with PA Cath placement
Slide 10
ALI/ARDS, AKI, SIRS, MI, TIA
Complications associated with CPB
Slide 36
The desired outcome of cardioplegia
Hypothermic, diastolic cardiac arrest
Slide 30
HAD2SUE
On-Pump checklist:
Heparin, ACT, Drugs/Drips, Swan, Urine, Emboli
Slide 26
List hemodynamic parameters for management of Aortic or Mitral Stenosis
Preload = up
Afterload = maintain
SVR = maintain
HR = 50 - 80
Slide 52