These specialized molecules are secreted to trigger a response in target cells either locally or over long distances.
What are signaling molecules?
These receptors are located inside the cell and bind hydrophobic signaling molecules.
What are intracellular receptors?
Epinephrine stimulates this process in the liver and skeletal muscles, releasing glucose into the bloodstream.
What is glycogen breakdown?
This receptor opens or closes in response to a ligand, allowing ions to pass through.
What is a ligand-gated ion channel?
This is the first stage of cell signaling, where a signaling molecule binds to a receptor.
What is reception?
Hormones travel through this to reach distant target cells in long-distance signaling.
What is the bloodstream?
This enzyme transfers phosphate groups from ATP to proteins in a signaling pathway.
What is a protein kinase?
These proteins regulate gene expression by turning specific genes on or off.
What are transcription factors?
This receptor is associated with a G-protein and activates a signal cascade when a ligand binds.
What is a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)?
This stage of cell signaling involves converting a signal into a form that can bring about a specific cellular response.
What is transduction?
This term describes the molecule that specifically binds to a receptor to trigger a cellular response.
What is a ligand?
This second messenger, derived from ATP, is common in many signal transduction pathways.
What is cyclic AMP (cAMP)?
This term describes the change in a cell’s activity caused by a transduced signal.
What is a cellular response?
hese receptors can activate multiple signaling pathways after ligand binding, often through phosphorylation.
What are receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs)?
Would this be an example of a negative or positive feedback loop?
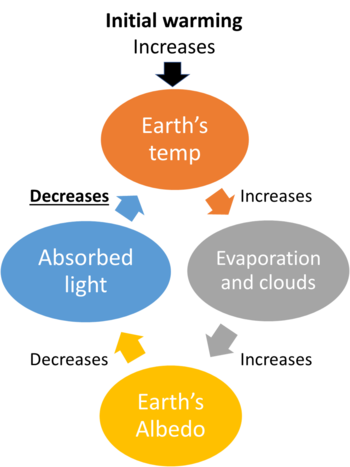
What is a negative feedback loop?
This part of cell signaling involves the binding of a signal molecule to a receptor, triggering a change in shape.
What is reception?
This process amplifies a signal through a series of phosphorylation events.
What is a phosphorylation cascade?
The opening of ion channels in a nerve cell membrane after ligand binding is an example of this type of response.
What is an electrical response?
The ability of ligand-gated ion channels to influence nerve impulses is critical for these cellular processes.
What are sensory functions (e.g., sight, smell, and taste)?
These small, non-protein molecules, such as calcium ions or cAMP, relay signals within the cell.
What are second messengers?
This type of signaling relies on direct cell-to-cell contact, like that seen in embryonic development.
What is local signaling?
These enzymes remove phosphate groups from proteins to deactivate signaling pathways.
What are protein phosphatases?
This type of cellular response involves activating metabolic pathways through enzymes.
What is a cytoplasmic activity?
A conformational change in these receptors occurs when a ligand binds, triggering downstream signaling.
What are transmembrane receptors?
This final stage of cell signaling results in a change in cellular activity, such as gene expression or enzyme activation.
What is the response?