What type of bond forms between water molecules and gives water its cohesive properties?
Hydrogen Bond
Which organelle is responsible for producing ATP in eukaryotic cells?
Mitochondria
What molecule serves as the main energy currency of the cell?
ATP
What is the stage of the cell cycle during which DNA replication occurs?
S phase (Synthesis).
What enzyme builds RNA from a DNA template during transcription?
RNA polymerase.
Which property of water allows it to resist changes in temperature due to hydrogen bonding?
High Specific Heat
What is the primary function of the rough ER?
Protein synthesis and modification (because ribosomes attach to it).
During cellular respiration, which stage produces the most ATP?
The electron transport chain (ETC) and oxidative phosphorylation.
What stage is depicted in the image below?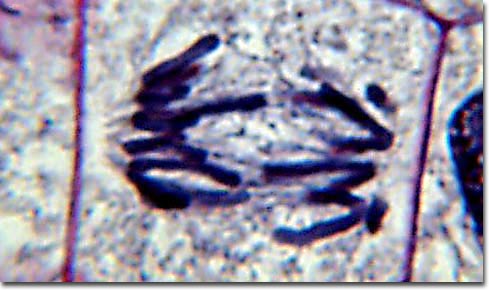
Anaphase
What is the difference between an intron and an exon?
Exons code for proteins; introns are removed during RNA processing.
What structural feature distinguishes saturated from unsaturated fatty acids?
Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds, creating kinks in the hydrocarbon chain.
Why are cells limited in size by their surface-area-to-volume ratio?
As cells grow, their volume increases faster than surface area, limiting diffusion and transport efficiency, so cells must remain small.
How does an enzyme lower the activation energy of a reaction?
Enzymes lower activation energy by stabilizing the transition state and bringing substrates together in the correct orientation.
What checkpoint ensures that all chromosomes are attached to spindle fibers before proceeding?
The Metaphase checkpoint (spindle checkpoint).
How do repressors regulate gene expression in prokaryotes?
Repressors bind to the operator to block RNA polymerase and stop transcription.
Which level of protein structure is directly stabilized by peptide bonds, and what does it represent?
Primary structure; it is the linear sequence of amino acids
How does the fluid mosaic model explain both the structure and dynamic nature of the plasma membrane?
The fluid mosaic model describes the membrane as a flexible phospholipid bilayer with mobile, embedded proteins.
What is the role of the proton gradient in oxidative phosphorylation?
The proton gradient powers ATP synthase, which synthesizes ATP as protons flow down their gradient.
How do microtubules function during mitosis to ensure accurate chromosome separation?
Microtubules attach to kinetochores and shorten or lengthen to pull sister chromatids apart, ensuring each daughter cell receives the correct set of chromosomes.
Describe one mechanism eukaryotes use to regulate gene expression after transcription.
Examples: alternative splicing, RNA interference (siRNA/miRNA), mRNA degradation, or regulation of translation initiation.
Explain why a slight change in pH can significantly disrupt enzyme activity, referencing the interactions responsible for tertiary structure.
Changes in pH alter the ionization of R-groups, disrupting ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds that maintain the tertiary structure, affecting enzyme shape and function.
Explain how the endomembrane system coordinates the production, modification, and secretion of a protein from start to finish.
Rough ER synthesizes proteins → Golgi modifies/sorts → vesicles transport → plasma membrane secretes proteins via exocytosis (endomembrane coordination).
Compare photophosphorylation in chloroplasts to oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria, explaining both similarities and key differences.
Both use electron transport chains and chemiosmosis; differences: chloroplasts use light energy and water as an electron source, produce NADPH/ATP; mitochondria use chemical energy from food and produce ATP only.
How do the spindle assembly checkpoint and kinetochore tension work together to ensure that sister chromatids separate accurately during mitosis?
The spindle assembly checkpoint ensures all kinetochores are attached to spindle fibers, and proper tension across sister chromatids confirms correct attachment, allowing the cell to proceed to anaphase and separate chromosomes accurately.
Explain how DNA methylation and histone modification can work together to regulate long-term gene expression.
DNA methylation generally silences genes; histone modification (e.g., acetylation) changes chromatin accessibility. Together, they establish long-term patterns of expression.