Did the medication work more effectively in the "Data A" group versus the "Data B" group?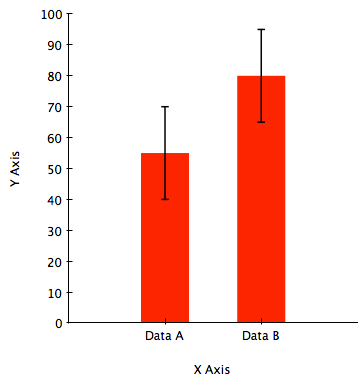
No, the error bars overlap, so there is statistically no difference (they have the same effect)
How would CO2 enter and exit the cell?
Passive transport - Diffusion through the membrane
What is the goal of photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and fermentation?
Photosynthesis - Make glucose
Cellular Respiration - Make ATP (energy)
Fermentation - Make ATP without oxygen available
What are the names of the stages of the cell cycle (in order)?
G1, S, G2, M
Bonus: G0 (resting phase)
What instrument did Ms. C play?
Trumpet
What are the 2 things that eukaryotes have and prokaryotes do not?
1 - nucleus containing DNA
2 - Membrane-bound organelles
Which organelle contains hydrolytic enzymes?
Lysosomes (Think hydrolysis - breaking down molecules)
What is the role of water in photosynthesis?
Water splitting replaces the electrons in PSII, and H+ ions for the proton gradient. (Oxygen from H2O will be released)
You walk outside in the winter with no jacket. You begin to shiver. Describe the stimulus, receptor, effector, and response.
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK LOOP
Stimulus: walking in the cold
Receptor: Temperature receptors on skin
Effector: Muscle cells contracting
Response: Shivering
What high school did Ms. C go to?
a. Speedway b. Brownsburg c. Harrison d. Lebanon
Harrison

What does it mean that water has a "high specific heat capacity"
It takes a lot of energy to raise the temperature of water
Describe an ideal surface area to volume ratio for a cell. How do organelles assist in the efficiency of cells?
High surface area to volume ratio. Organelles compartmentalize the cell. Many chemical reactions can occur at the same time without interfering.
What is the role of NADPH, NADH, and FADH2?
What do growth factors typically signal for?
Cell division (mitosis)
What does Ms. C's fiance do for work?
Science! Develops new formulations for herbicides. 
Describe each level of protein structure
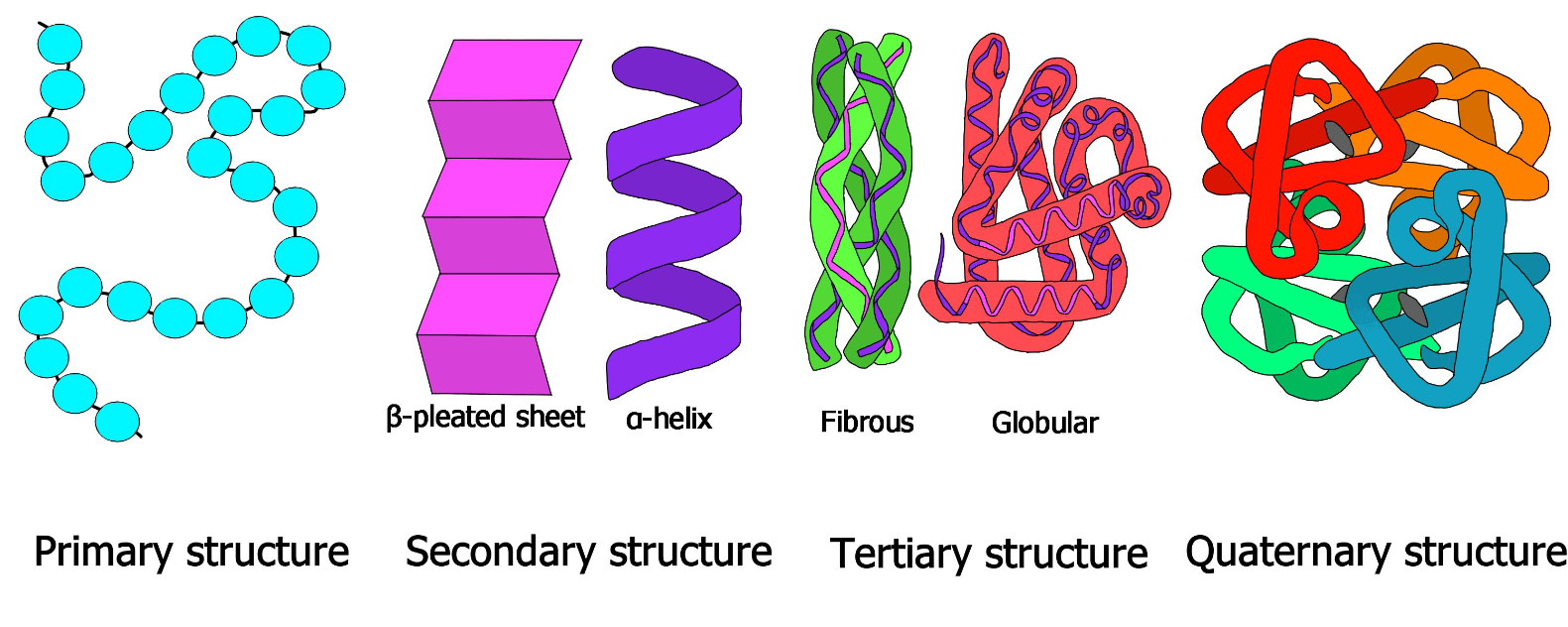 Primary - chain of amino acids
Primary - chain of amino acids
Secondary - Beta pleated sheet or alpha helix
Tertiary - 3D folding based
Quaternary - 2 or more polypeptides
Describe the solute in a solution compared to the cell for isotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic solutions. What happens to the cell in each of these?
Isotonic - same amount of solute in and out of cell (cell stays same size)
Hypotonic - low amount of solute outside of the cell (cell swells)
Hypertonic - high amount of solute outside of the cell (cell shrinks)
Carbon Fixation - CO2 attaches to RuBP. Rubisco catalyzes the reaction. Creates 3-PGA
Reduction - ATP and NADPH change 3-PGA into G3P (sugar)
Regeneration of RuBP - 5 G3P molecules are used to regenerate RuBP using 3 ATP
Explain the steps of a signal transduction pathway
1. Reception - signal binds to receptor
2. Transduction - secondary messengers and protein cascades relay the message. Kinase phosphorylates proteins to activate them
3 - Response - Cellular process is changed (transcription, cell division, apoptosis, etc.)
a. $7.50 b. $8.25 c. $7.05 d. $9.75
$7.50