Meiosis is the specific cell division for gametes. These are the products of meiosis (# cells and amount of DNA).
What are 4 haploid daughter cells (or 1/2 DNA)?
Prokaryotes typically contain one main, single, circular chromosome. They can also have this specific type of small, extra-chromosomal double-stranded DNA molecule.
What are plasmids?
Translation, the protein-building step in the cytoplasm involving ribosomes, is initiated when the ribosome interacts with this specific codon.
What is AUG?
According to Darwin's theory of natural selection, __ for limited resources results in differential survival.
What is competition?
In general, the smaller the organisms, the ____ the metabolic rate.
What is higher?
These 2 processes occur during meiosis and contribute to the variation of offspring from sexually reproducing organisms.
What are crossing-over and independent assortment?
DNA will always be synthesized in the 5' - 3' direction. This leads to the production of one ___ strand and one ___ strand.
What are leading and lagging strands?
These changes can affect gene expression through reversible modifications of DNA or histones.
This is measured by reproductive success.
What is evolutionary fitness?
This level of an ecosystem will affect the number and size of all other trophic levels.
What is the producer level?
A homozygous dominant fish for large fins mates with a homozygous recessive fish with small fins. The percent of their offspring will have large fish if this trait follows Mendelian inheritance?
What is 100%?
This enzyme is responsible for the extension of a growing mRNA strand.
What is RNA polymerase?
This results in differential gene expression and influences cell products/function.
What is gene regulation?
Humans can impact variation in populations, and example of this type of selection.
What is artificial?
This type of organism can make its own food - it can use chemicals, inorganic compounds, or light.
What are autotrophs?
DNA is found in all mitochondria and chloroplasts. Unlike nuclear DNA, this DNA is passed on to future generations in this way.
What is maternally?
Transcription occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotes. mRNA is produced and then needs to be processed before it is exported out of the nuclear pore. This portion of the nascent mRNA must be excised before it moves out.
Introns ("junk" or non-coding regions)
These are spontaneous changes to one or many DNA nucleotides. They can be silent or cause changes to a phenotype.
What are mutations?
These are two types of genetic drift.
What are the bottleneck effect and the founder effect?

This age diagram shows a population with this type of growth rate.
The idea that chloroplasts and mitochondria were once free-living prokaryotes is explained by this theory.
What is the endosymbiotic theory?
Eukaryotic mRNA transcripts are protected from damage before leaving the nucleus. These 2 features are added to the mRNA.
5' cap and poly-A tail
This is the process whereby cells take up foreign DNA and integrate it into their own DNA.
What is transformation? (Remember GFP and transformation lab...)
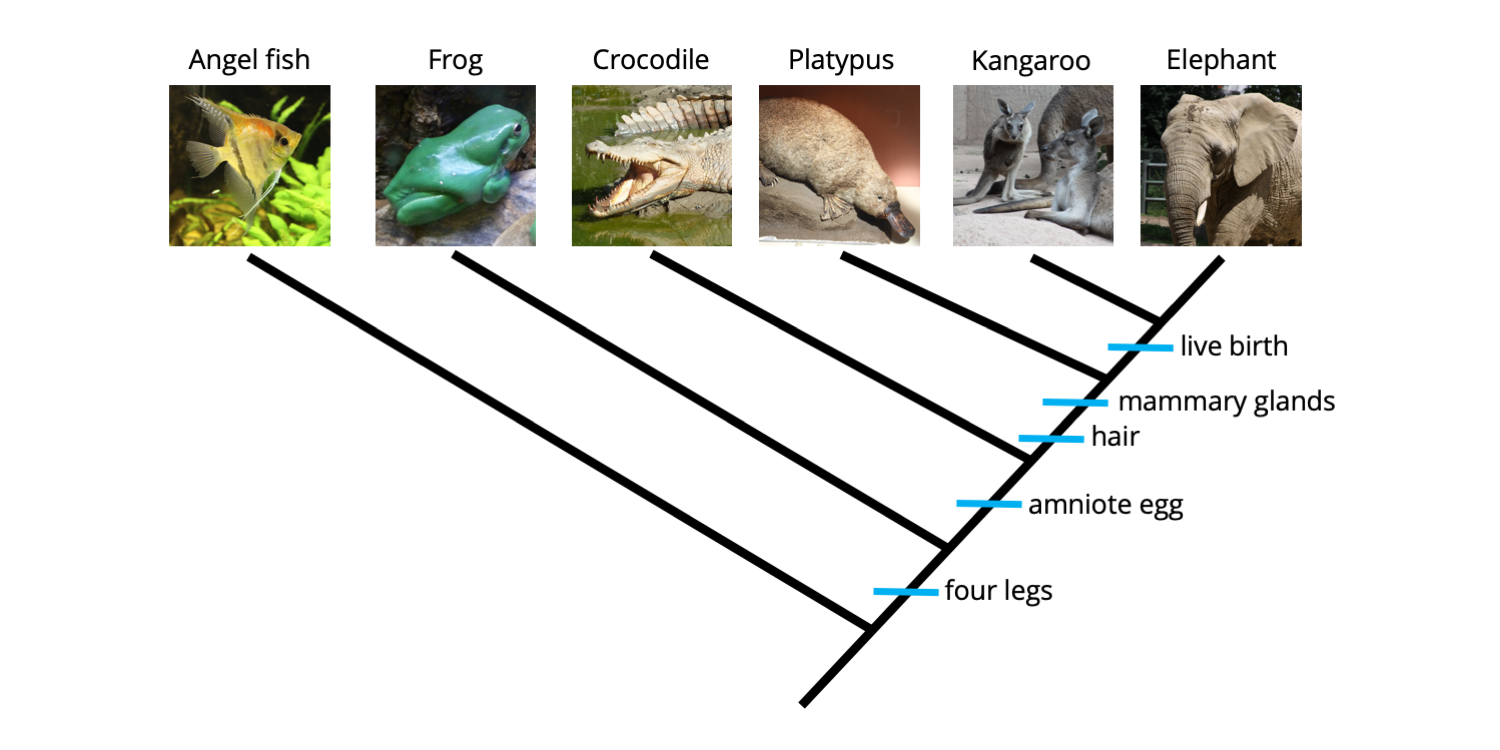
According to this cladogram, why is the platypus (and not the frog) more closely related to the elephant?
Because the elephant and platypus share a more recent common ancestor.
A measure of this within an ecosystem will allow biologists to predict the health of an ecosystem.
What is biodiversity?