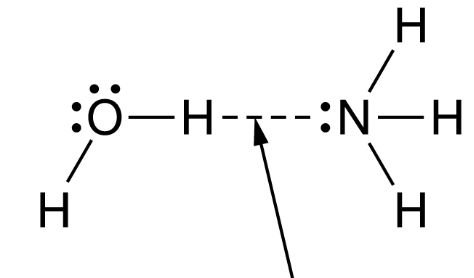
What is hydrogen bonding?
A fertilizer contains a lot of nitrogen and phosphorous. The nitrogen and phosphorous will be incorporated into this macromolecule.
What are nucleic acids?
This is a waste product of the krebs cycle
What is CO2?
This second messenger links cell surface reception with signal transduction
This property of water is responsible for making water less dense in its frozen state.
What is H bonding?
This is the end where nucleotides are added onto a nucleic acid.
What is 3' end?
This cell structure is directly involved in apoptosis since it has digestive enzymes.
What is a lysosome?
Adding acid to an enzyme messes with this protein structure since it can interrupt H-bonding, ionic bonding, and hydrophobic interactions
What is tertiary structure?
This enzyme is responsible for adding phosphate groups to other enzymes.
What is a kinase?
The cell wall is made out of this carbohydrate.
What is cell wall?
This many waters is required to hydrolyze this amino acid.
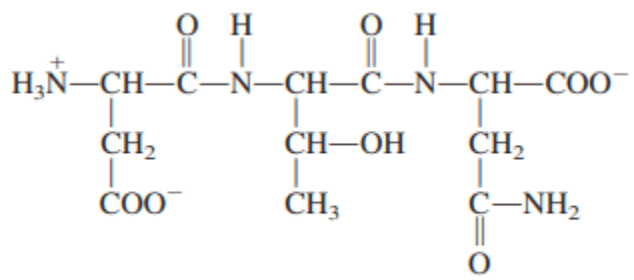
What is 2?
This is an example of which kind of movement across a cell membrane.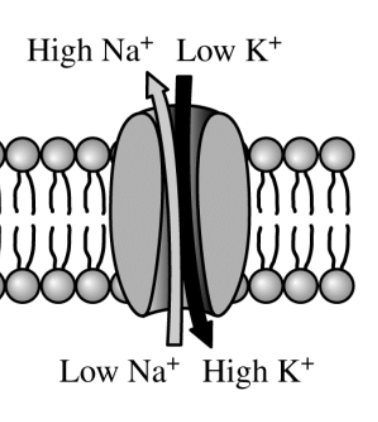
What is active transport?
This metabolic process serves as evolution as it has been conserved throughout all of life.
What is glycolysis?
During labor, the position of the baby’s head keeps stimulating uterine contractions until the baby is born.
What is a positive feedback loop?
This cell structure is where a protein would go after being made at the endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the golgi body / golgi apparatus?
This property of water explains why coastline cities have moderate temperatures compared to inland citiies.
What is high specific heat capacity?
ATP synthase uses this kind of movement across a cell.
What is facilitated diffusion?
This is an intermediary electron acceptor in the krebs cycle and glycolysis
What is NAD+?
This part of cell communication is why different cells can respond to the same ligand differently.
What is signal transduction?
This property of mitochondria and chloroplasts are necessary to making them efficient in producing and capturing energy.
What is surface area?
Adding heat to a protein will alter these protein structures.
What is secondary, tertiary, and quaternary?
Water enters and leaves the plant cells primarily by this regulated process.
What is osmosis?
The hydrolysis of this molecule is an energy-releasing reaction that is often coupled with reactions that require an input of energy.
What is ATP?
A newly developed medication for pulmonary hypertension targets blood vessels in the lungs, but does not affect blood vessels in the liver because the ligand is not able to bind to this.
What is a receptor?
This is two are evidence for endosymbiotic theory (name 2).
What is a double membrane?
What is circular DNA?
What is reproduction? (They reproduce the same as bacteria.)